Proche
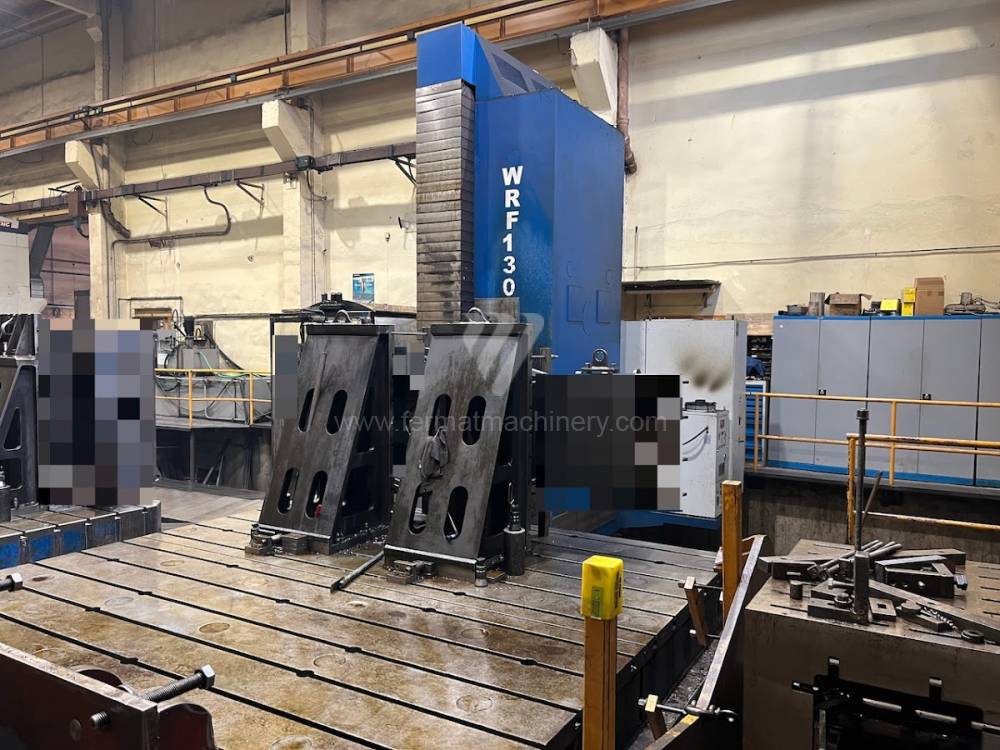
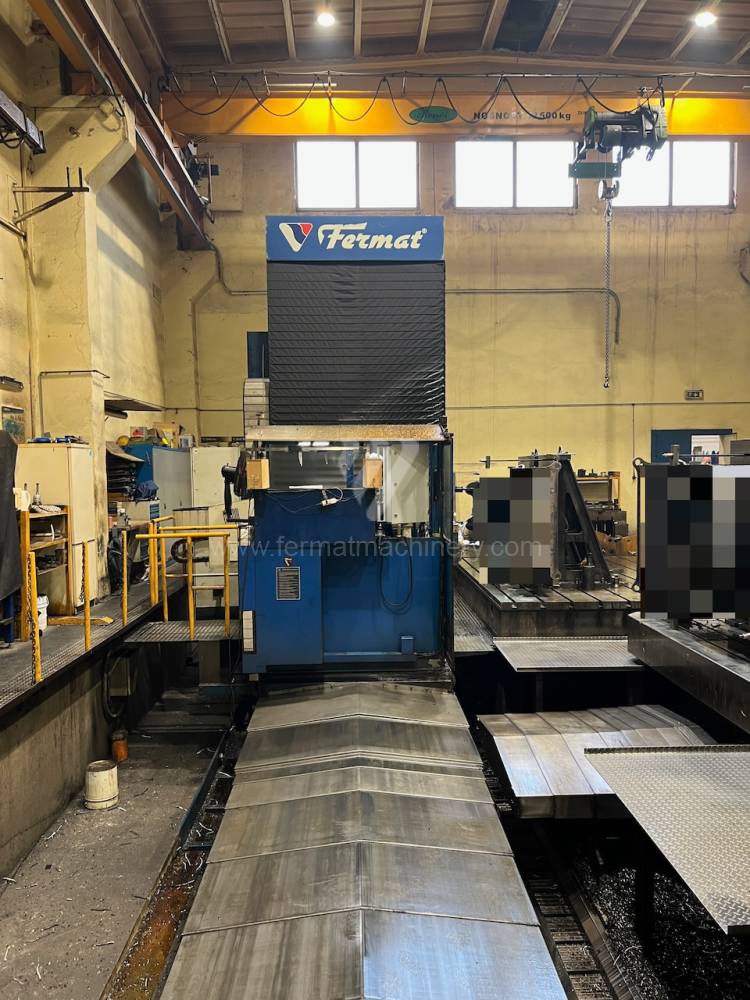
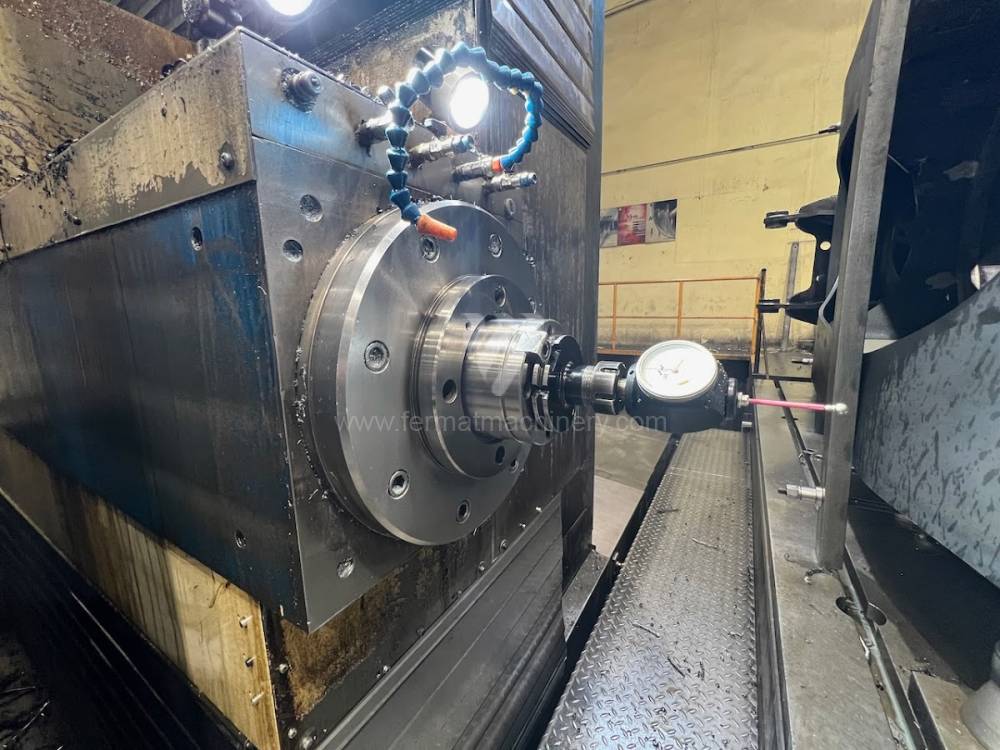
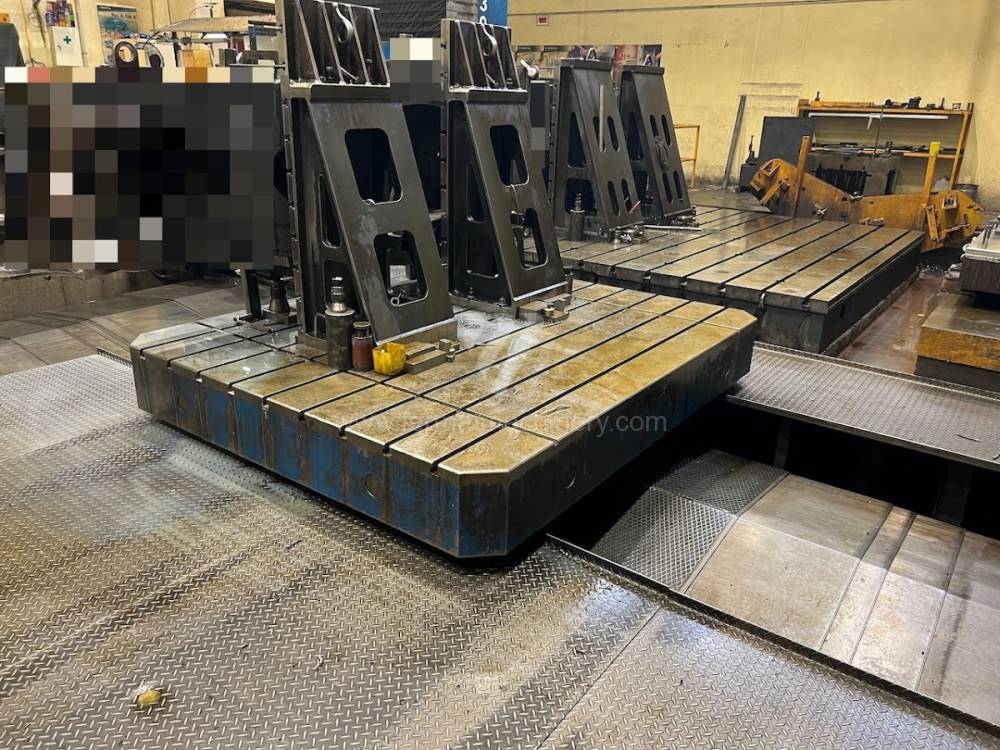
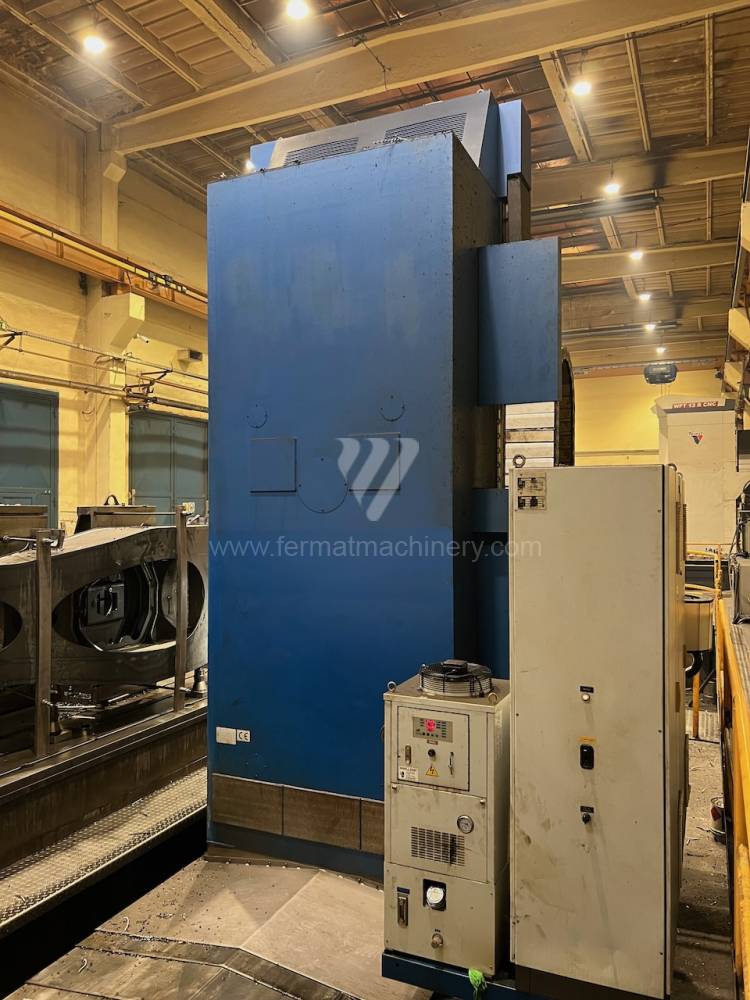
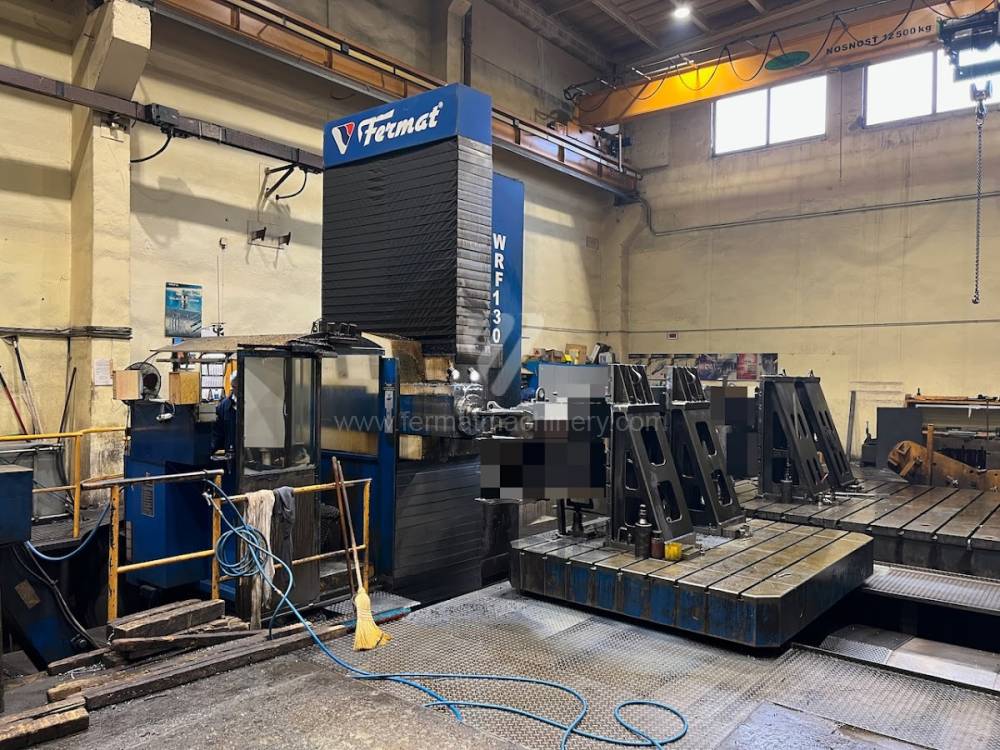
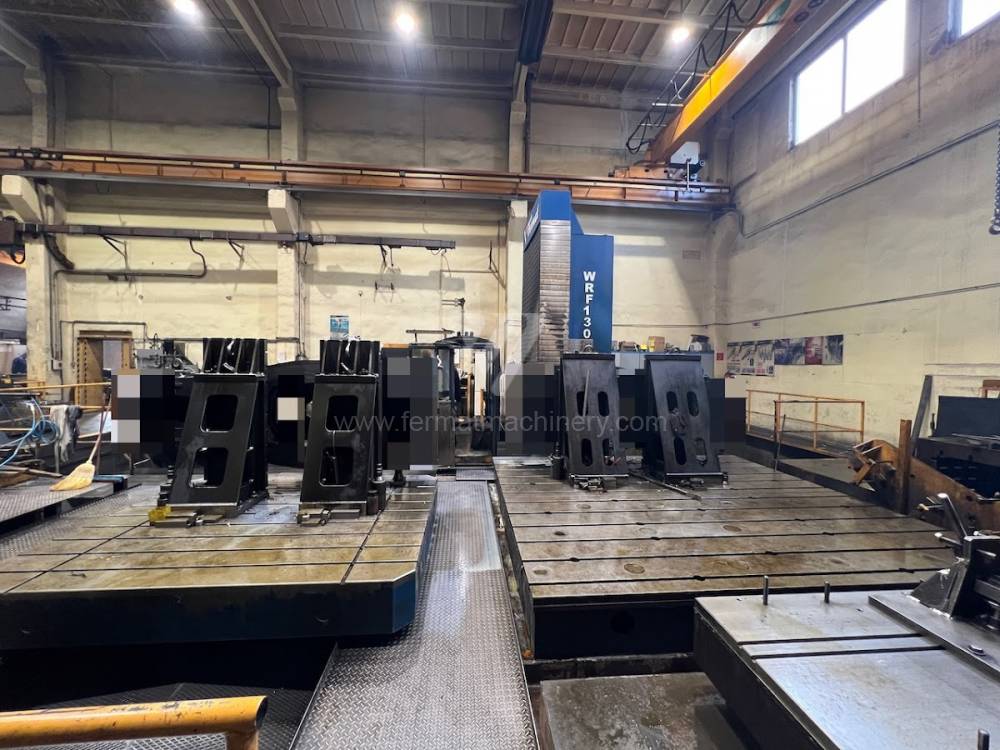




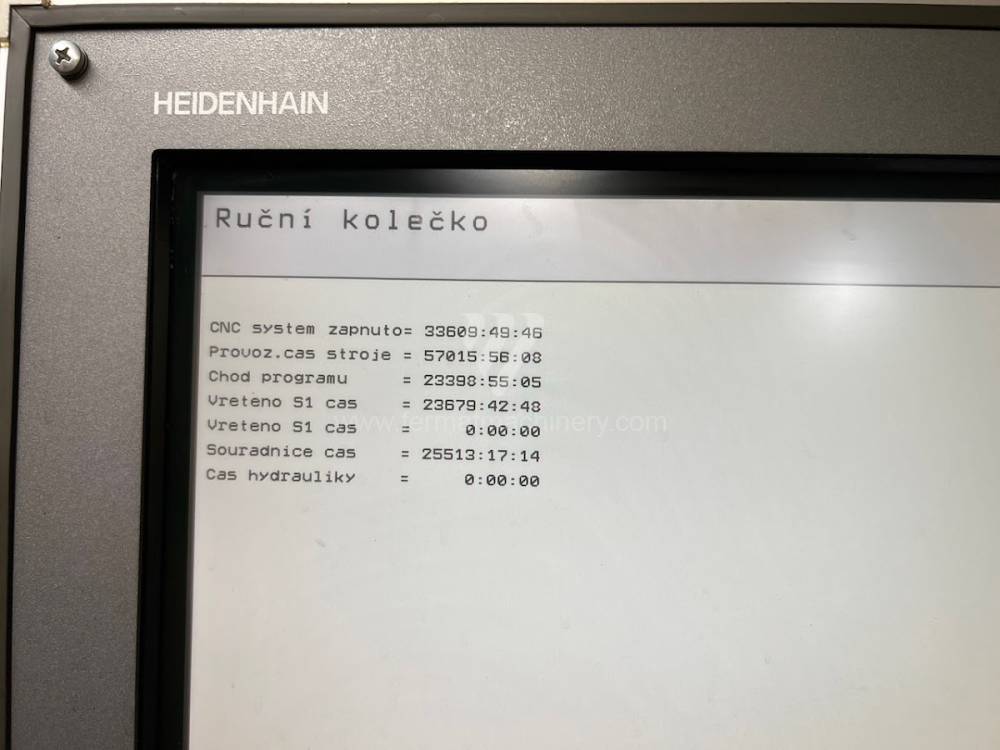








Année de production:2008
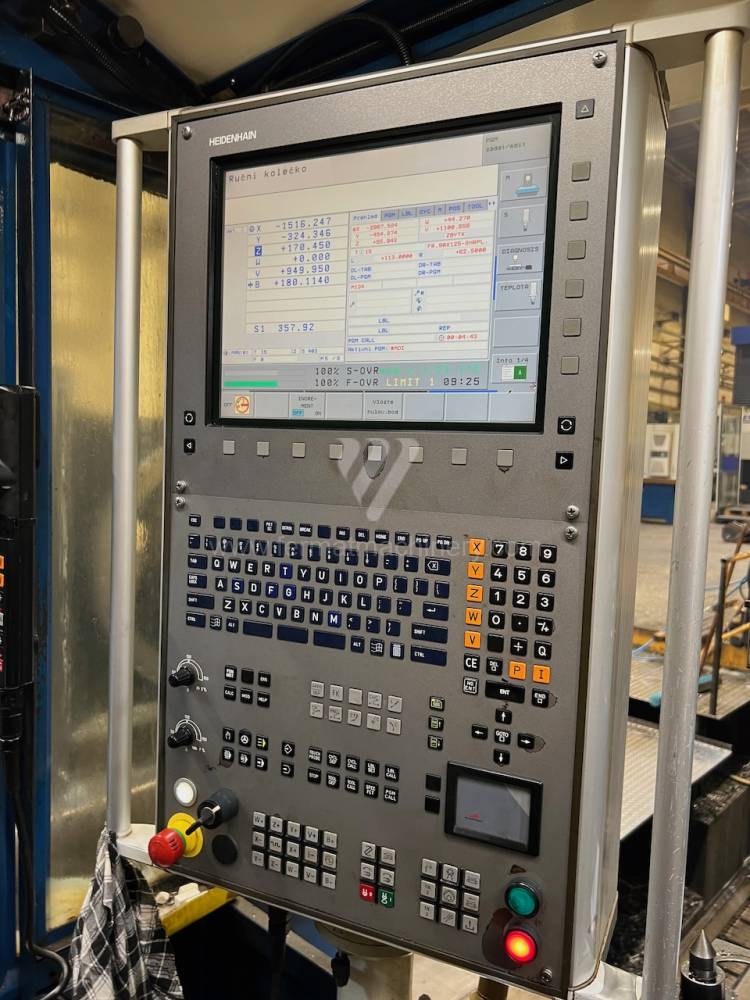
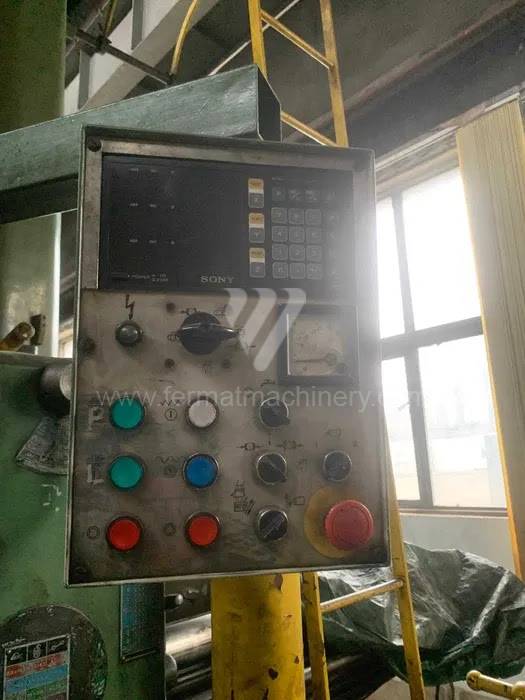
Système de contrôle Heidenhain: TNC 530
Diametre de travaille de broche: 130 mm
Course X: 8000 mm
Course Y: 3000 mm
Vitesse de broche: 10 - 3000 /min.
Extension du curseur (W): 730 mm
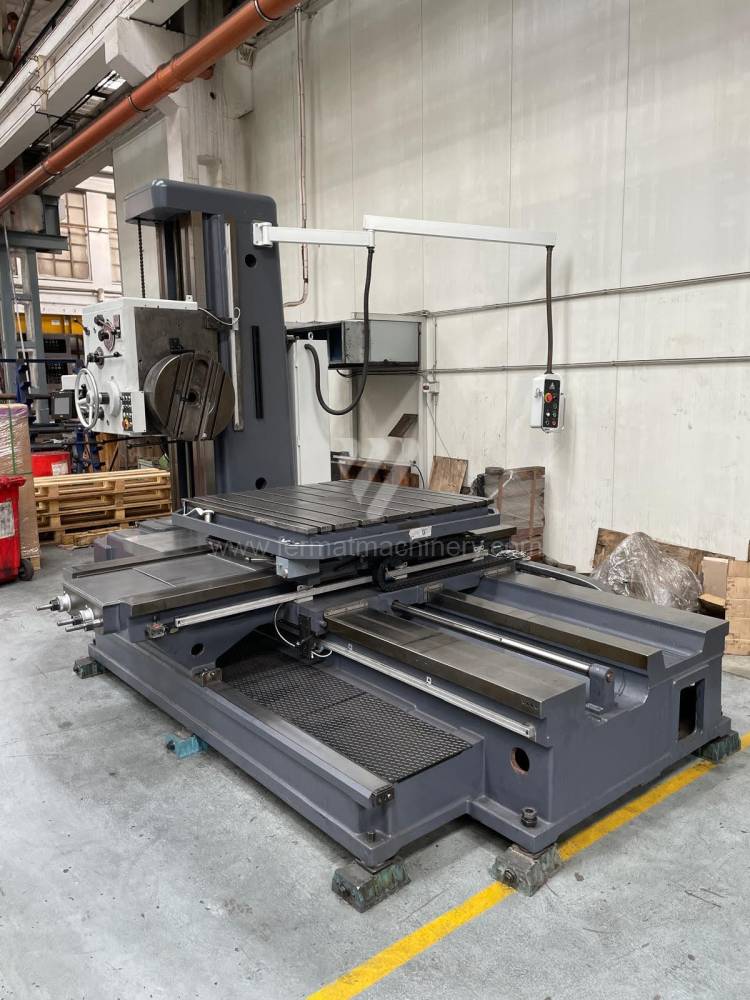
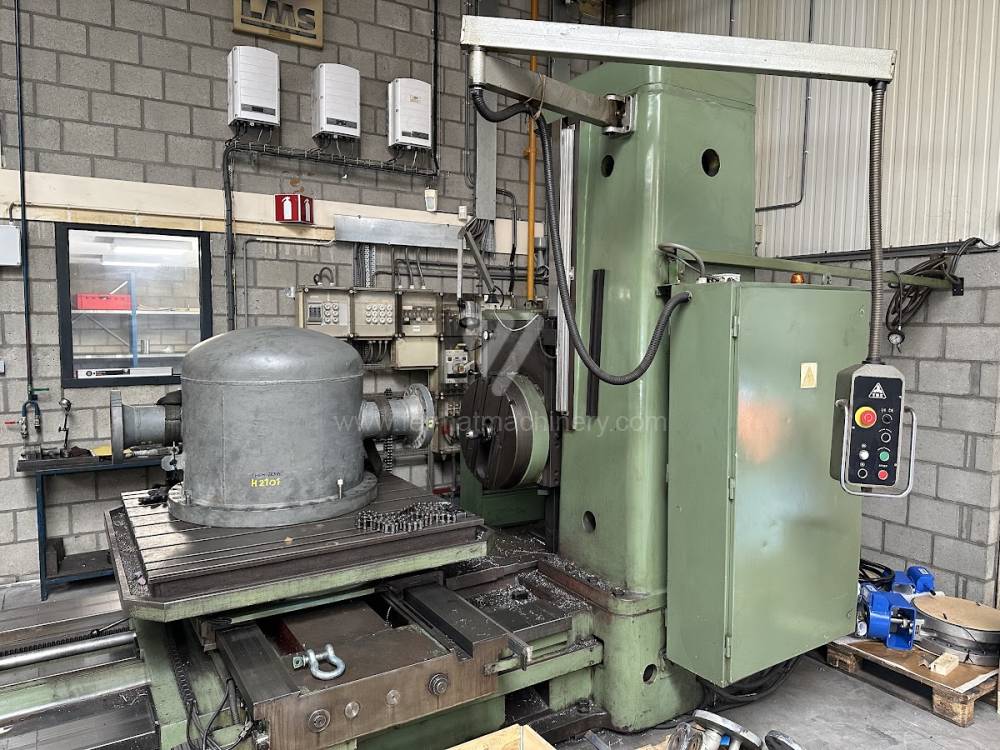
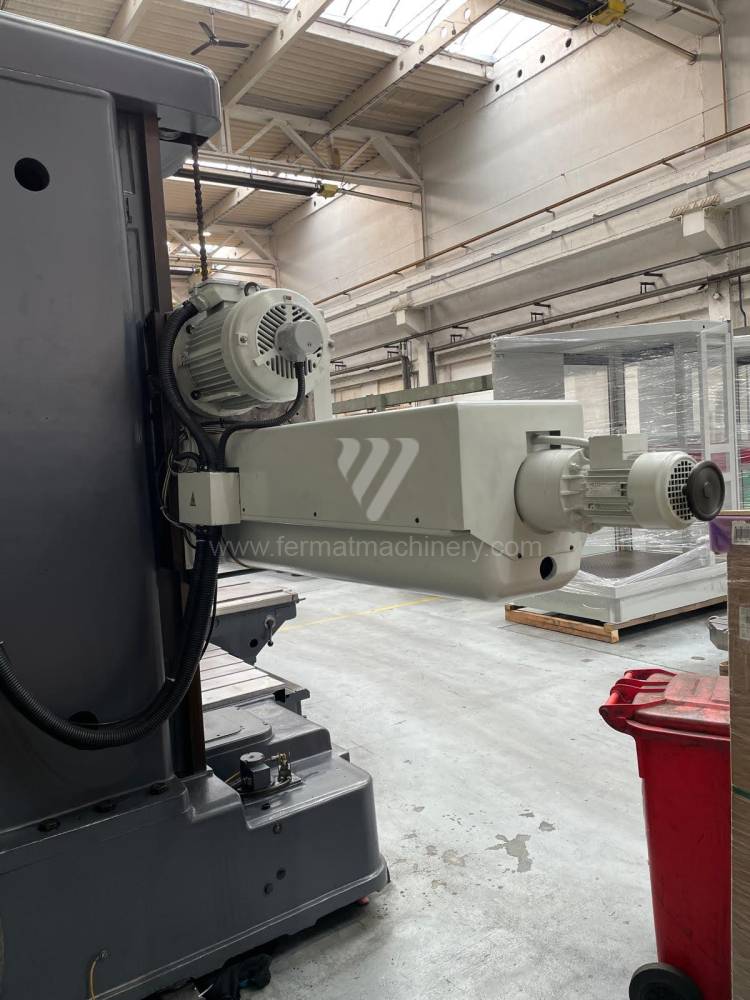
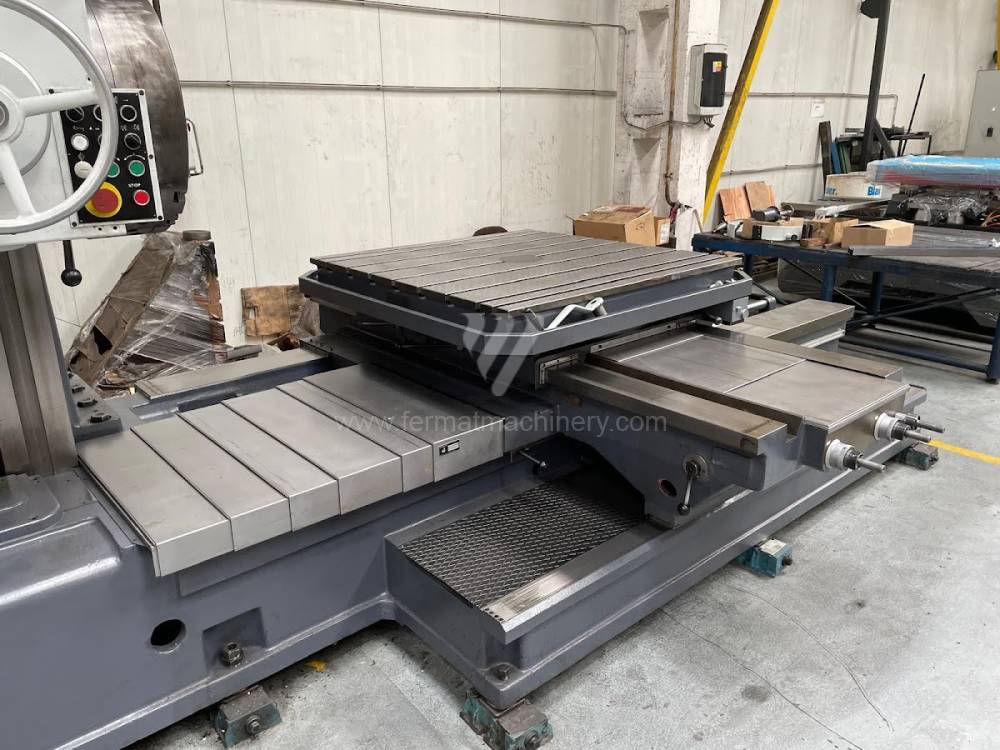
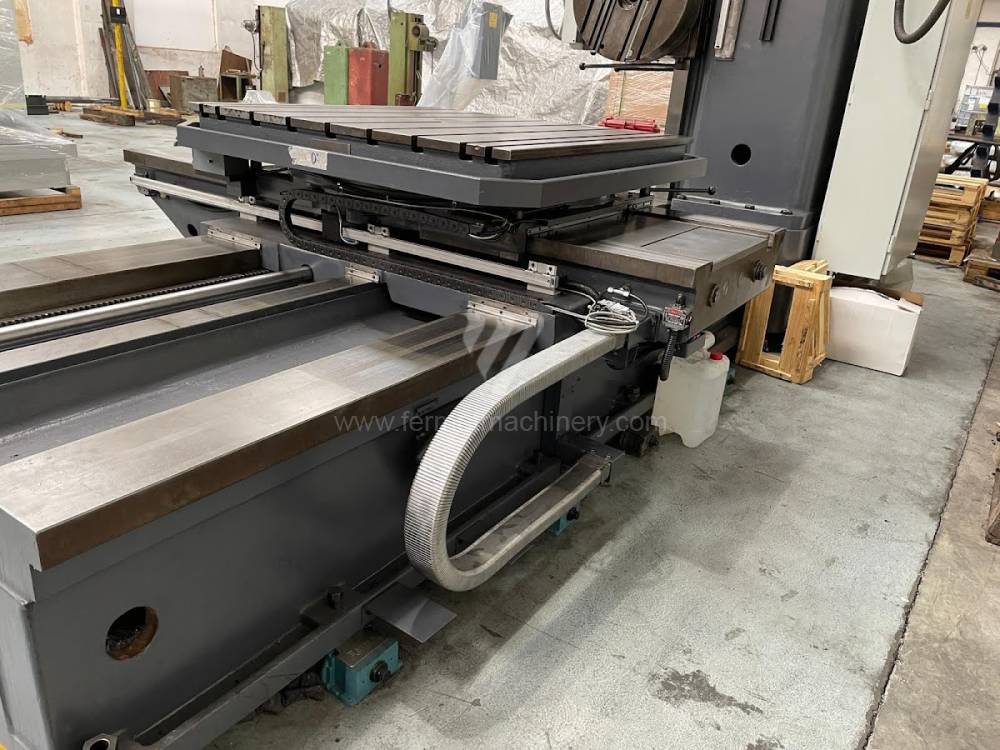
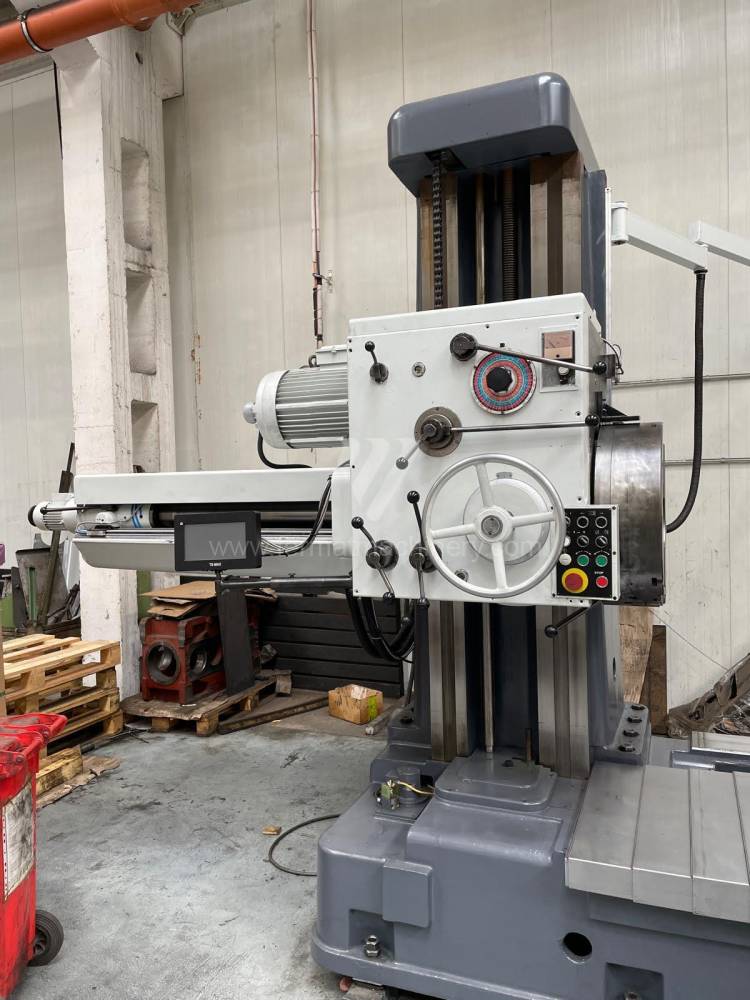
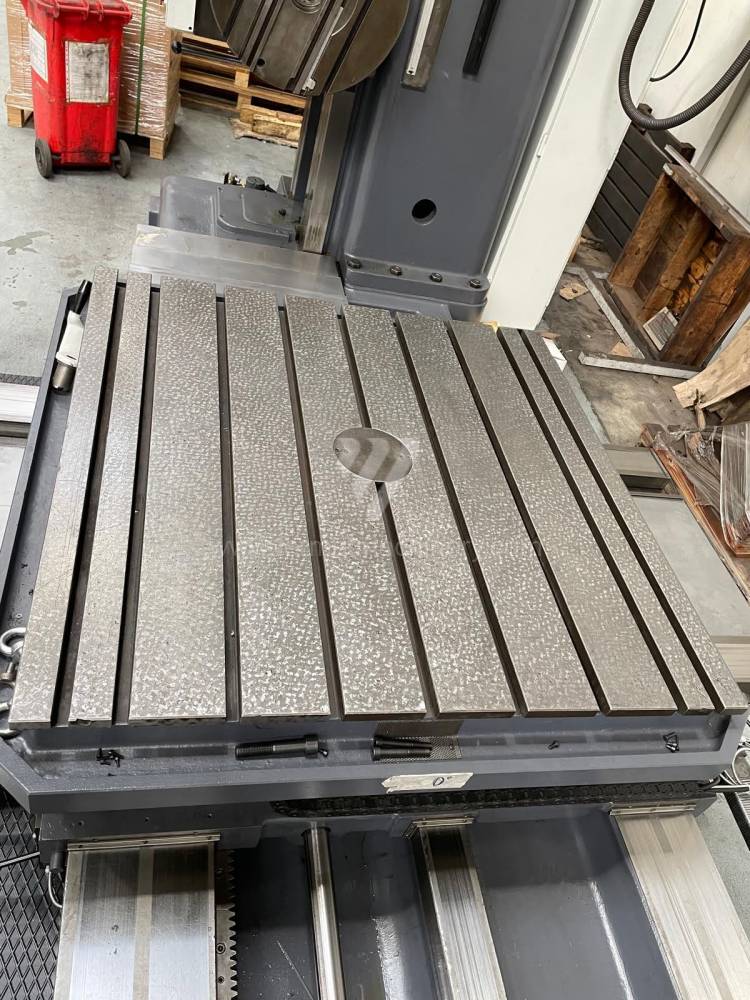
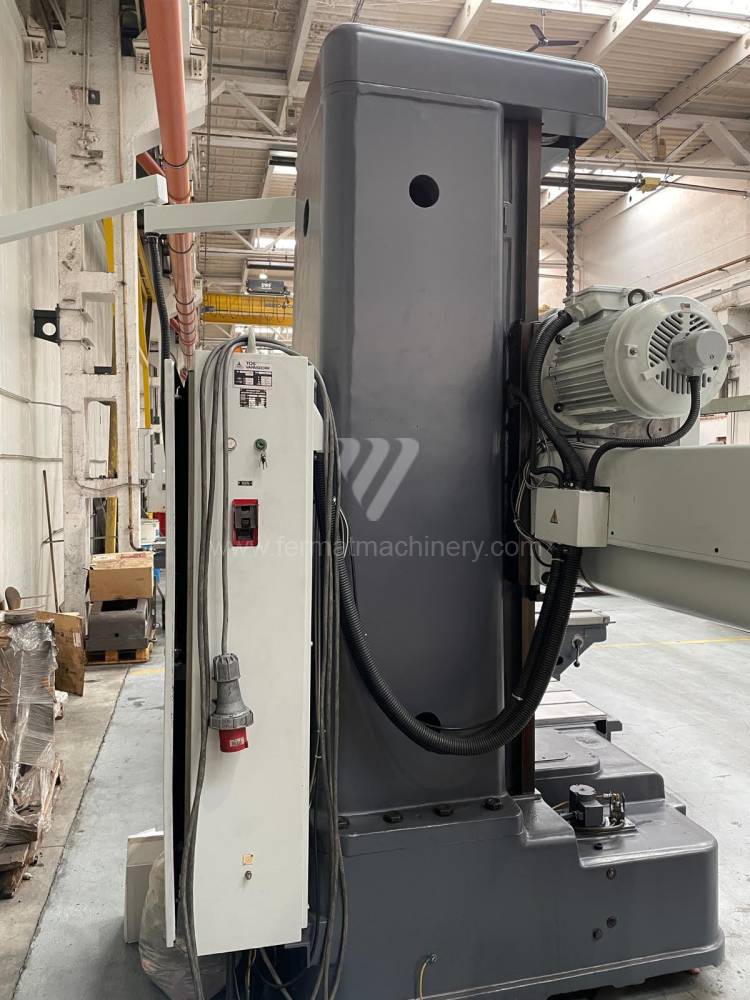
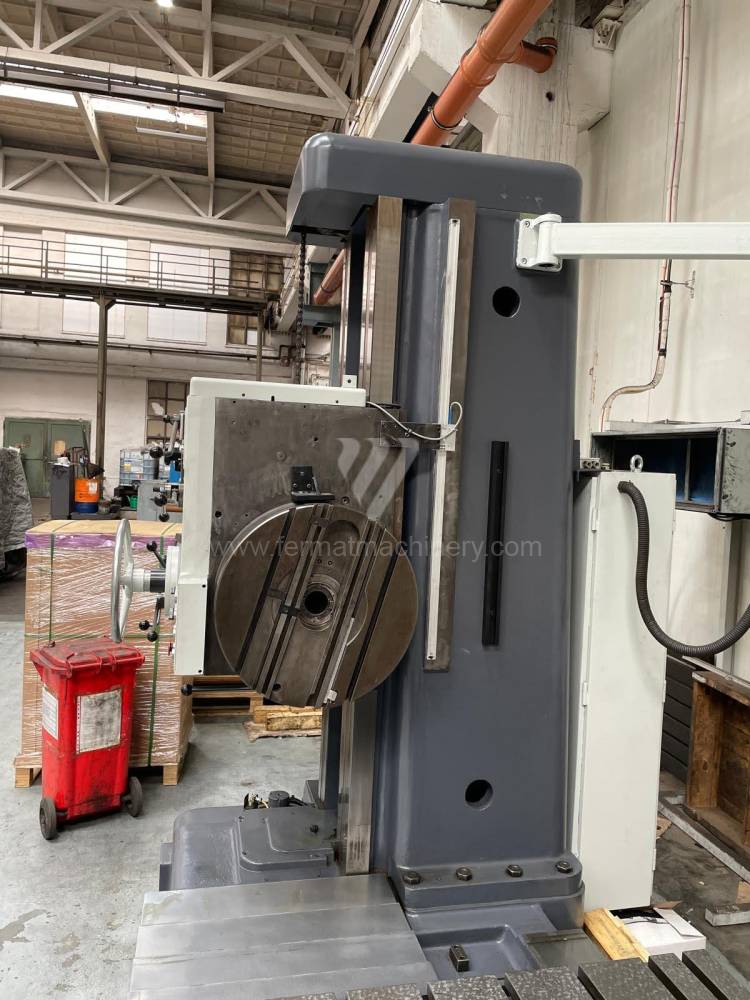
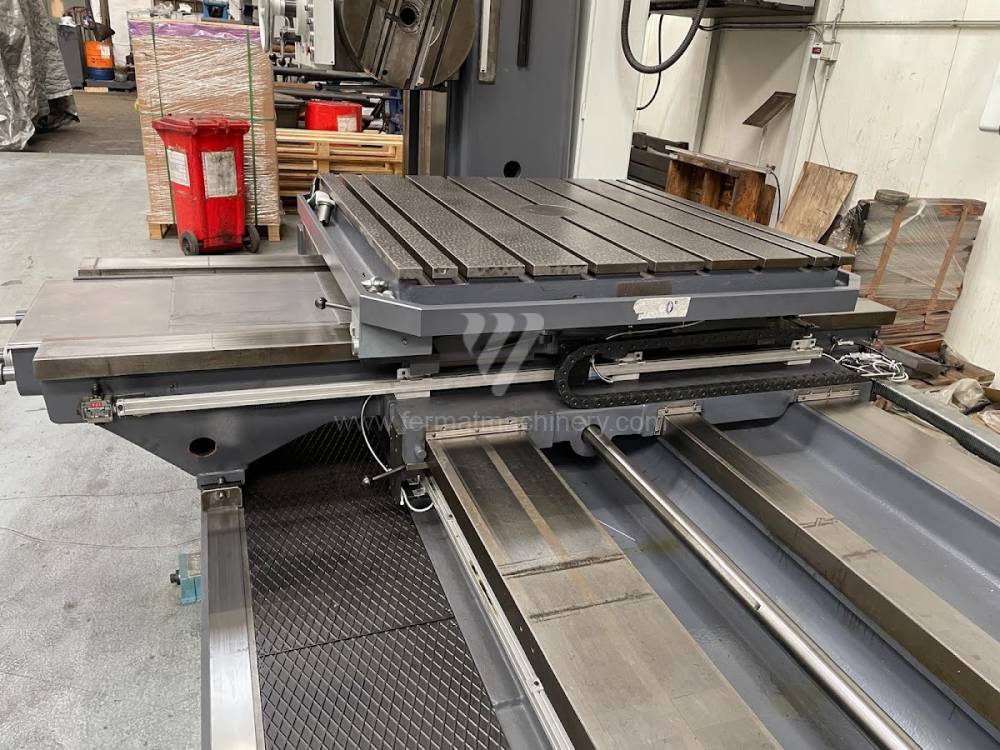
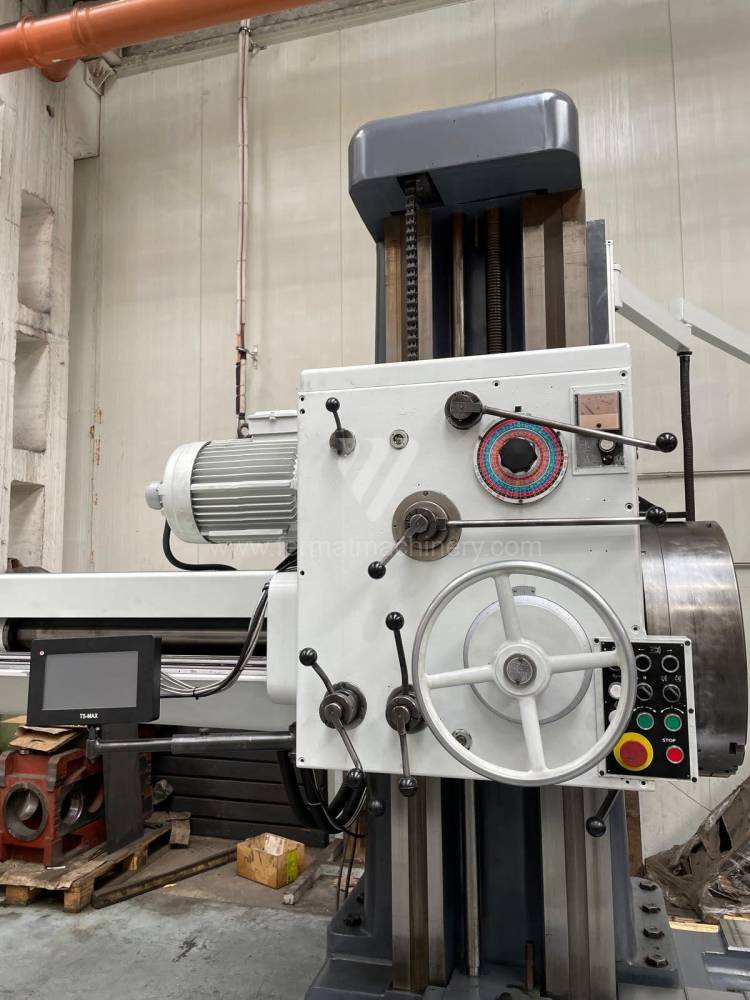












Année de production:1992
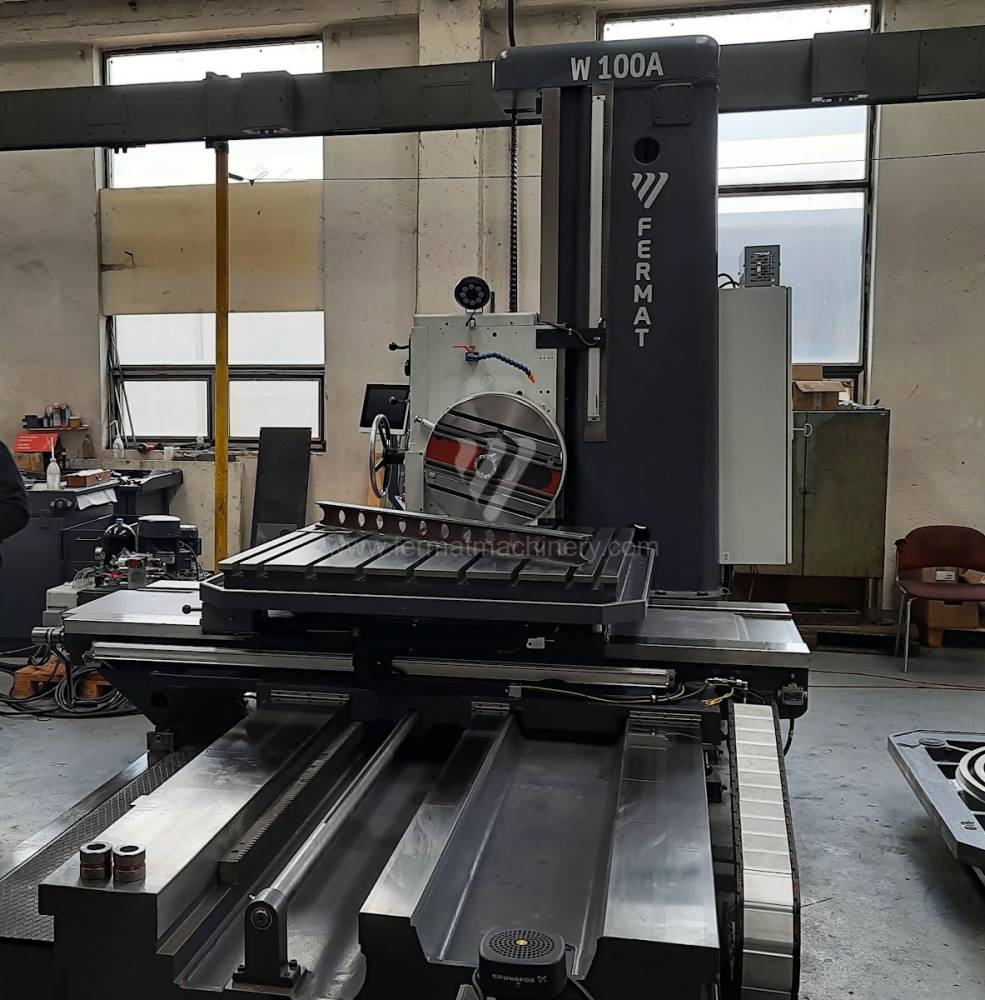
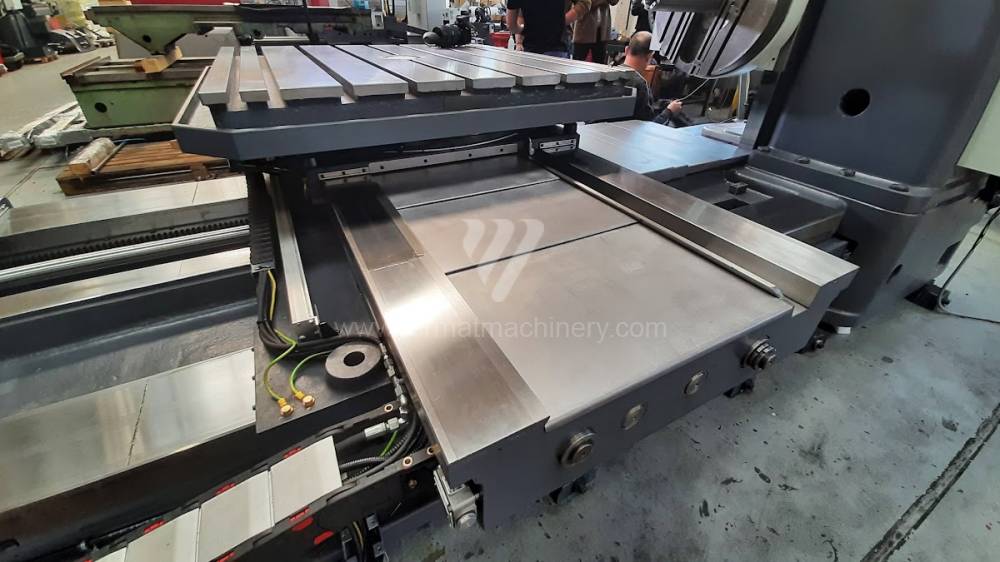
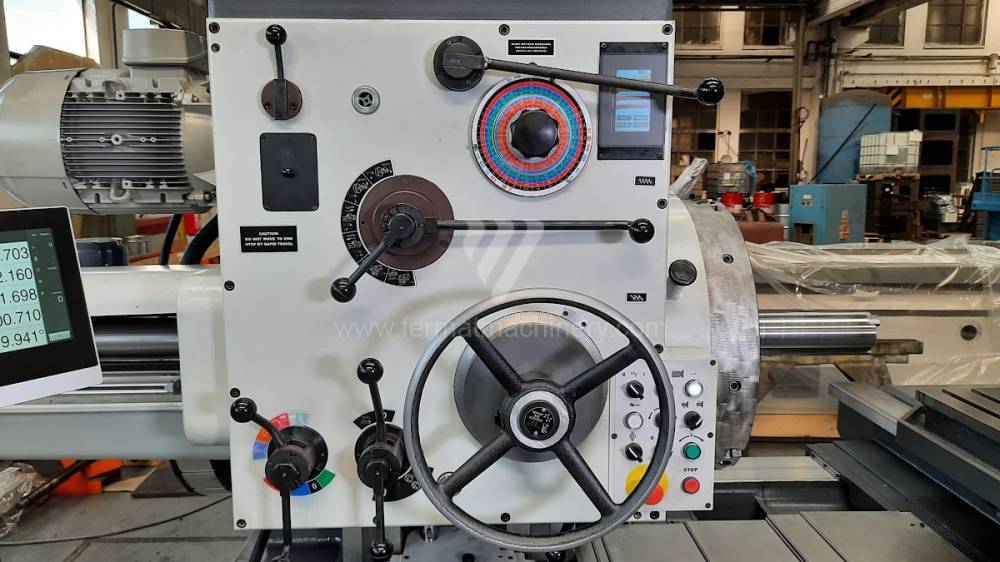
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1500 mm
Course Y: 1250 mm
Vitesse de broche: 7 - 1120 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): mm
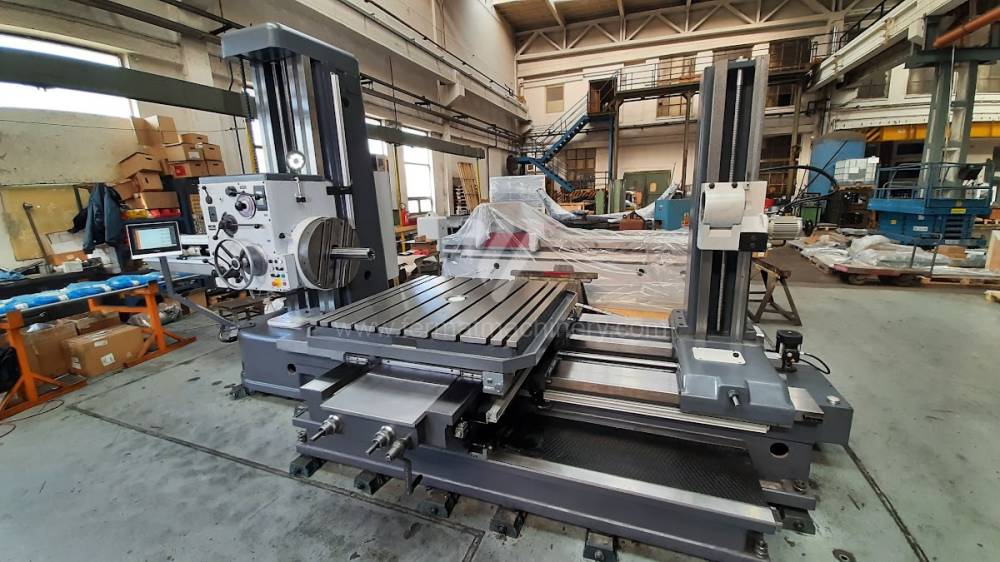
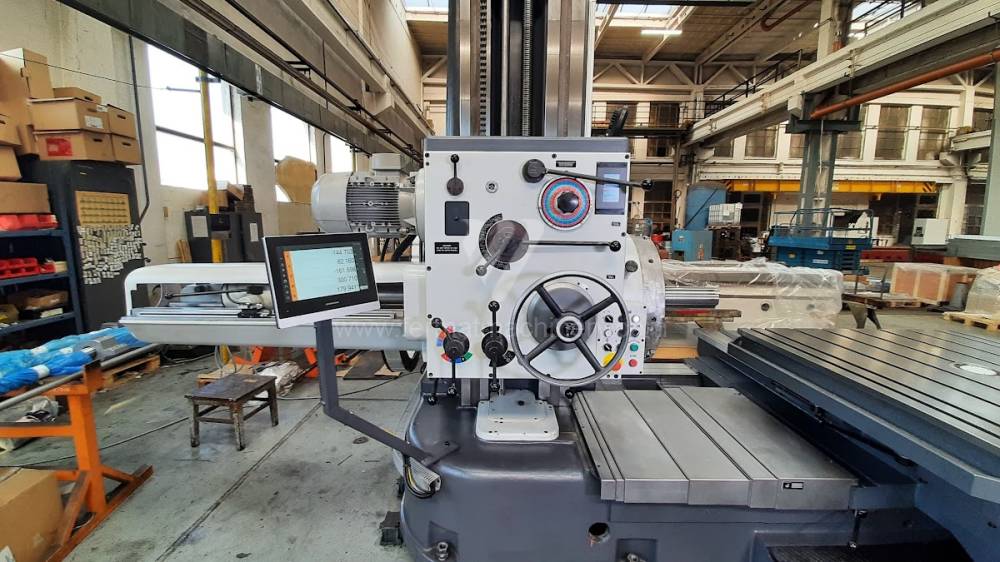
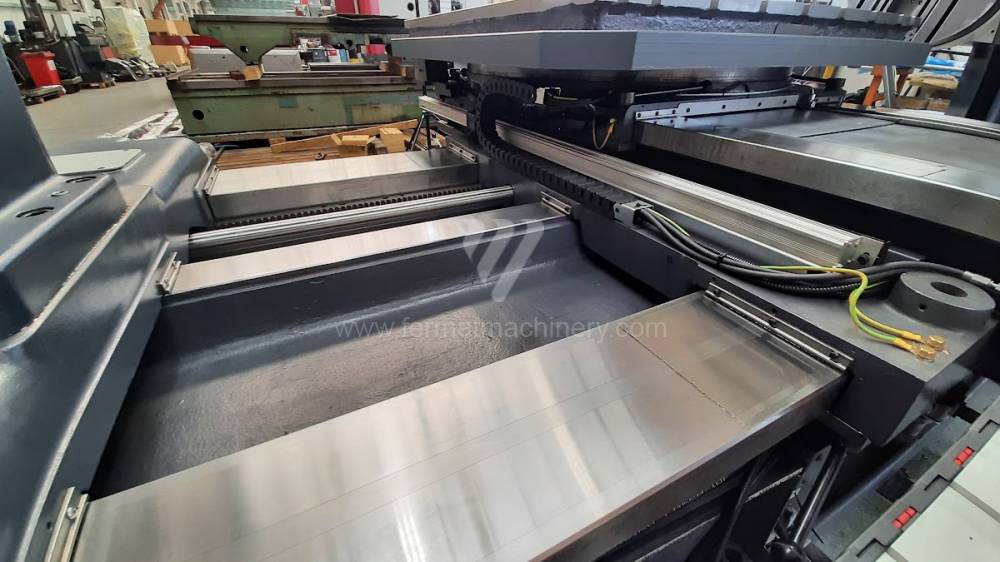
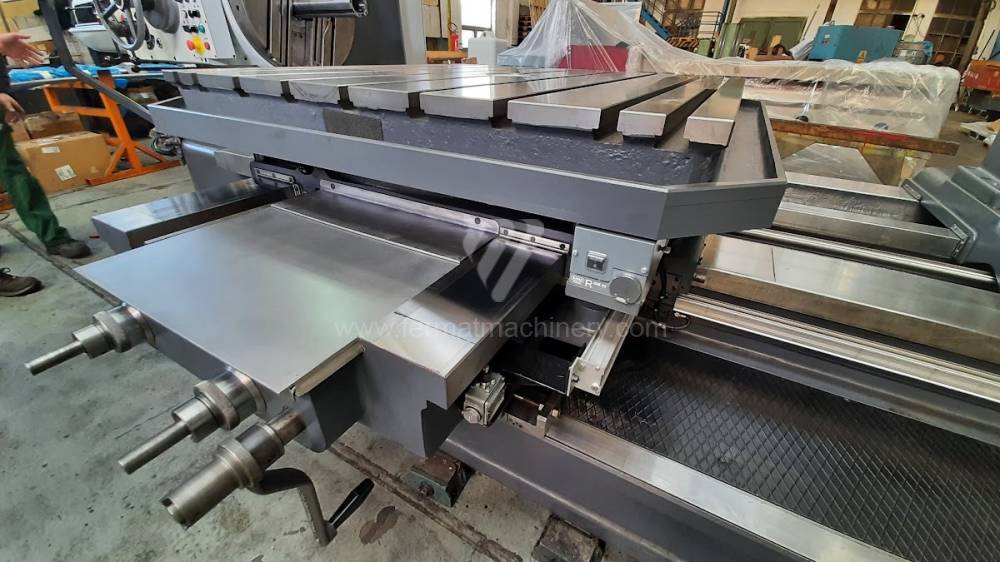
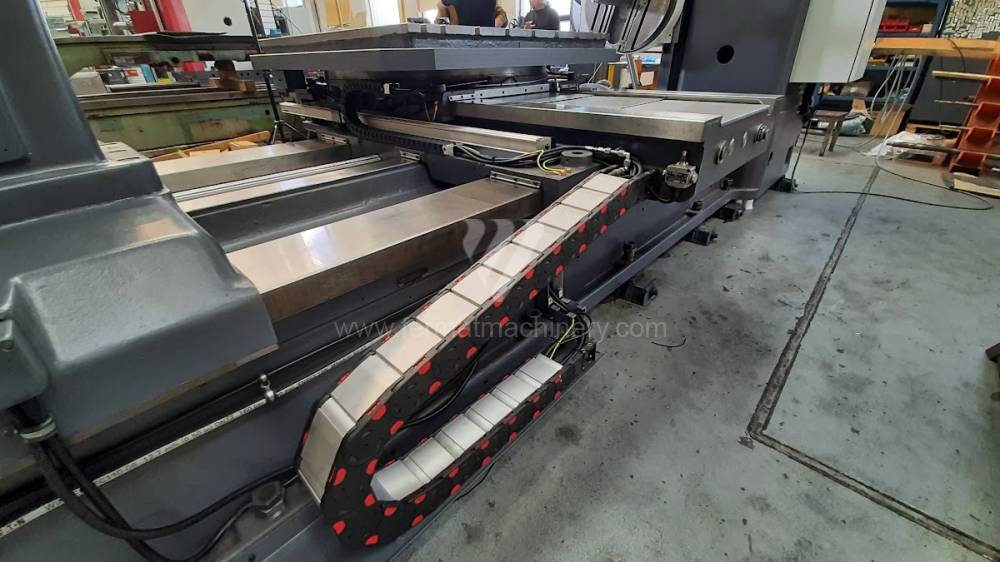
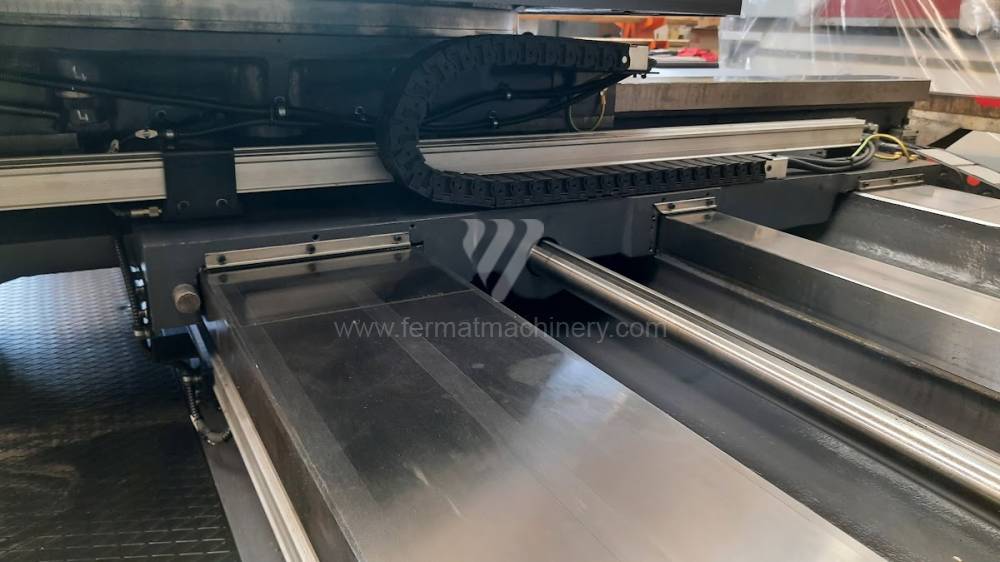
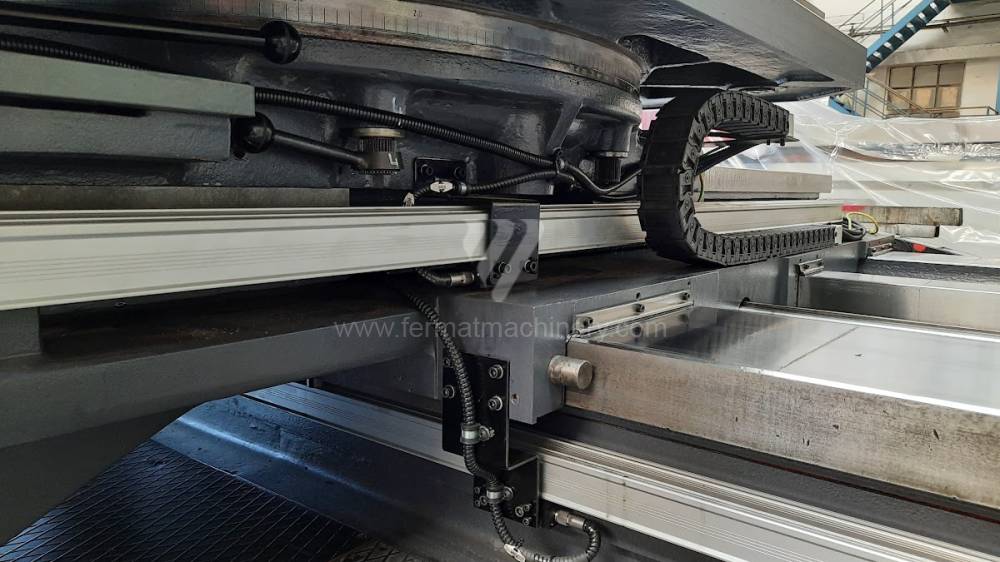
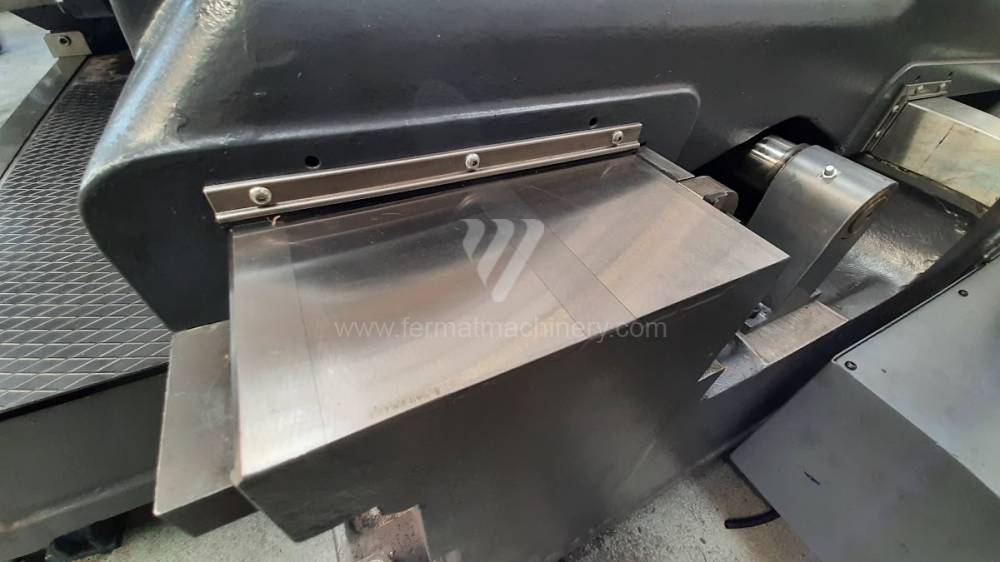
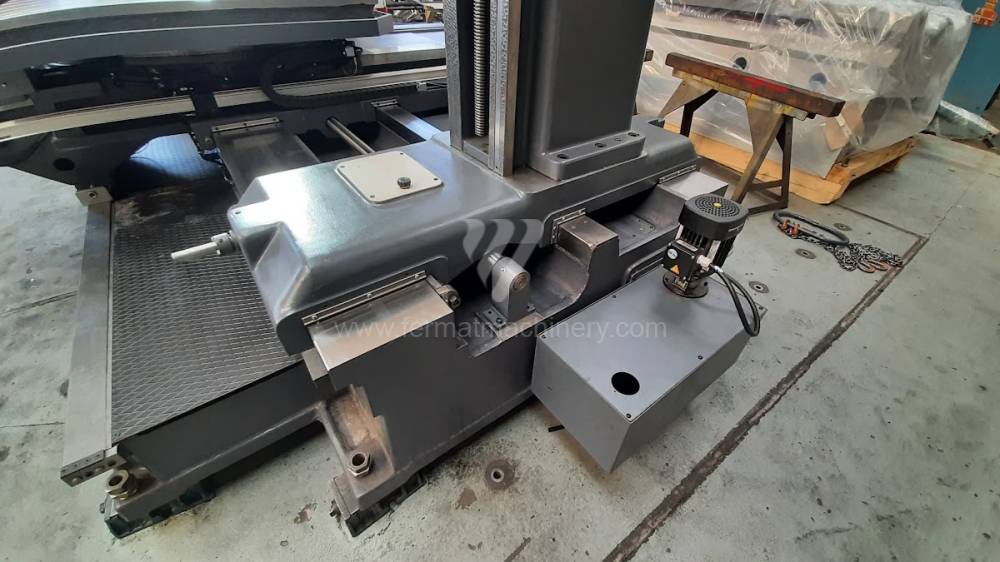
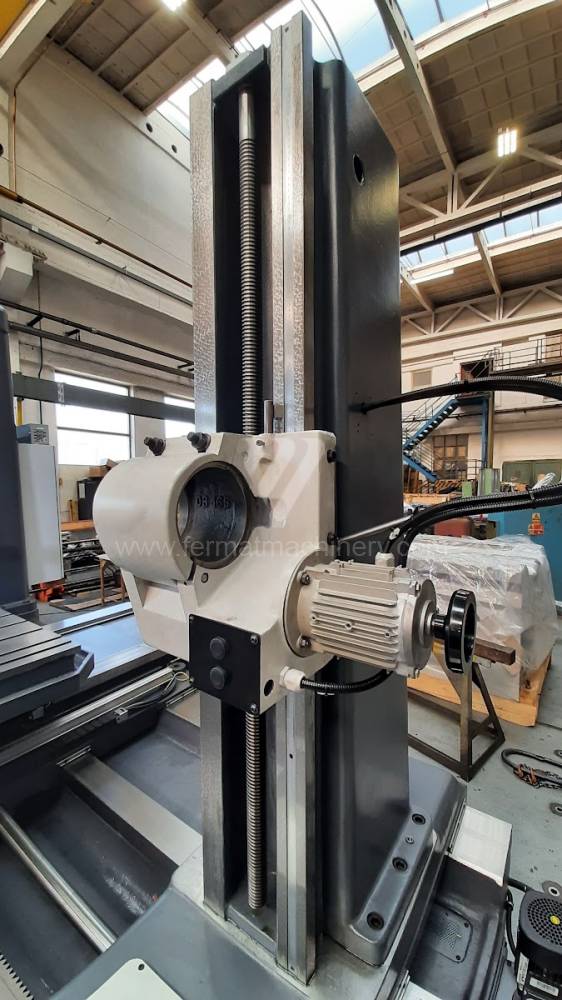























Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1600 mm
Course Y: 1120 mm
Vitesse de broche: 7 - 1120 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 900 mm
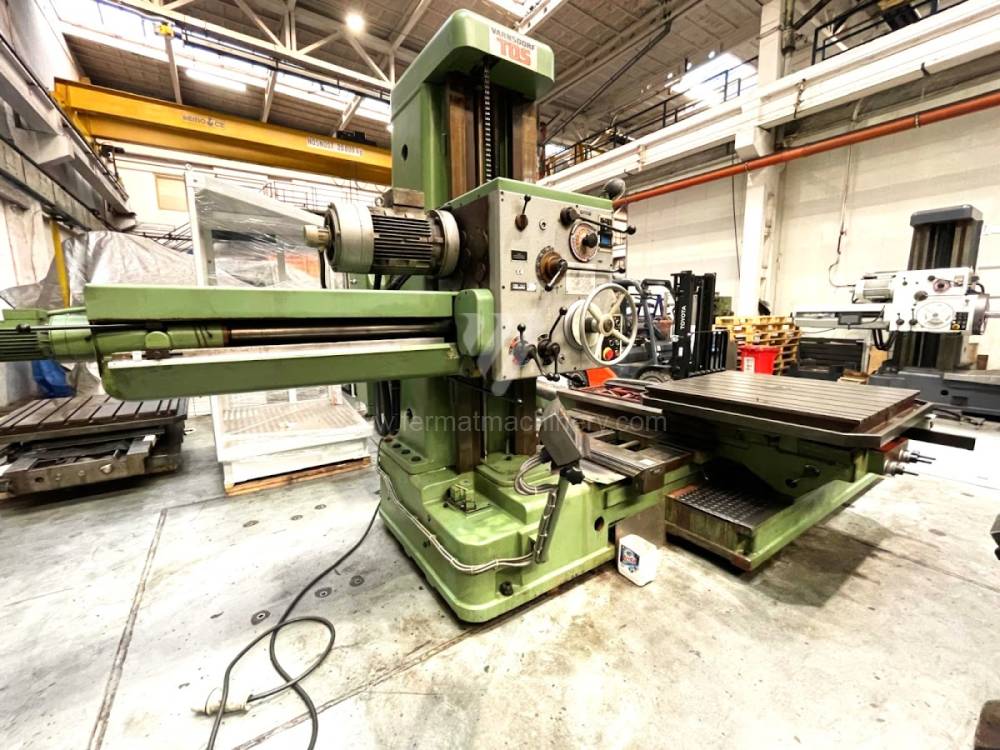
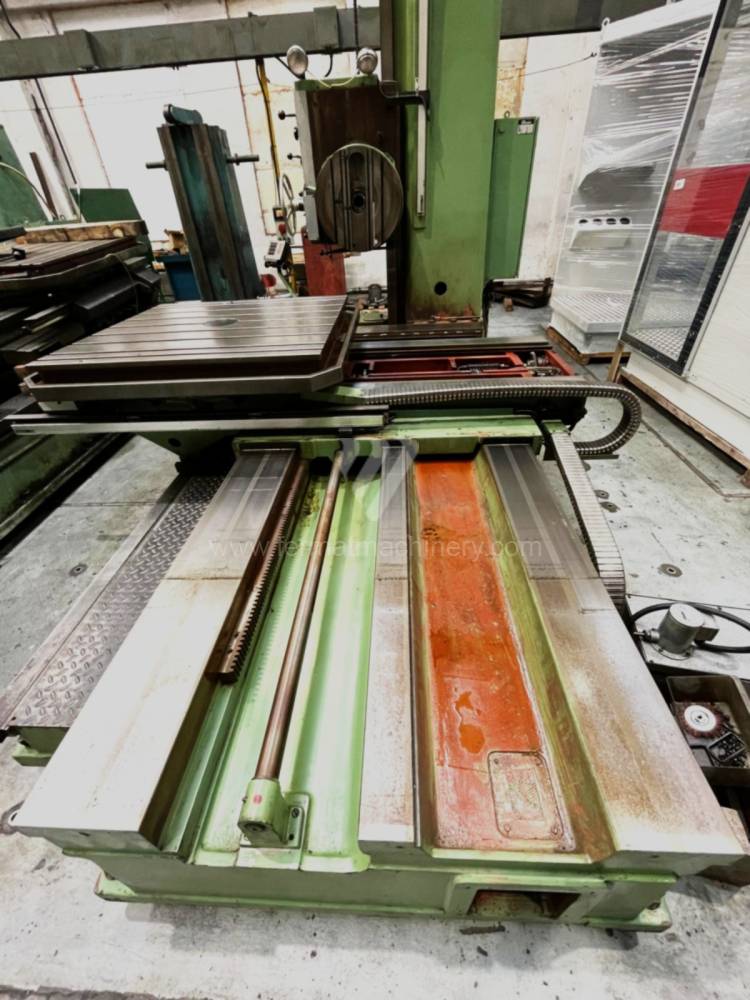
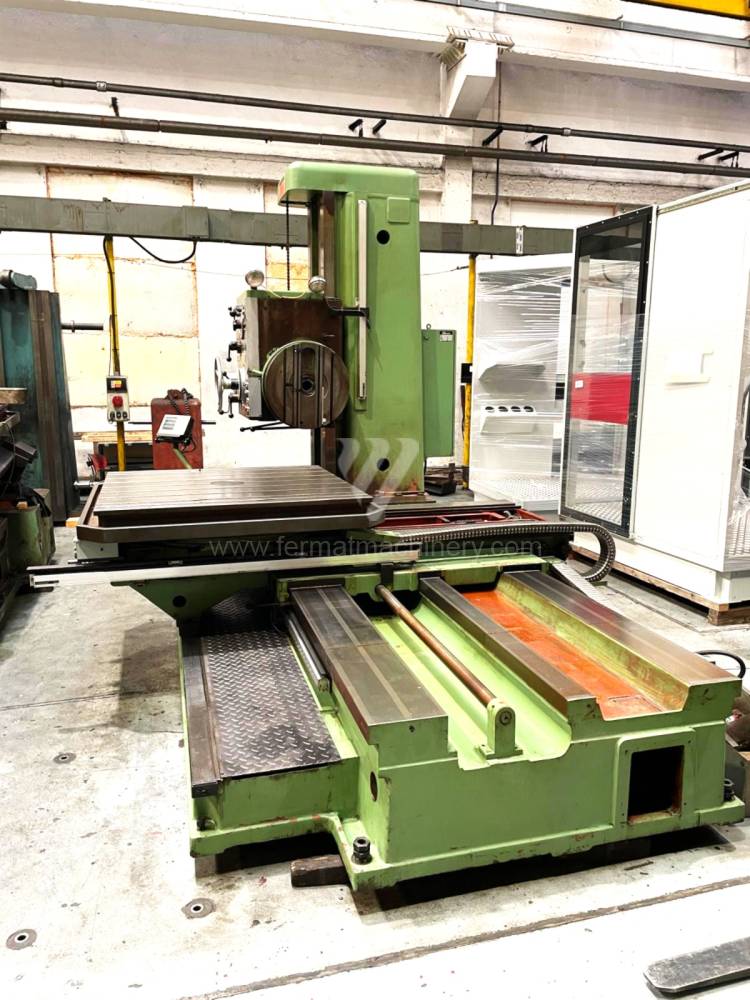
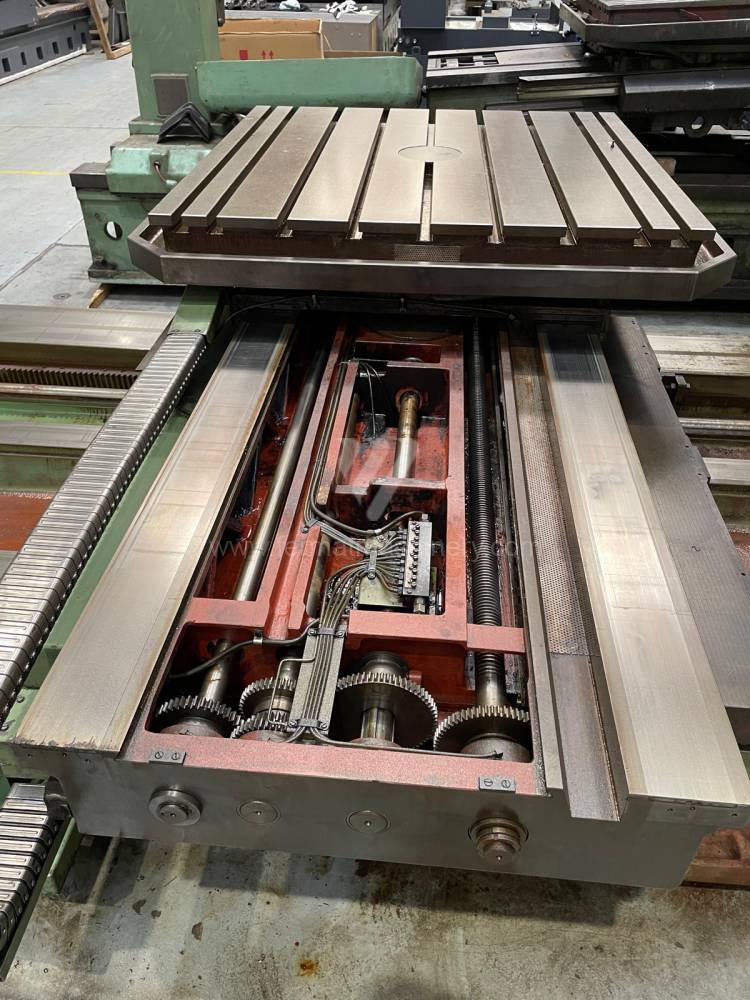
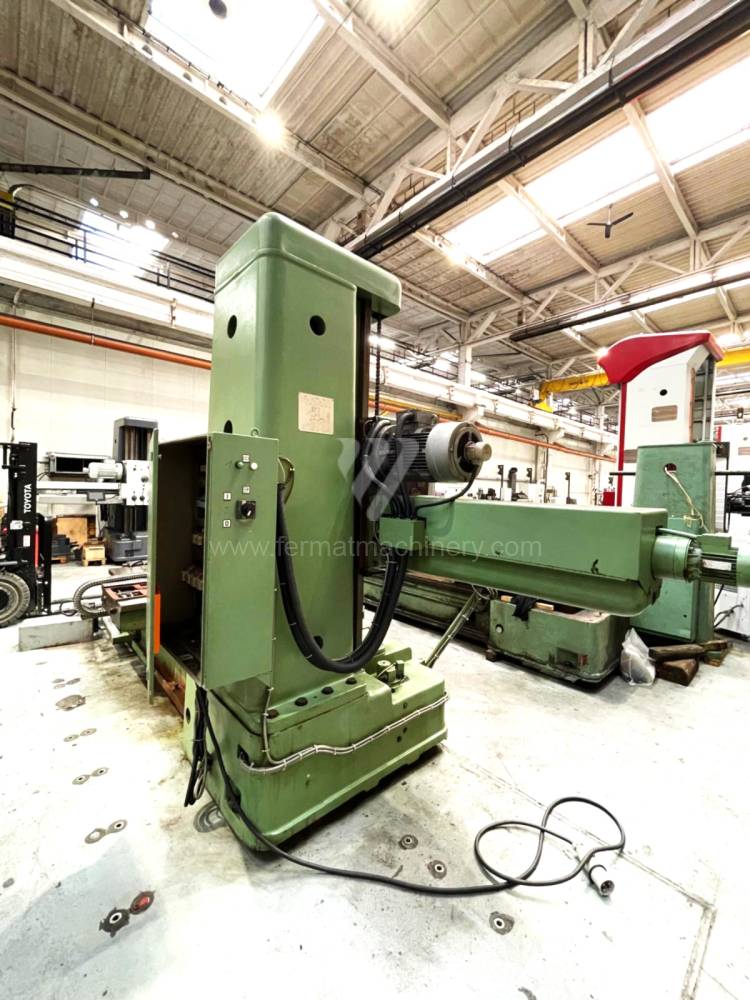
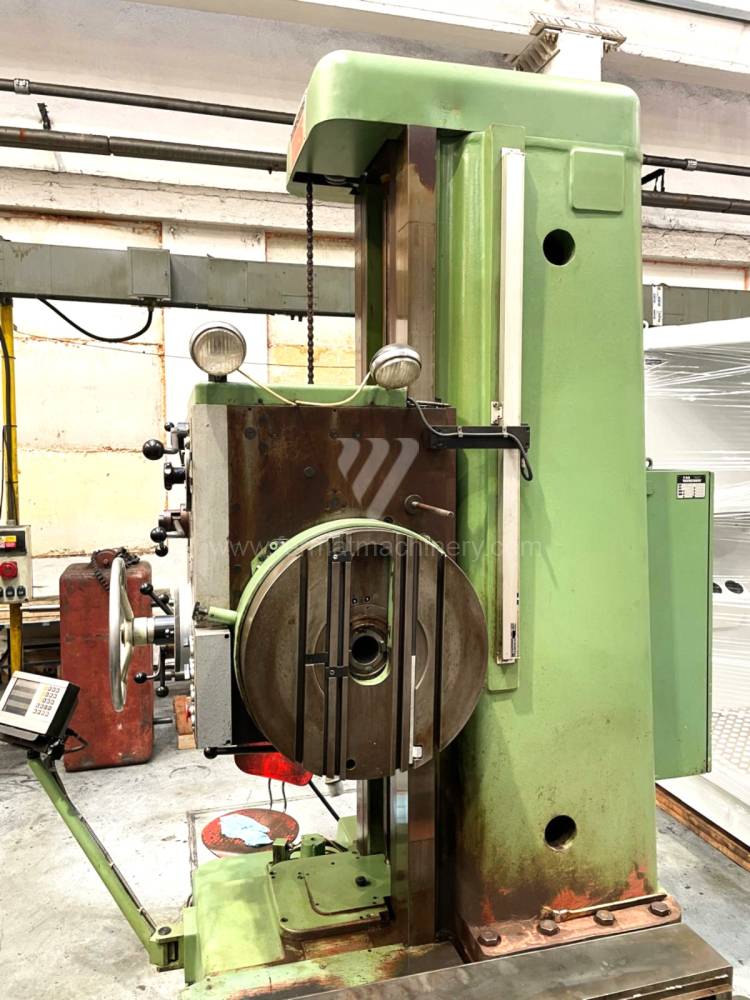
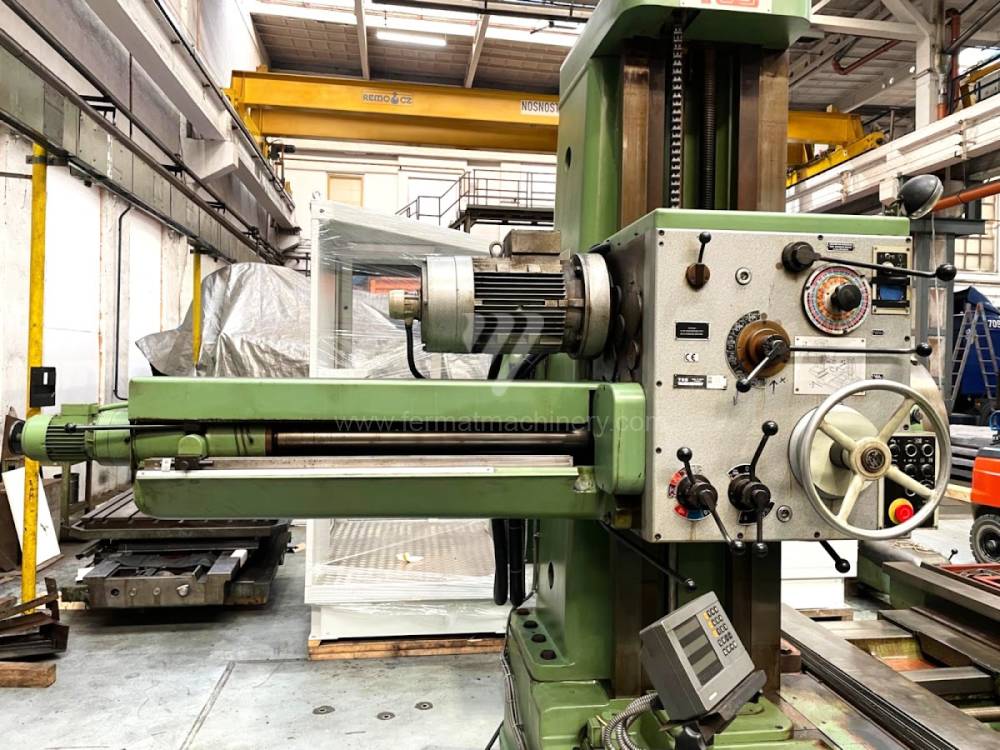
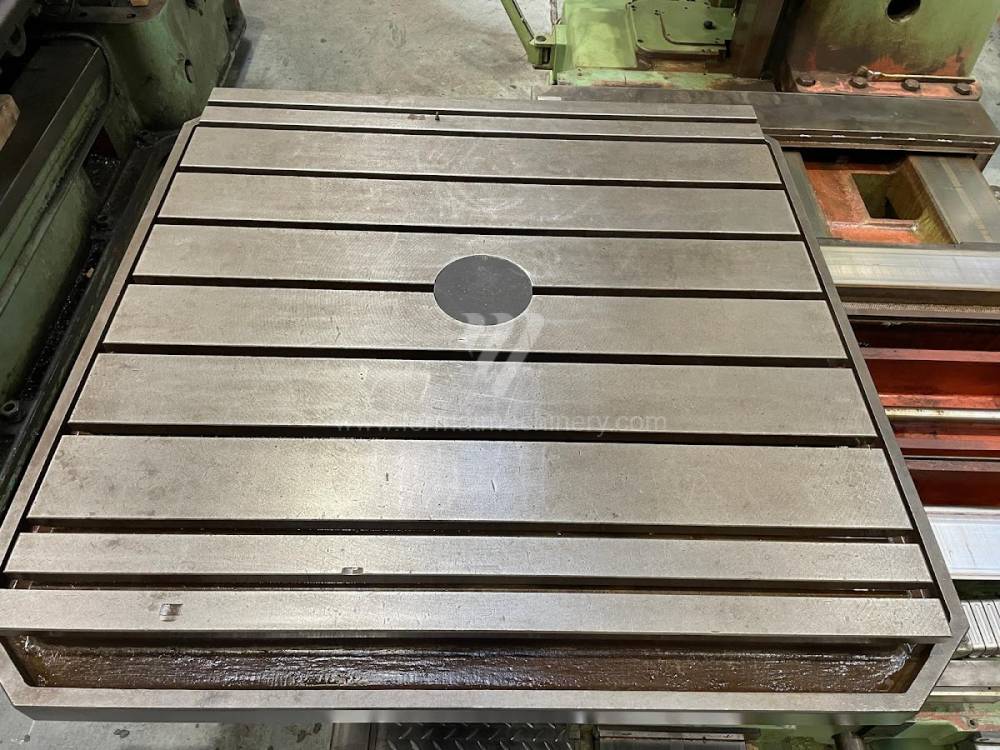
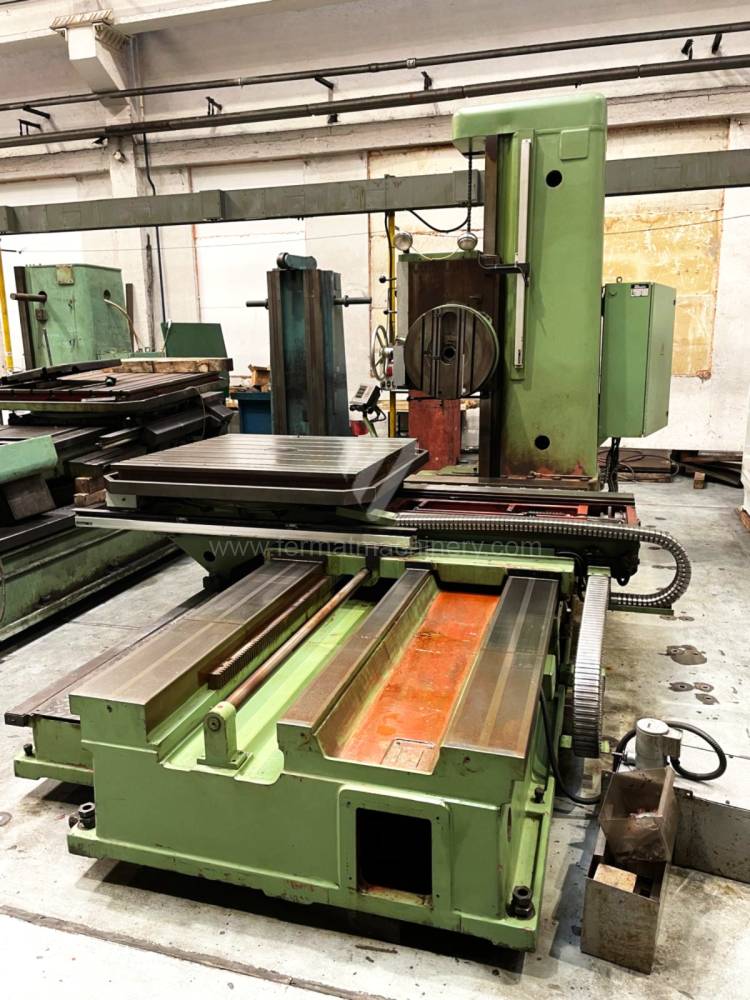










Année de production:1995
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1600 mm
Course Y: 1120 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 1120 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 900 mm
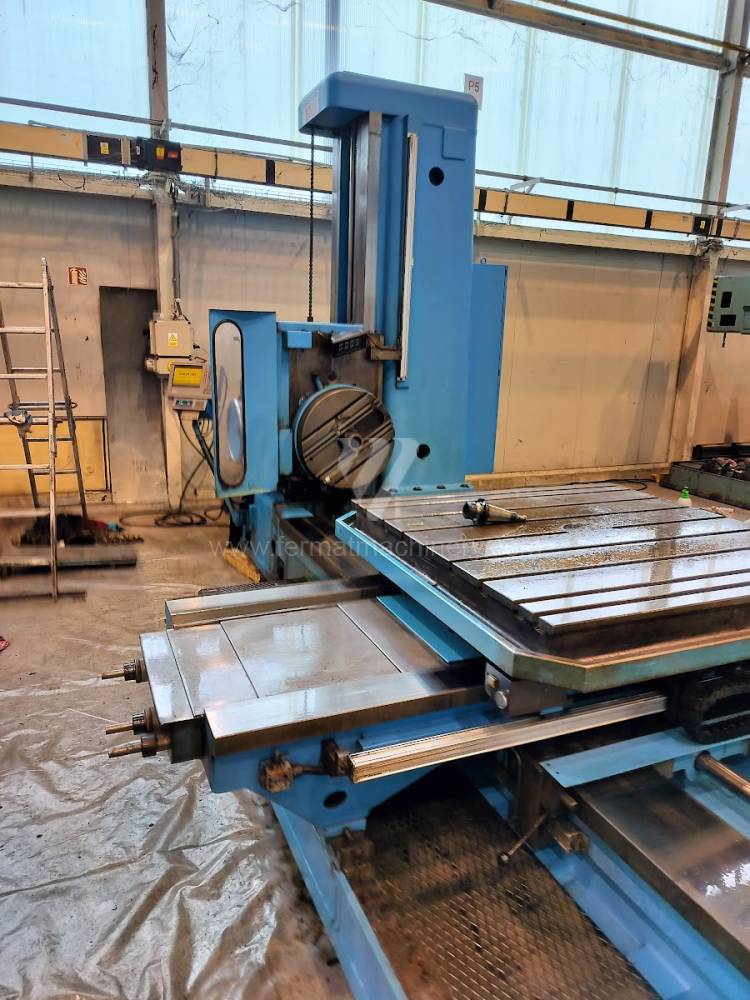
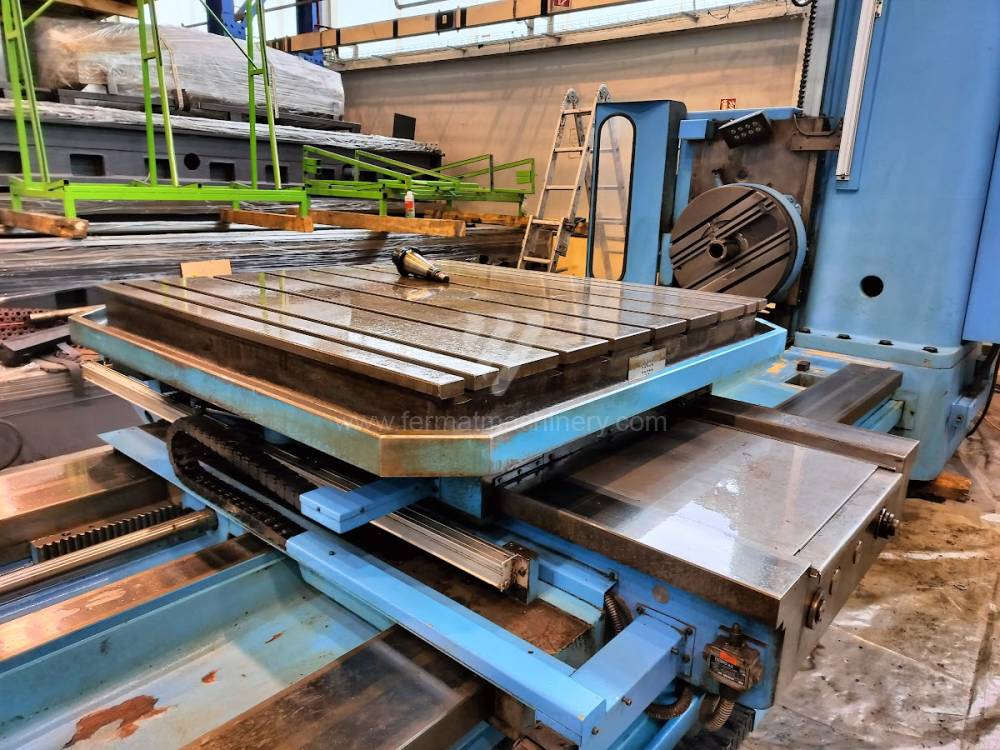
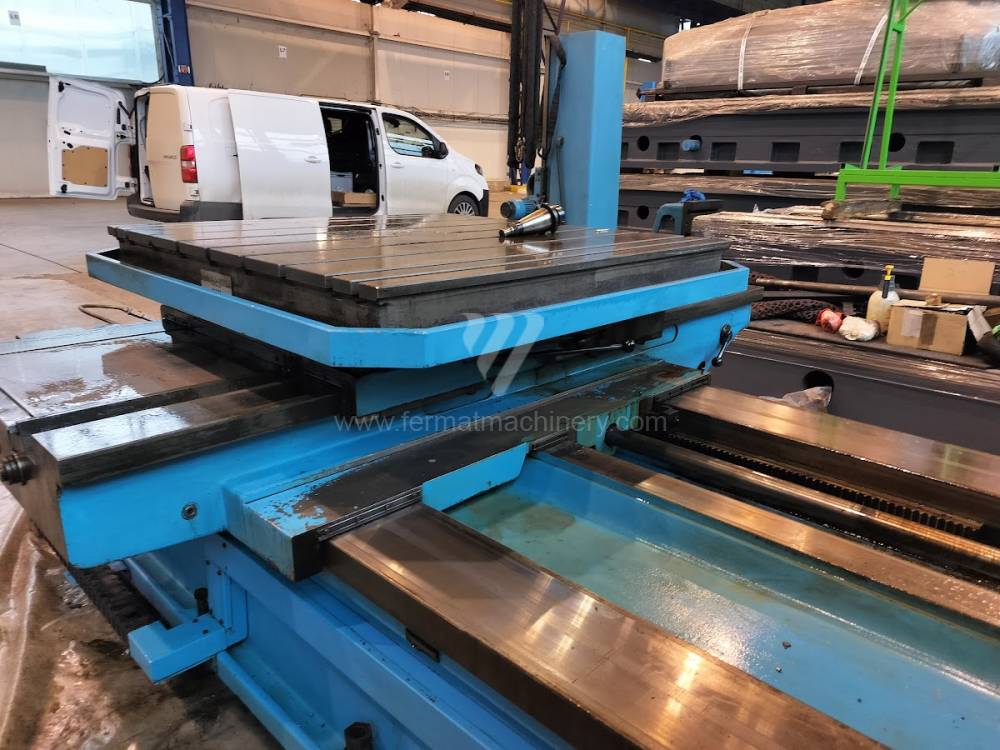
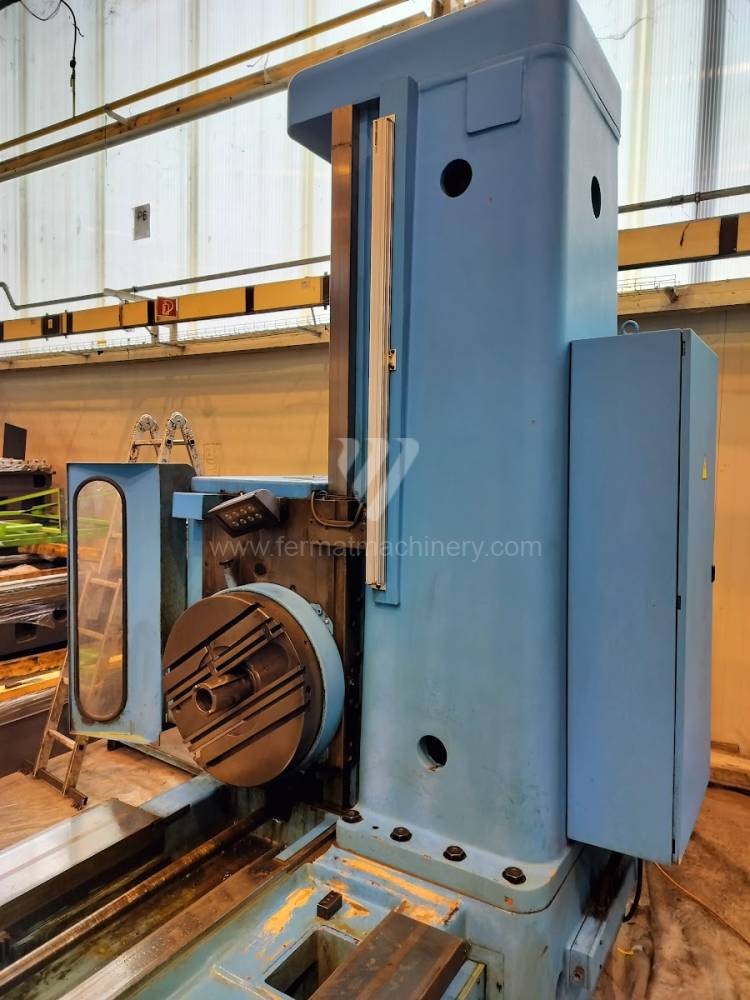
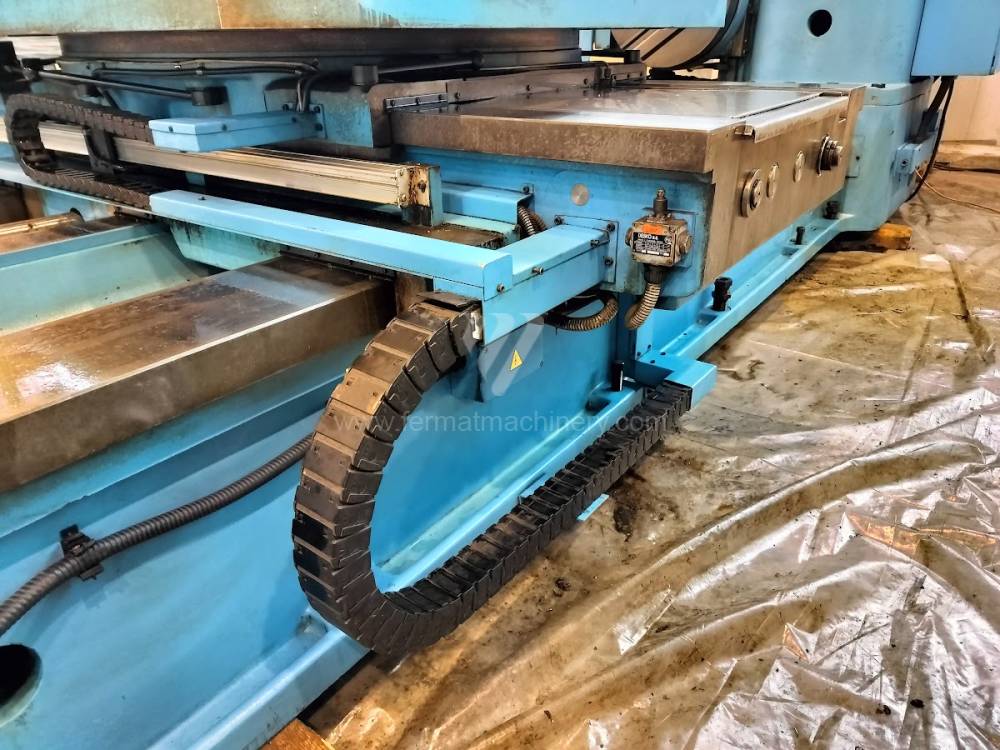
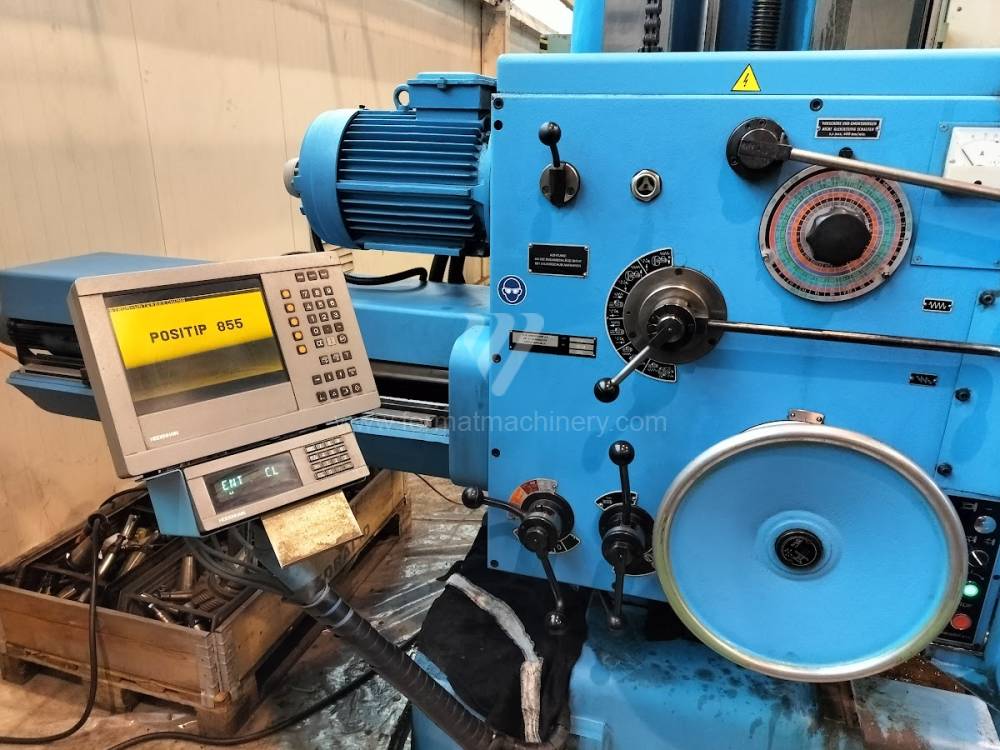
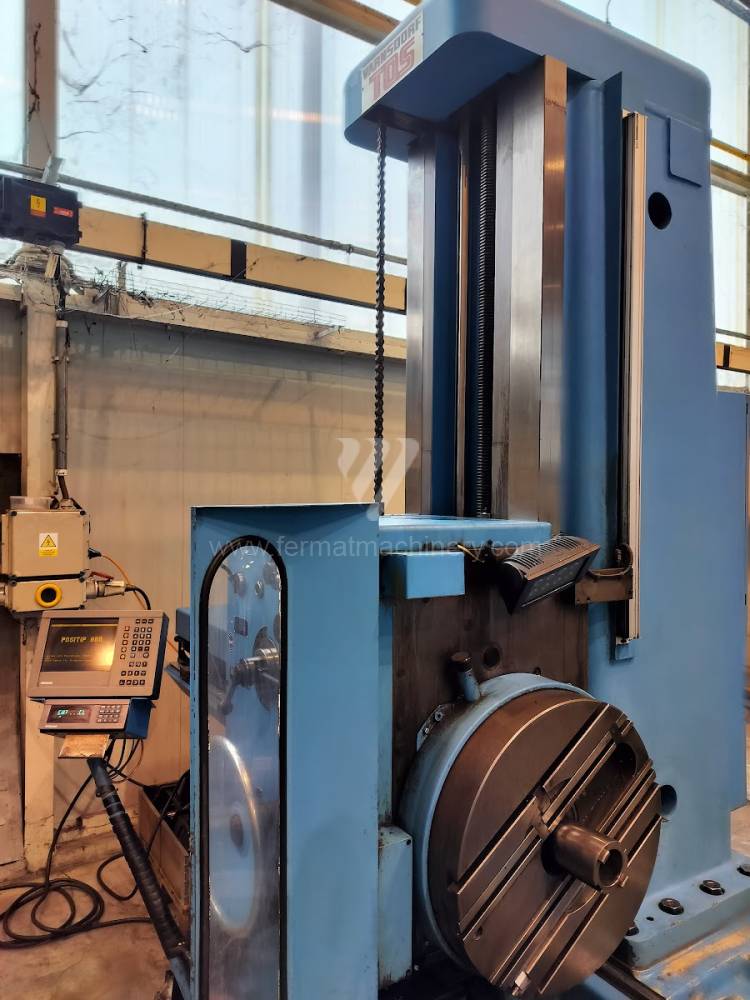
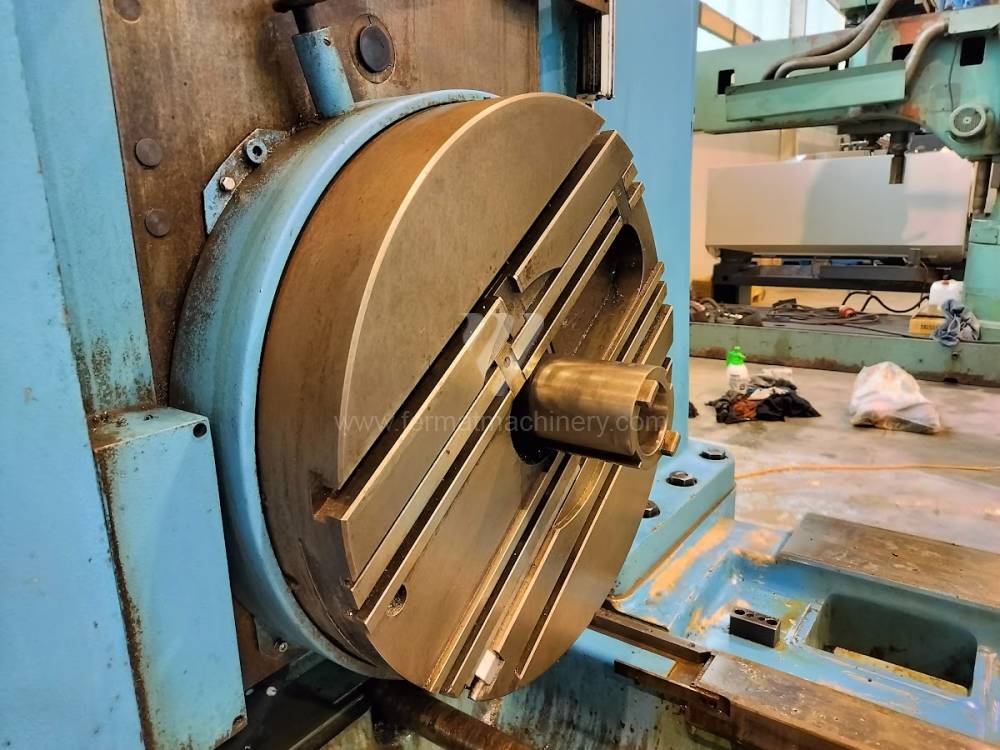
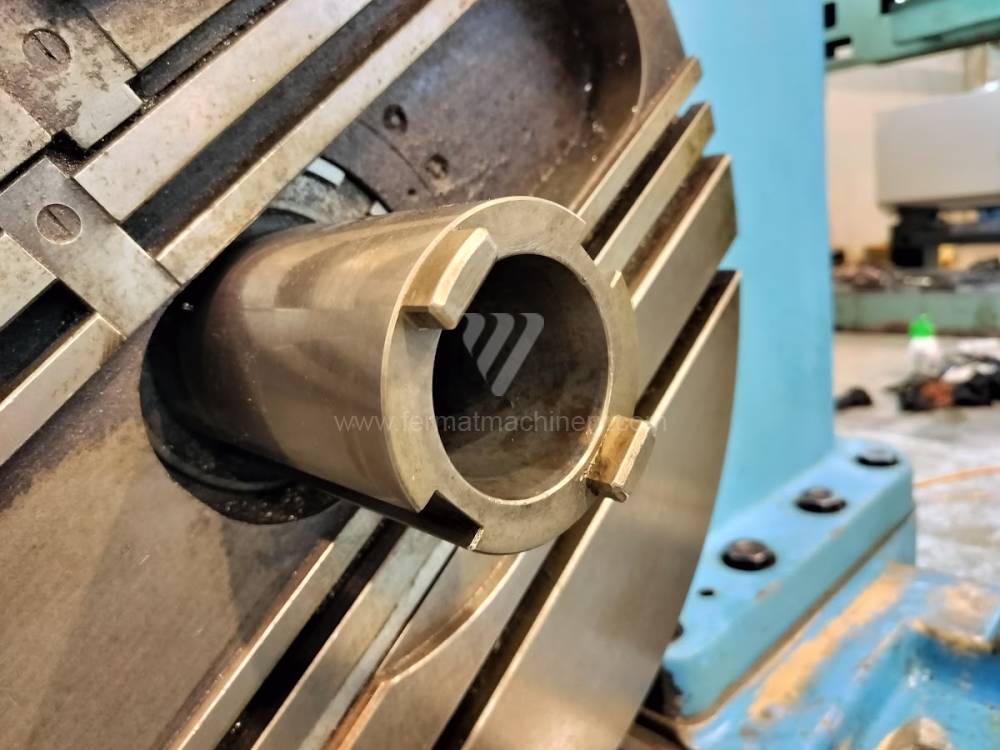
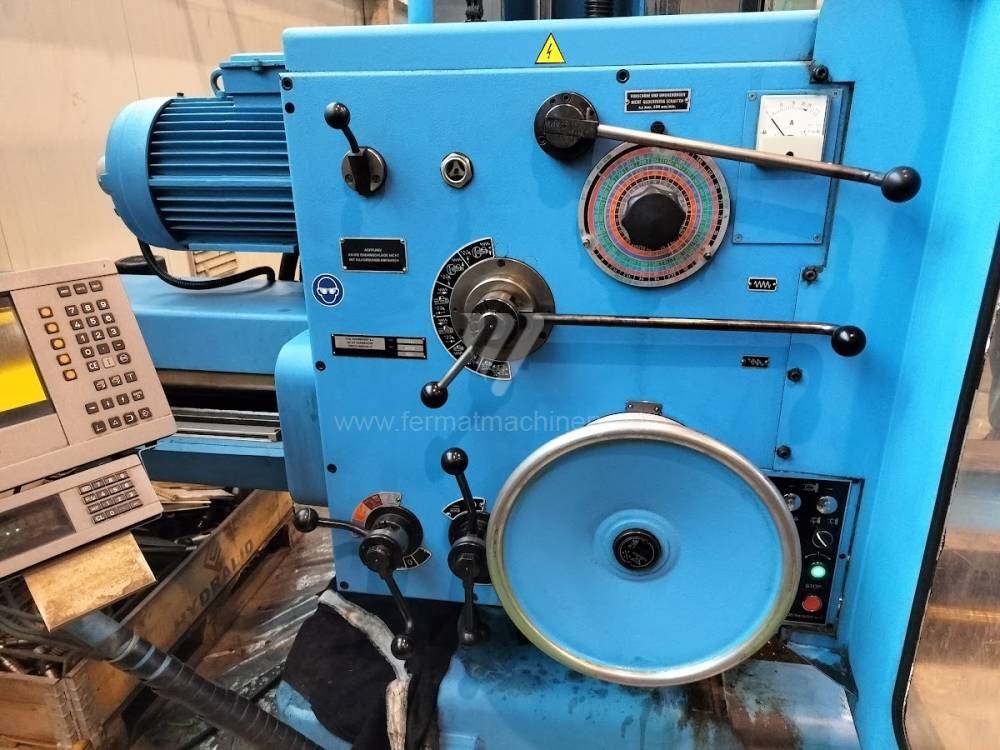
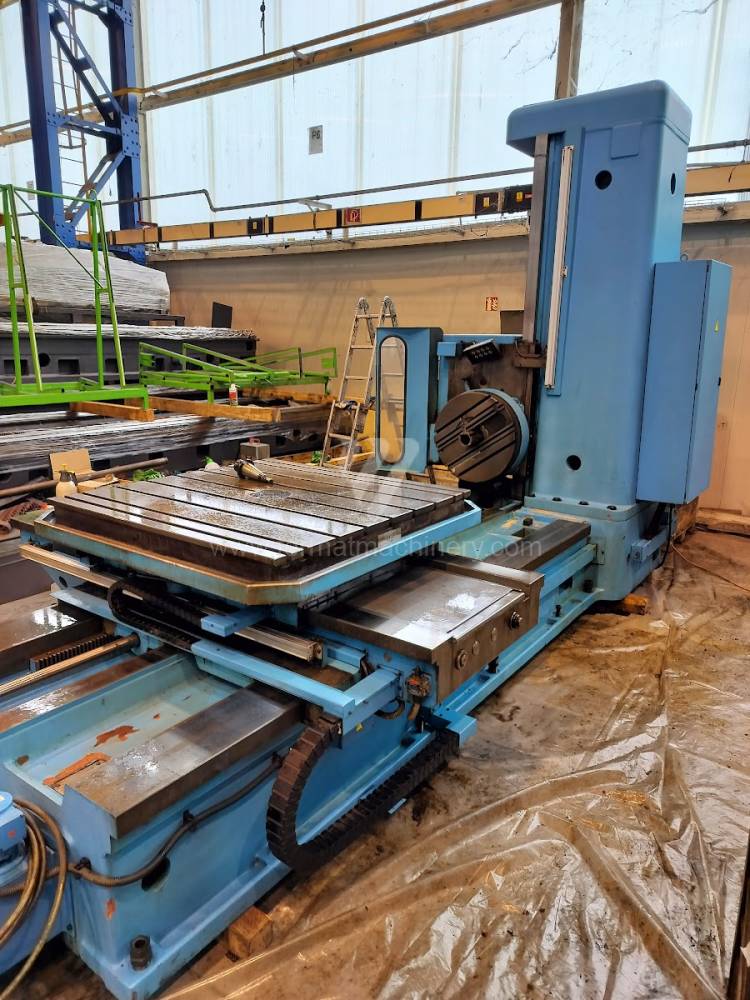





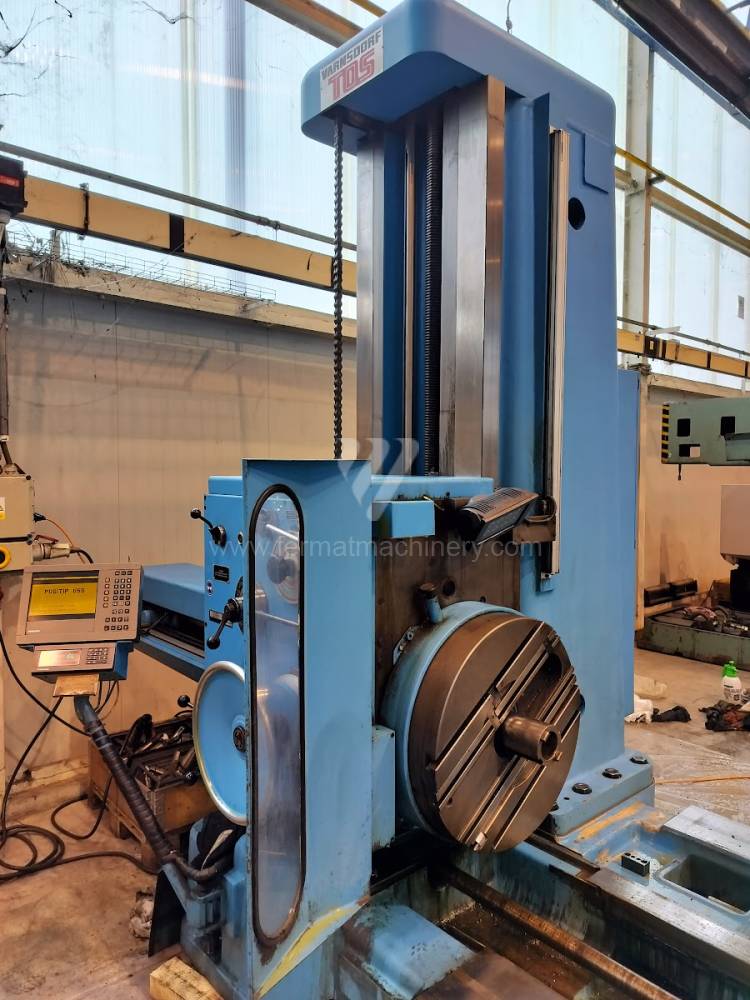











Année de production:2004
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1600 mm
Course Y: 1120 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 1120 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 900 mm
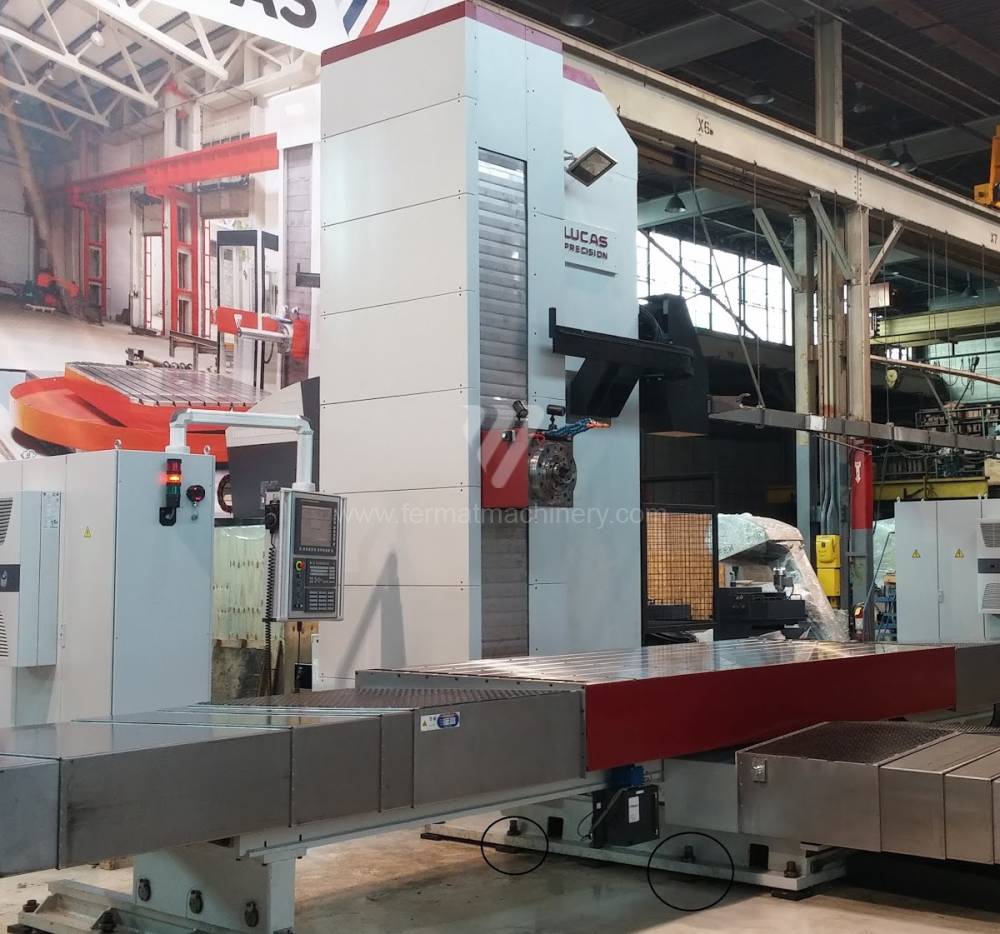
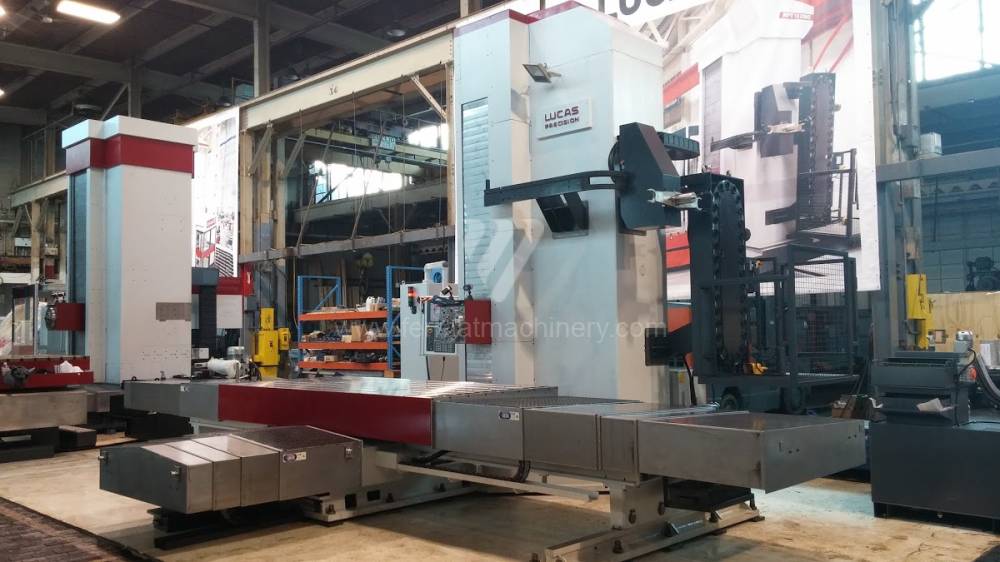


Année de production:2018
Système de contrôle Fanuc: 0i-MF
Diametre de travaille de broche: 130 mm
Course X: 3657 mm
Course Y: 3048 mm
Vitesse de broche: 10 - 3000 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: OUI
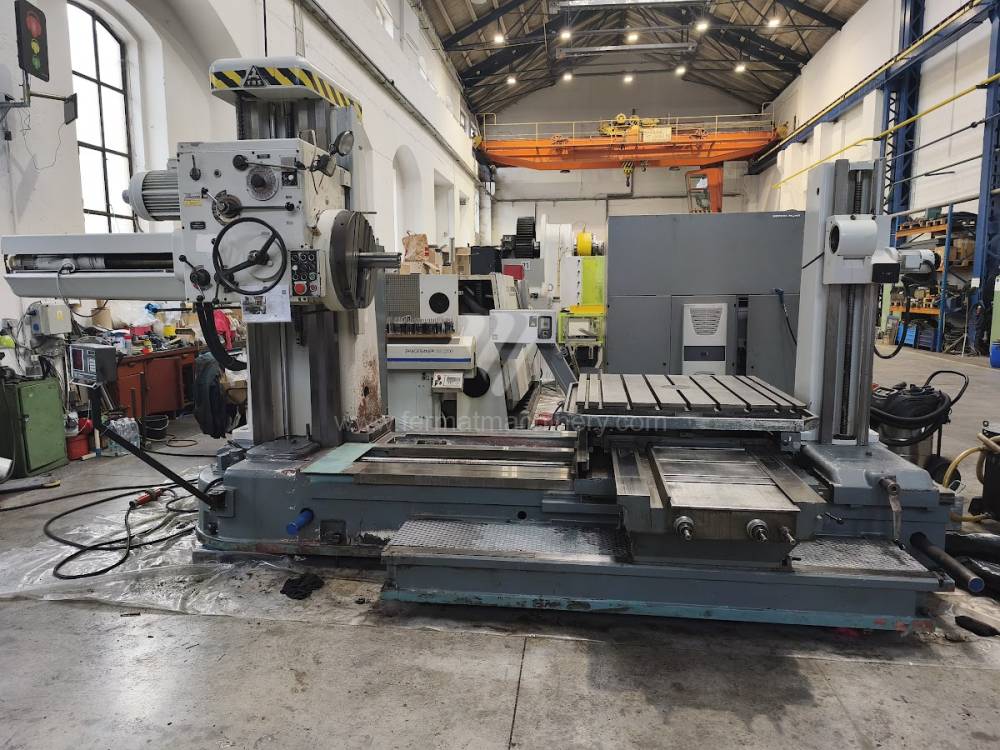
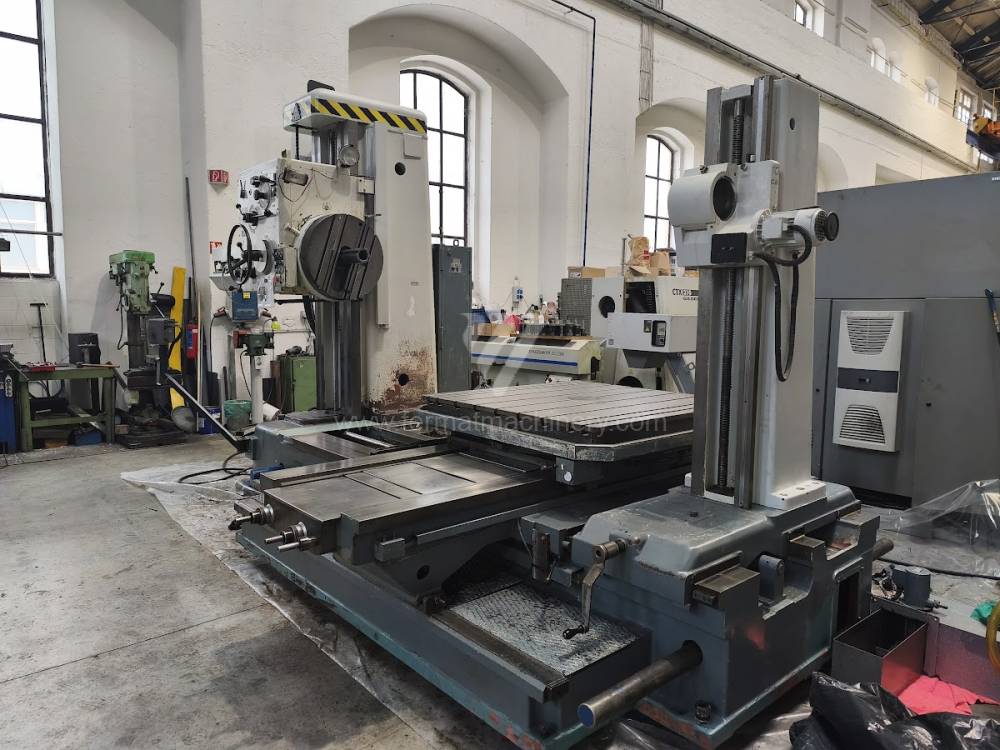
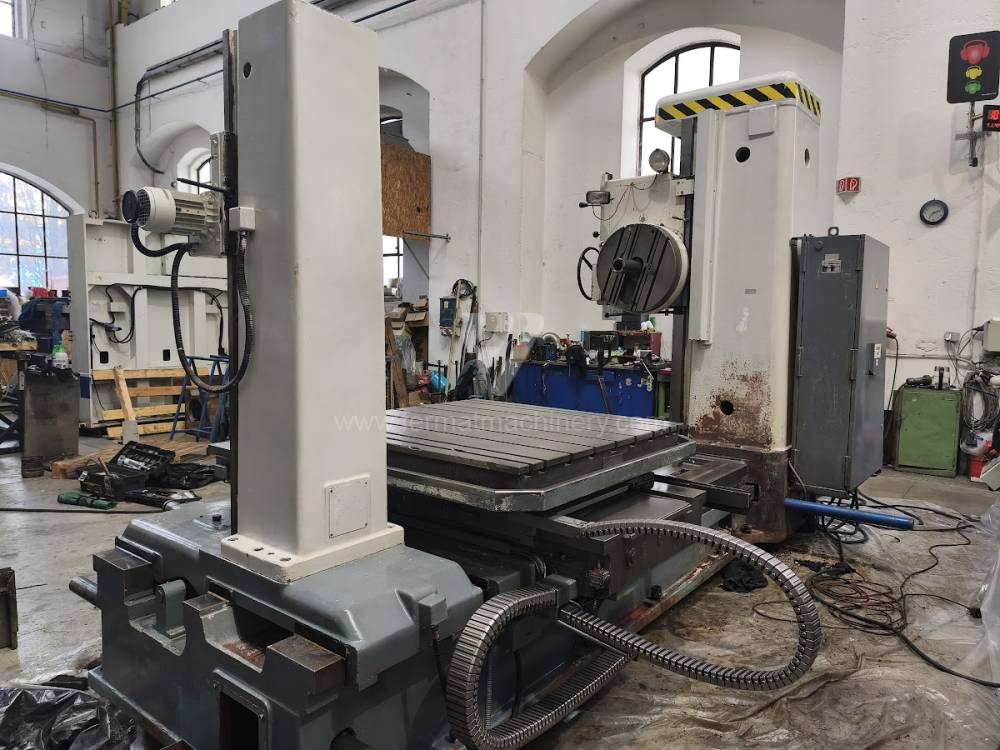
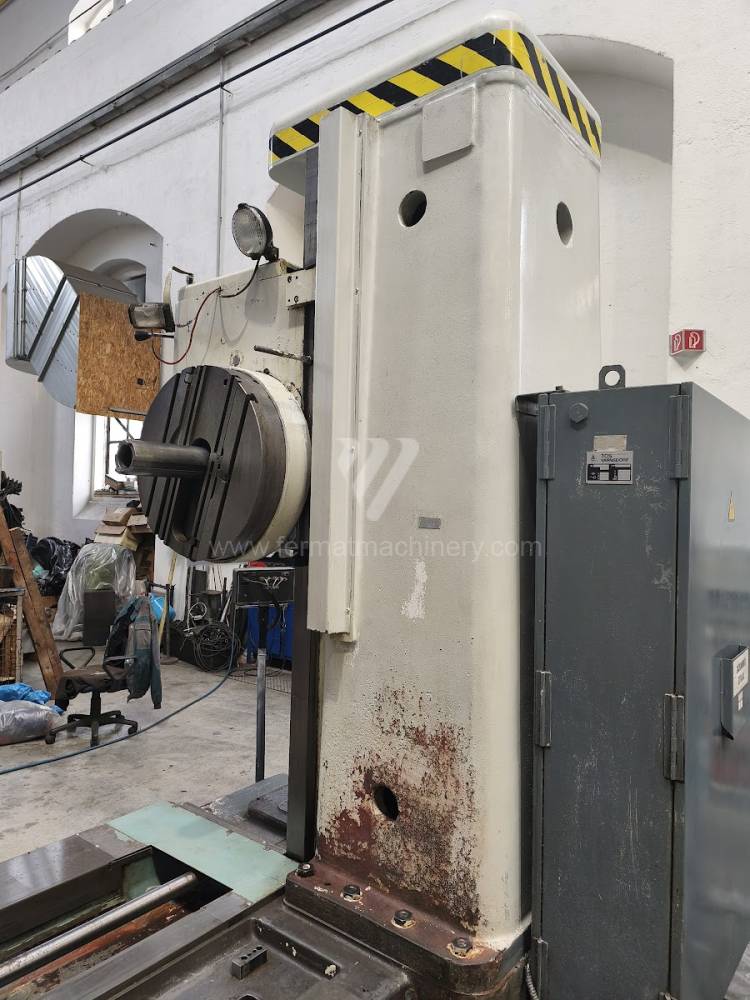
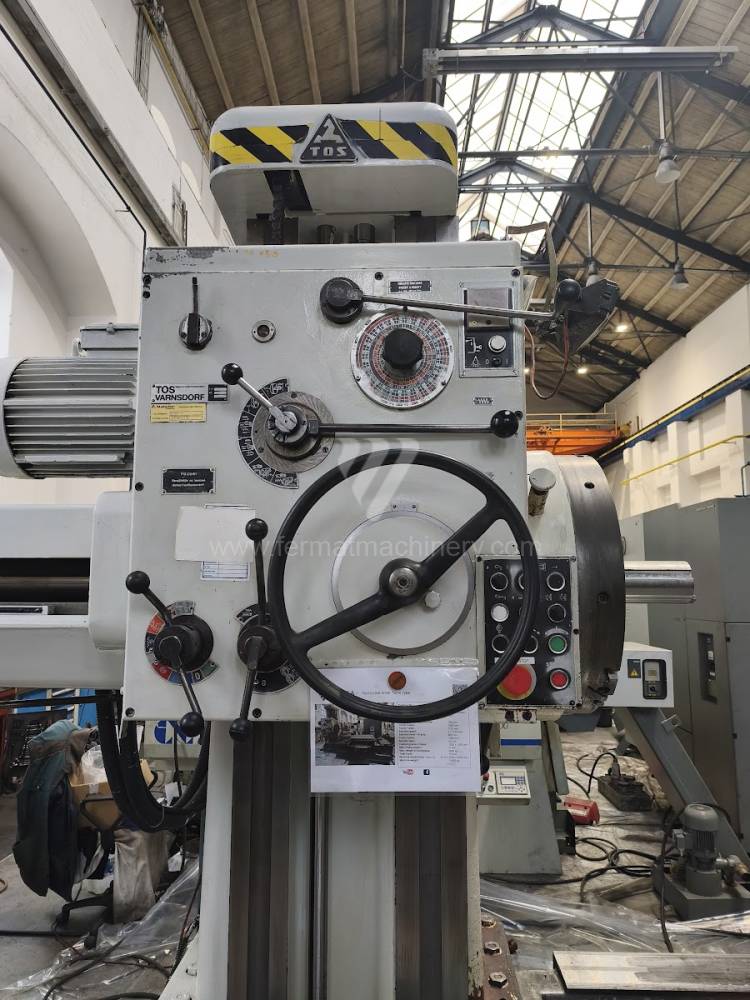
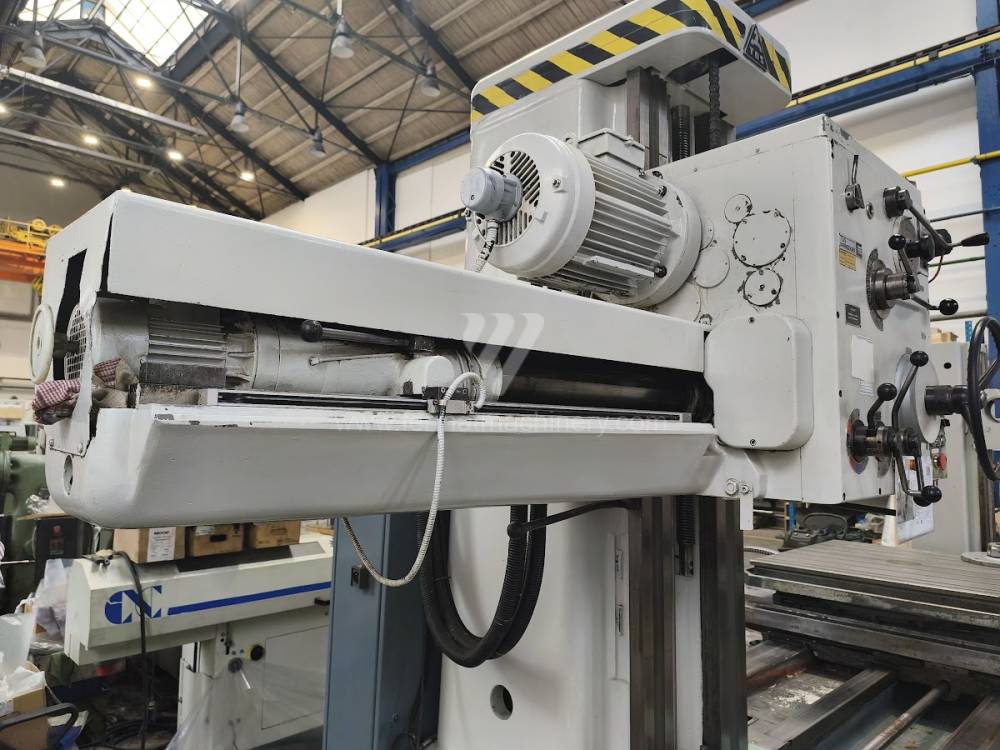














































Année de production:1991
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1600 mm
Course Y: 1120 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 1200 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 900 mm
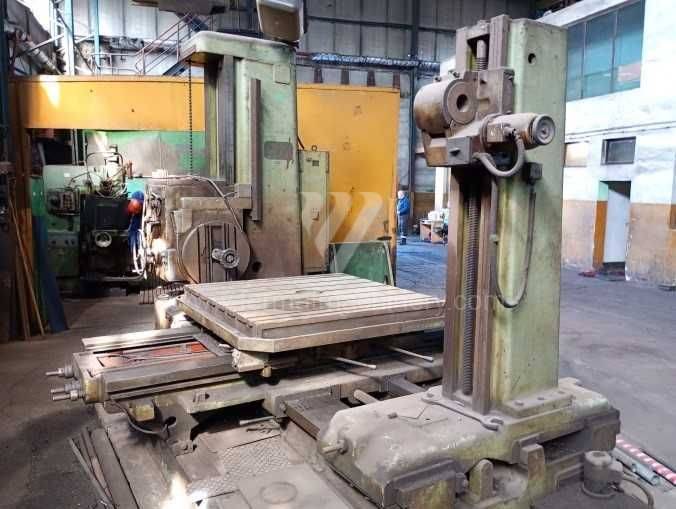
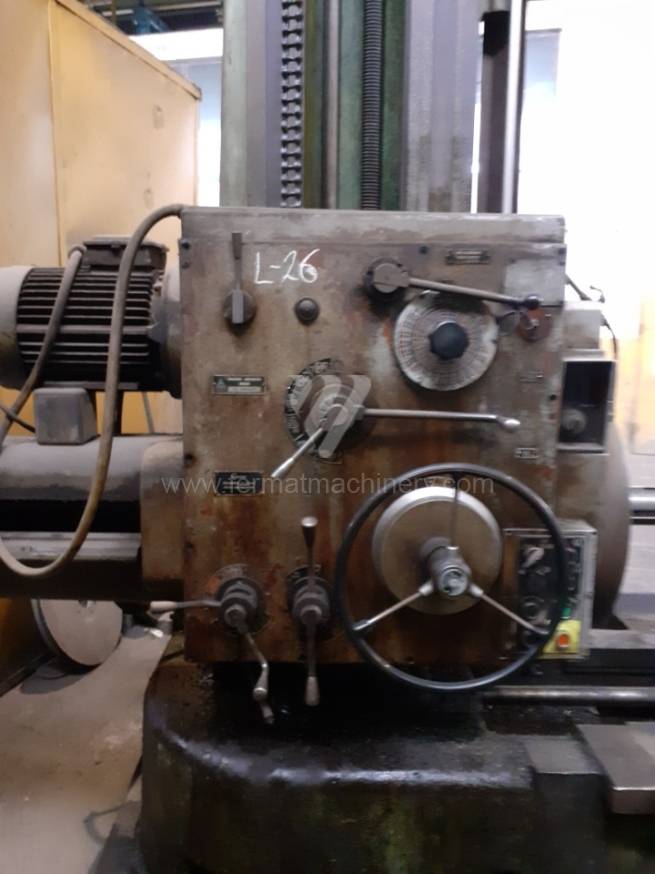
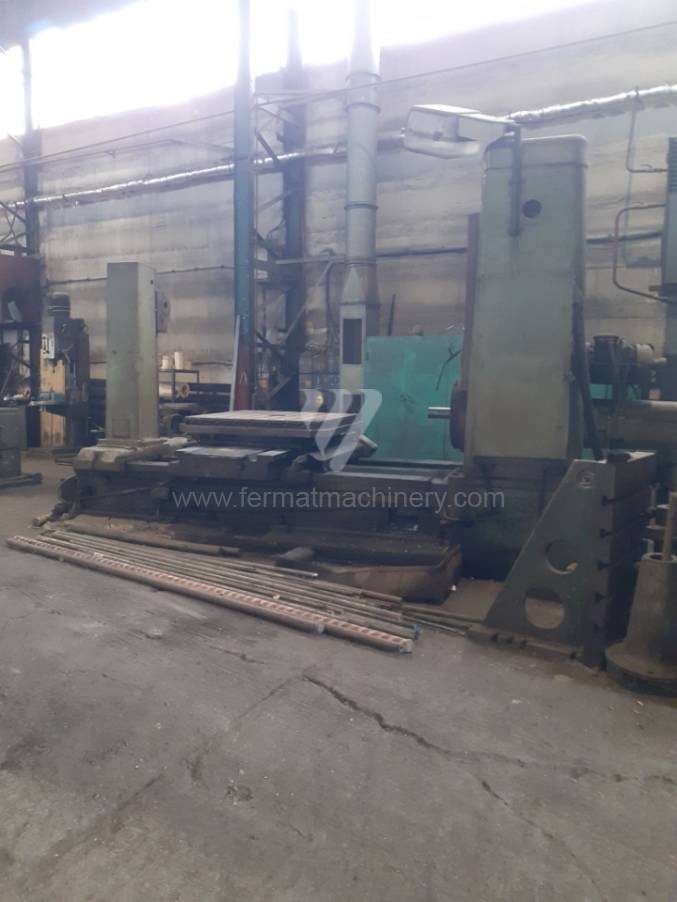





Année de production:1976
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1000 mm
Course Y: 700 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 1200 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 900 mm



Année de production:1982
Système de contrôle Mefi: CNC 859
Diametre de travaille de broche: 90 mm
Course X: 1250 mm
Course Y: 900 mm
Vitesse de broche: 10 - 1100 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON



Année de production:1996
Diametre de travaille de broche: 75 mm
Course X: 1250 mm
Course Y: 900 mm
Vitesse de broche: 18 - 1800 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 560 mm
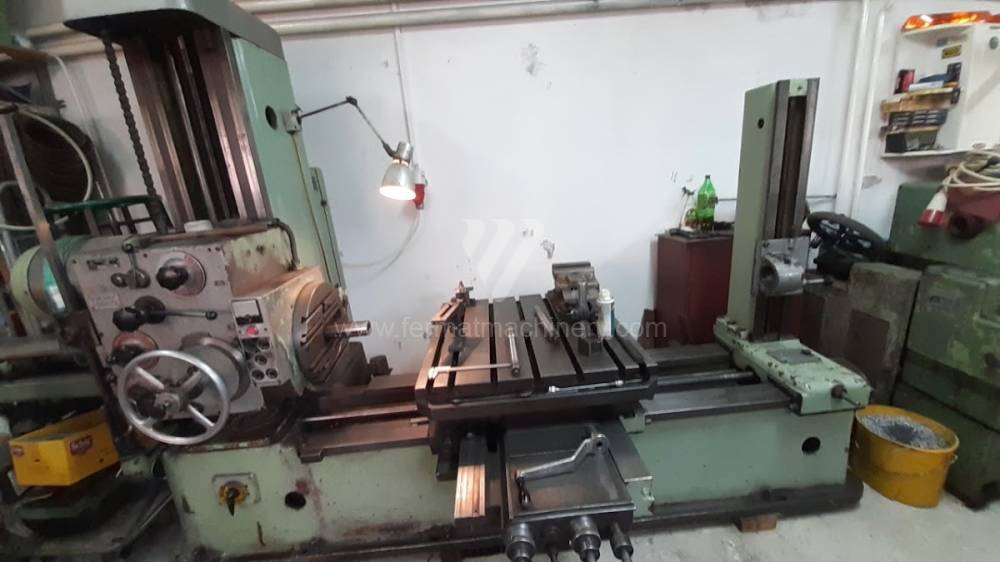
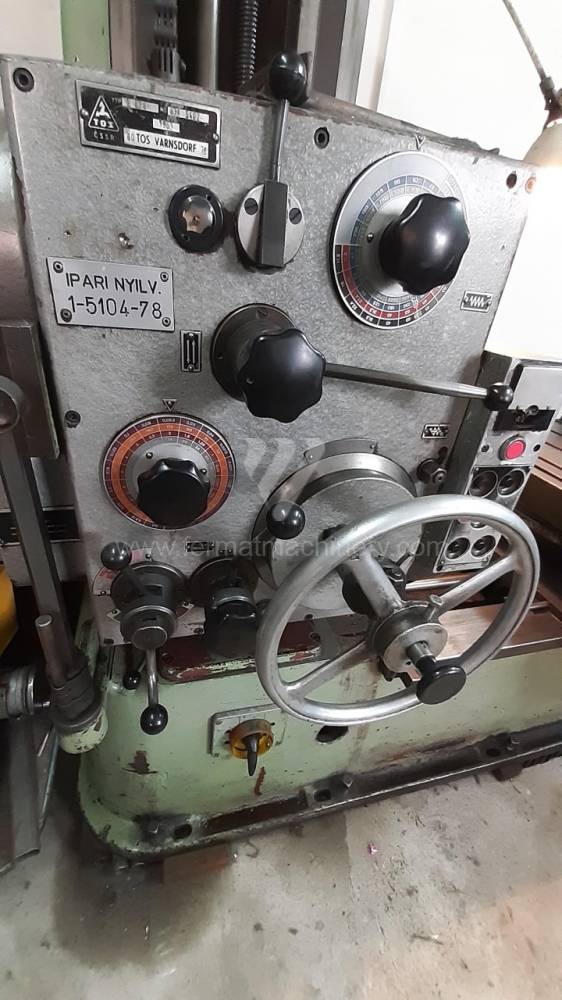






Année de production:1963
Diametre de travaille de broche: 63 mm
Course X: 1050 mm
Course Y: 610 mm
Vitesse de broche: 8 - 1400 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 560 mm
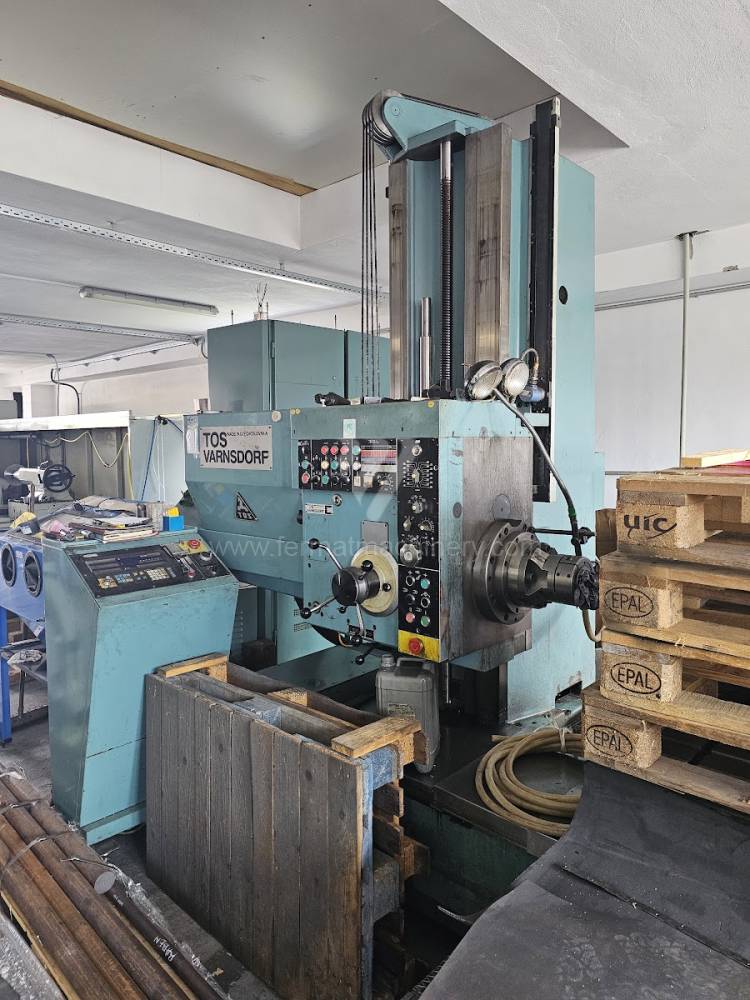
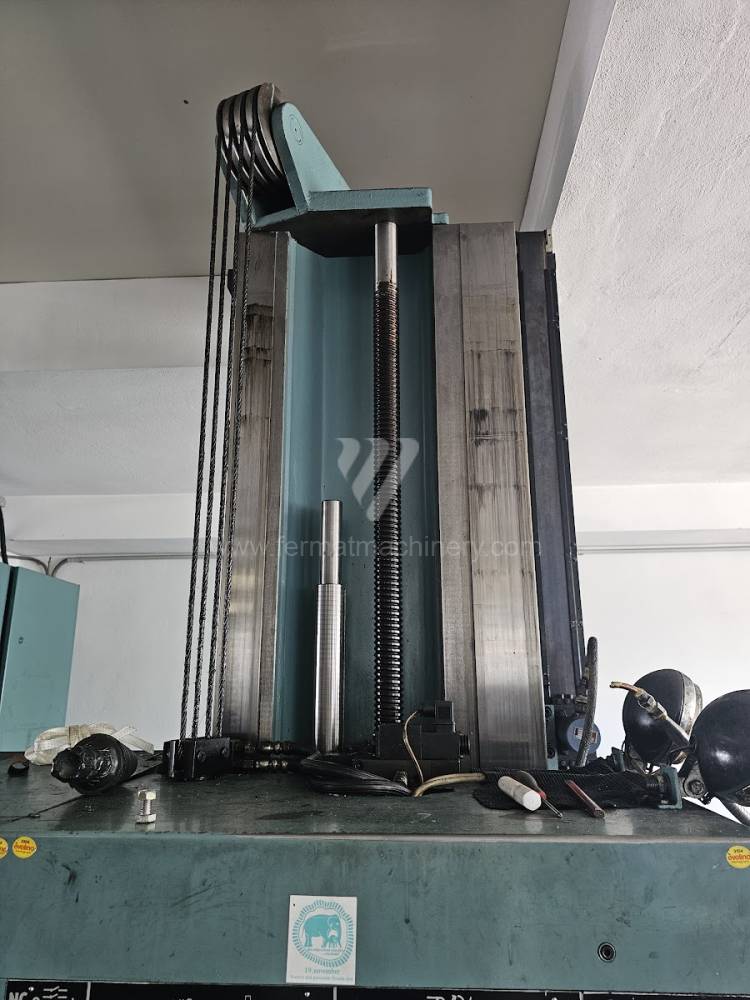
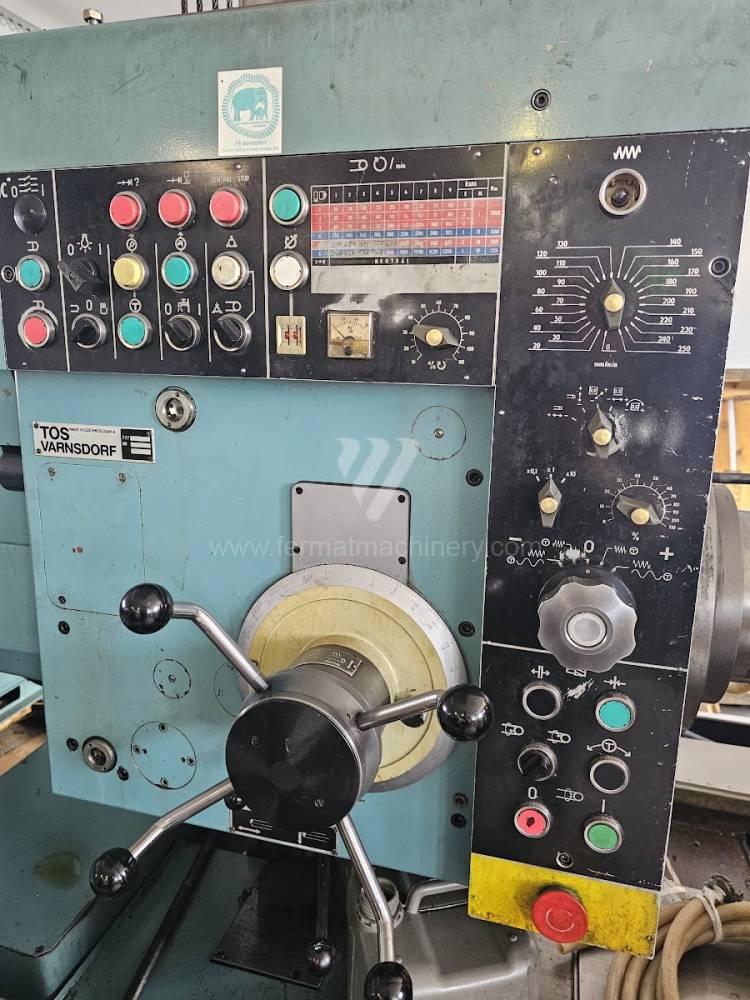
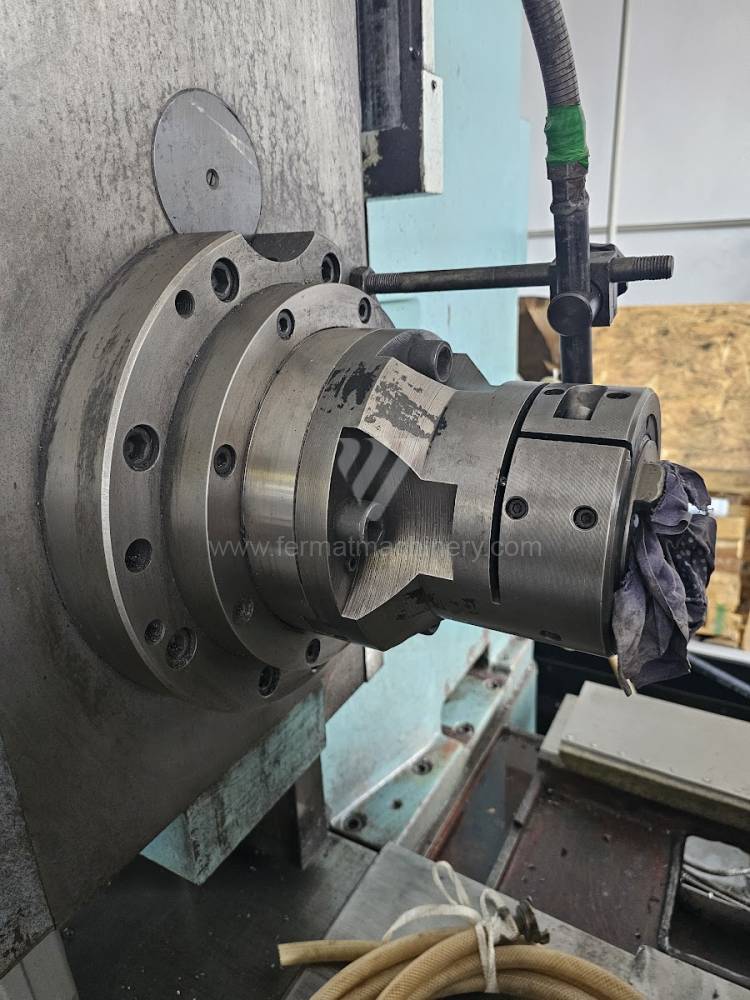





Année de production:1991
Système de contrôle Tesla: NS 670
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1250 mm
Course Y: 900 mm
Vitesse de broche: 16 - 1250 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
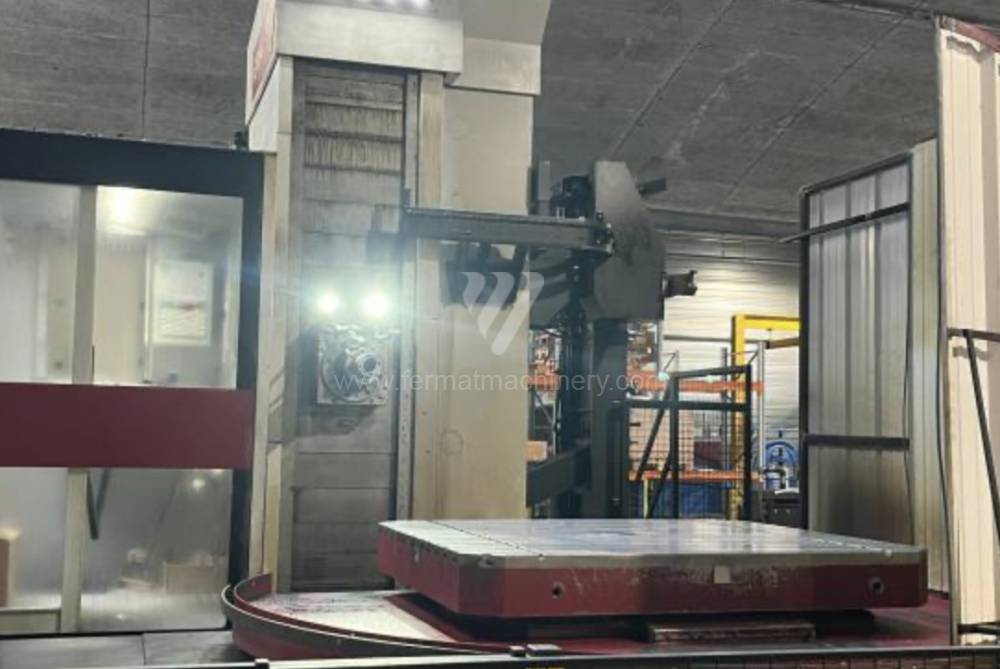
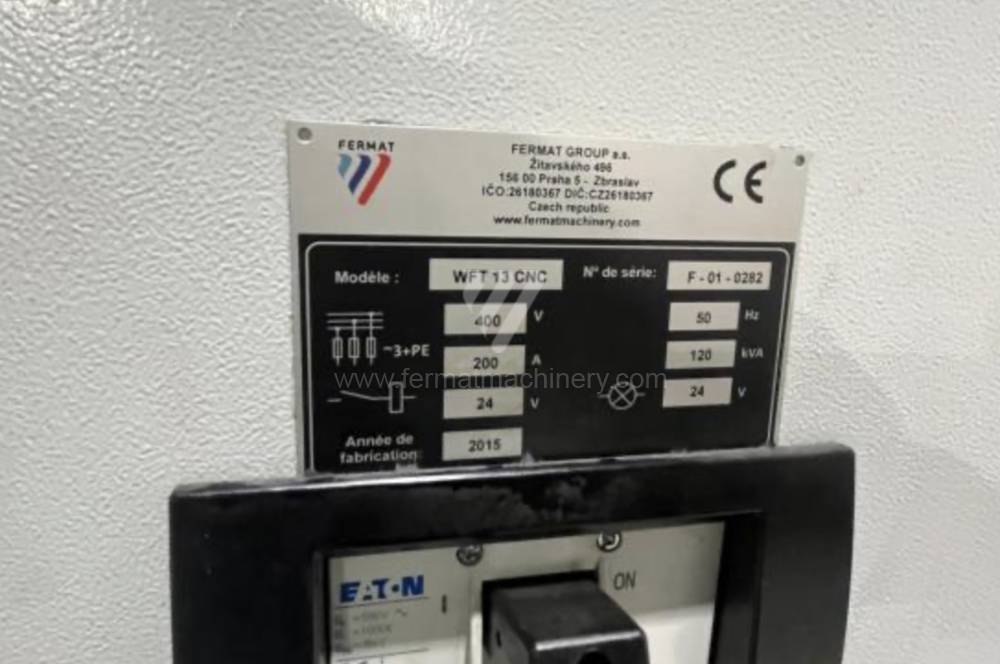
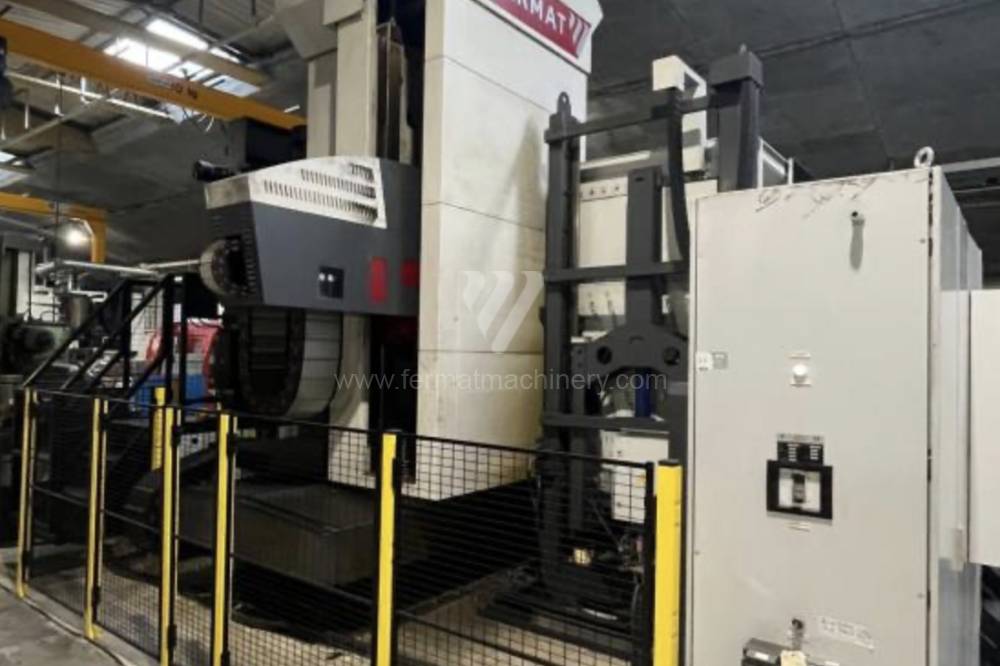
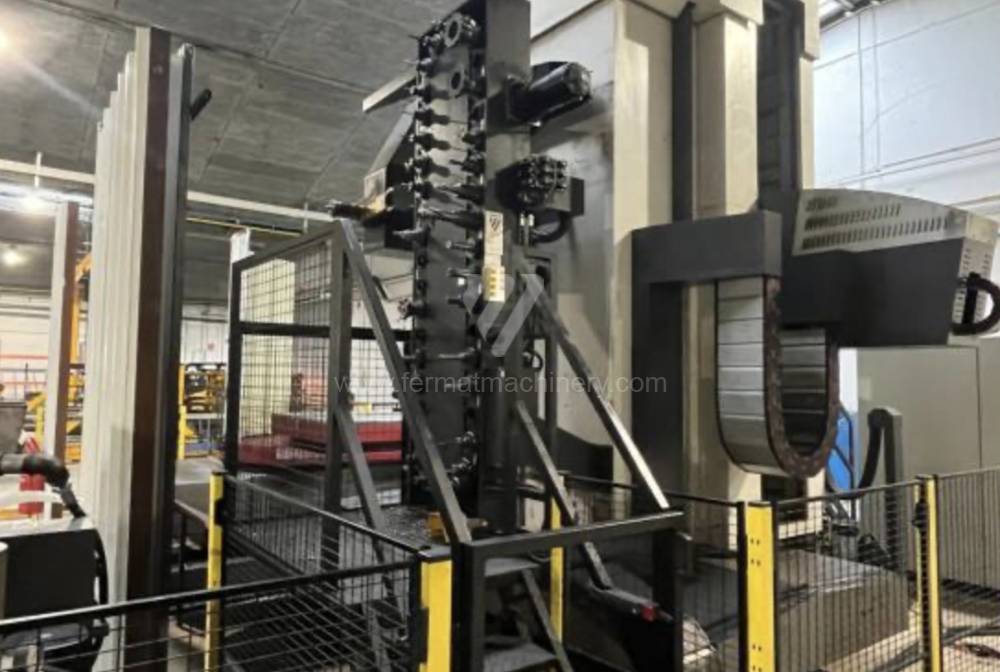
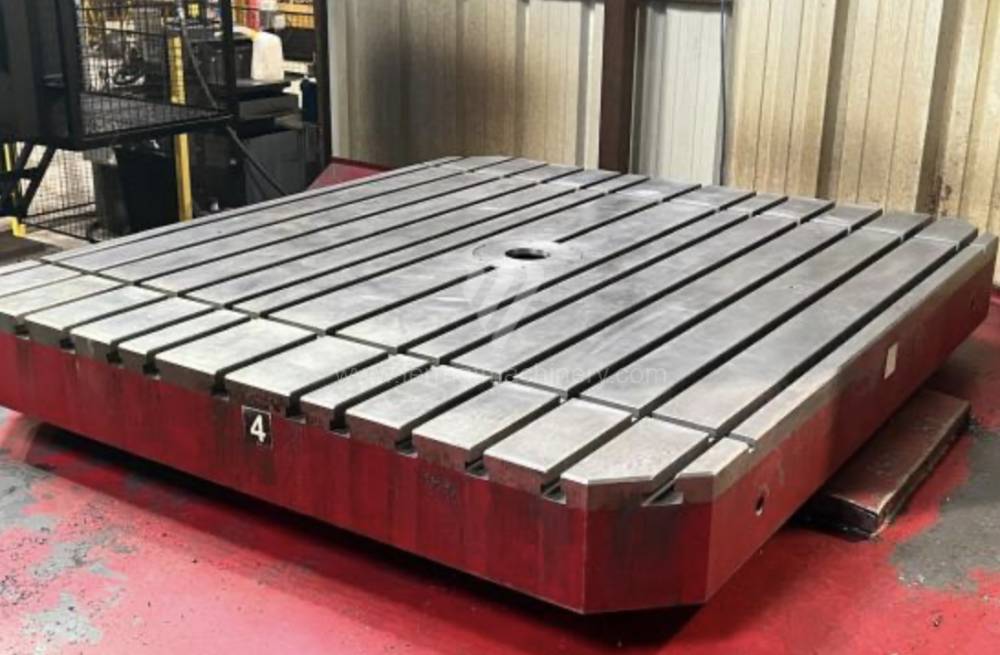
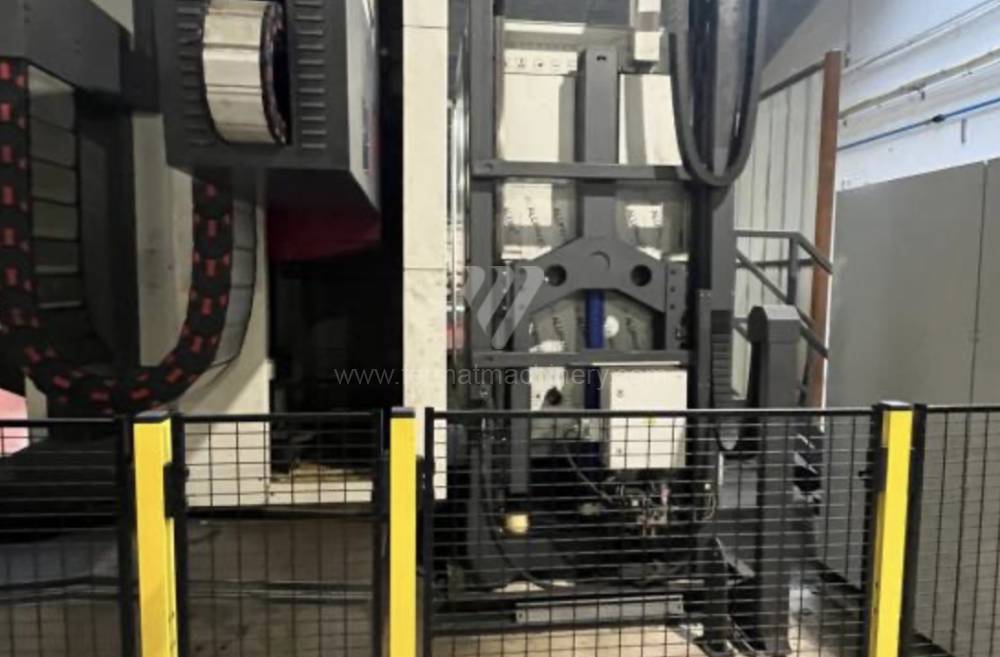
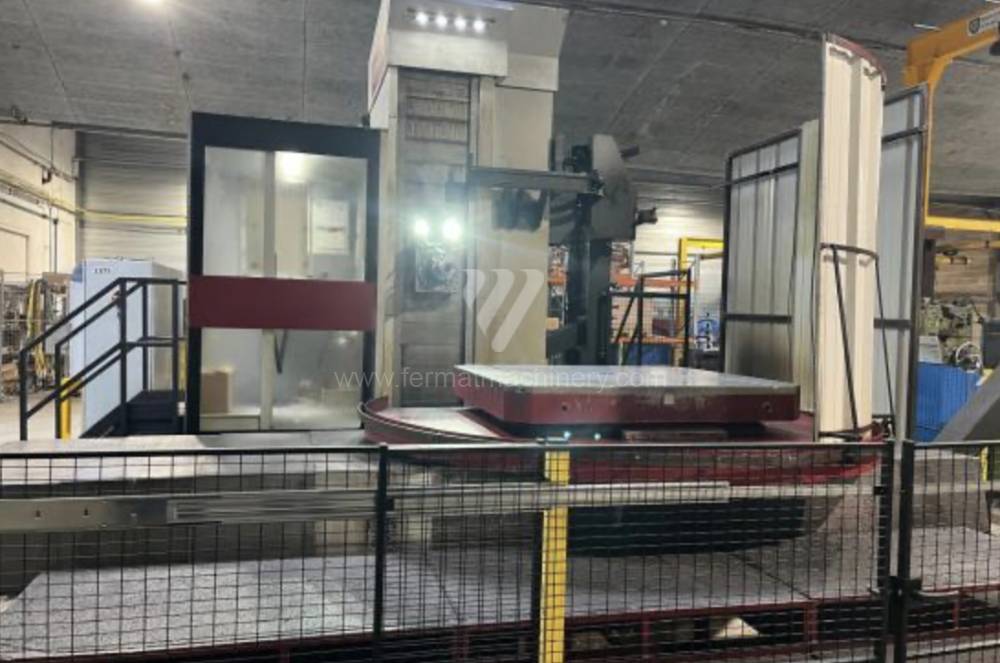













Année de production:2015
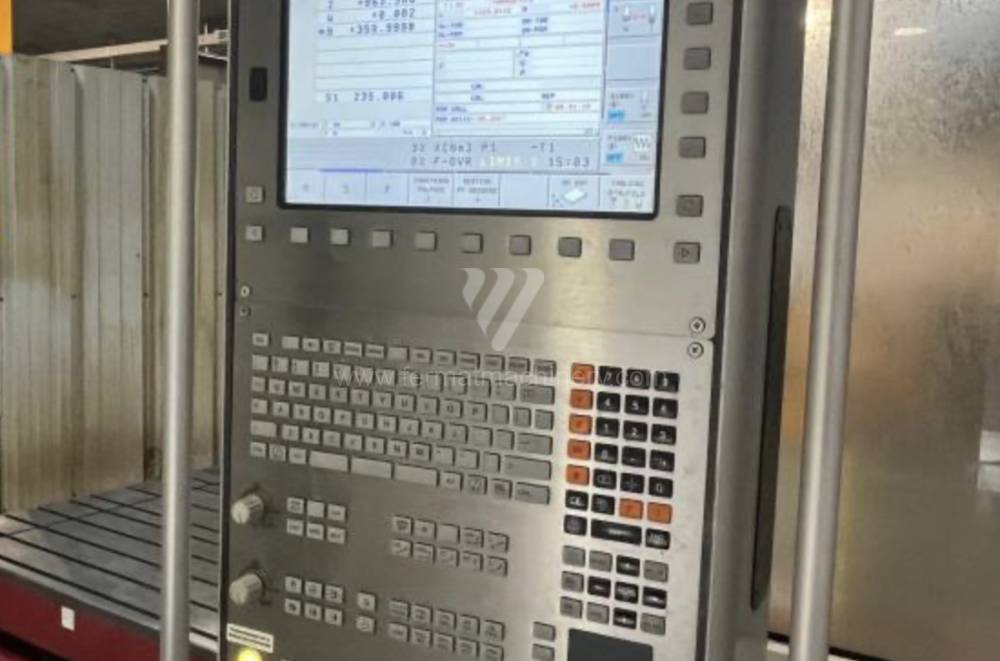
Système de contrôle Heidenhain: TNC 530
Diametre de travaille de broche: 130 mm
Course X: 3000 mm
Course Y: 2000 mm
Vitesse de broche: 10 - 3000 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: OUI
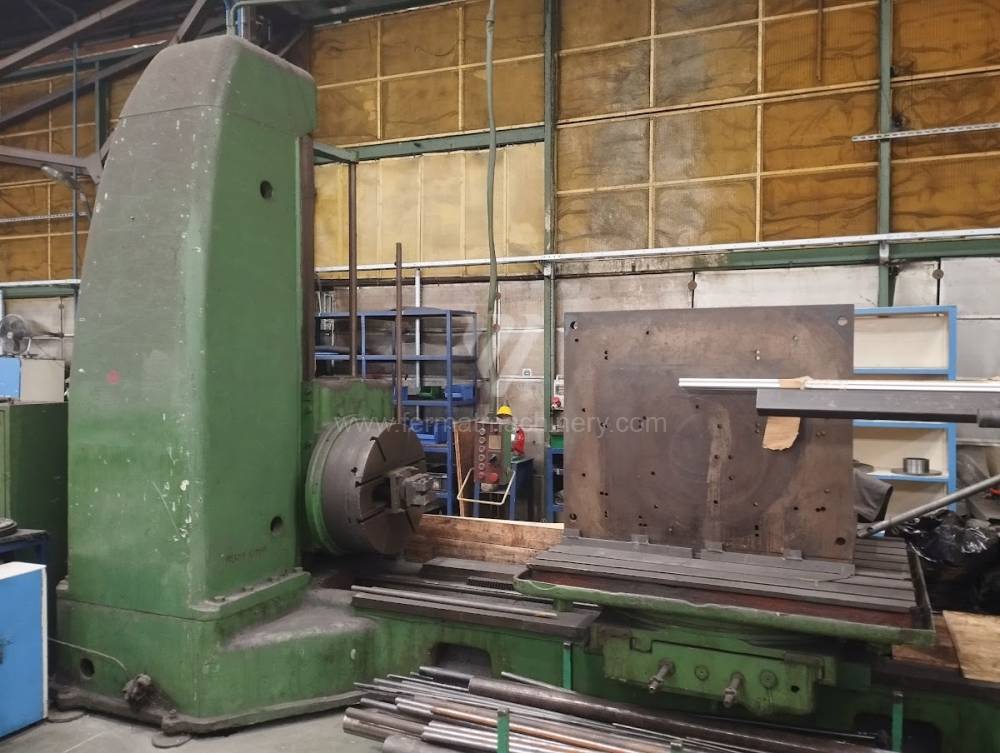
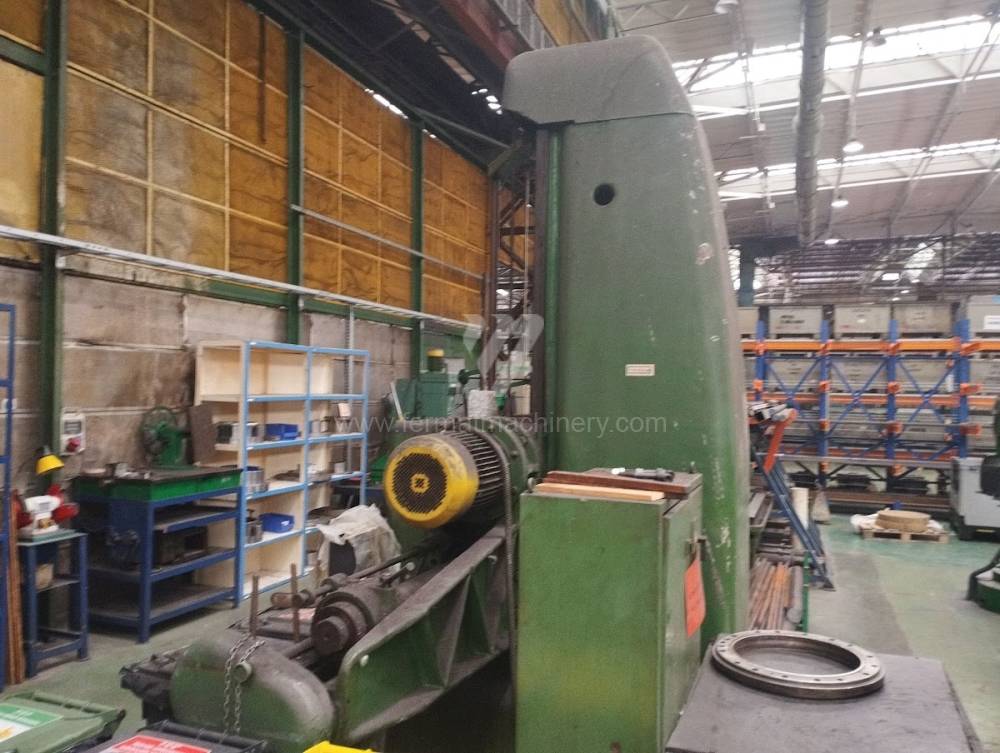
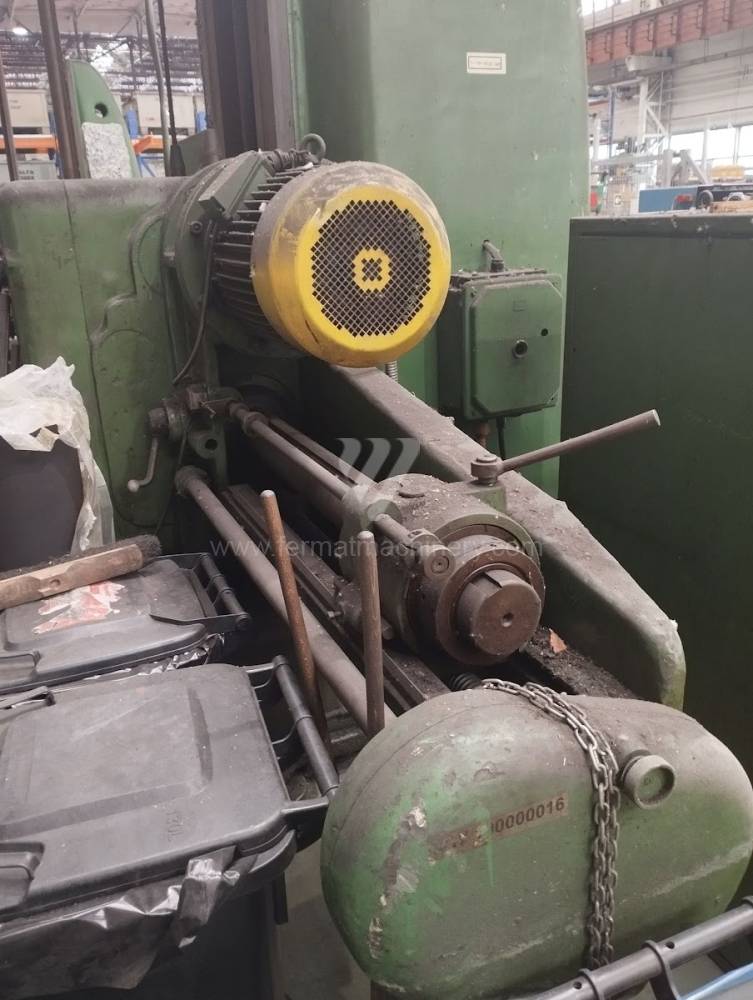
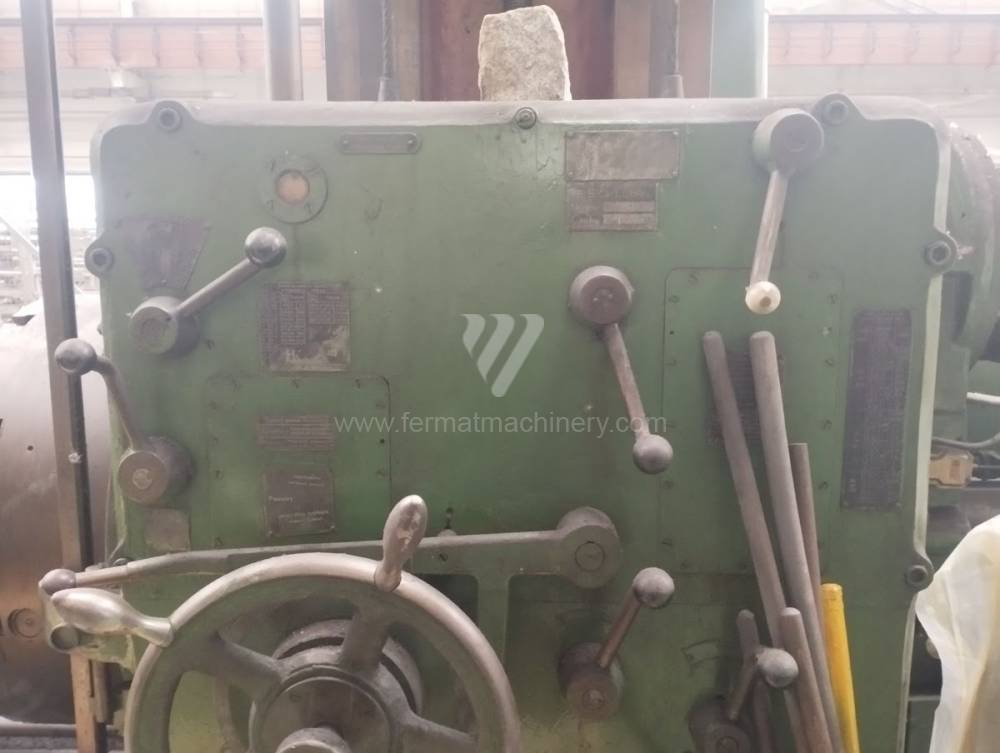
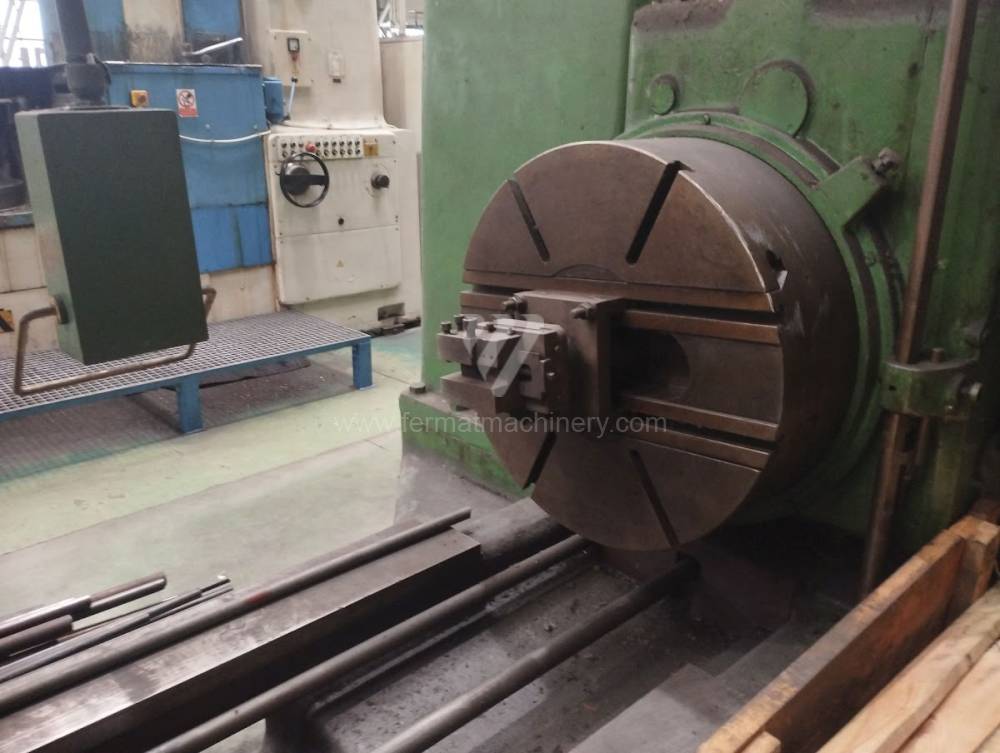
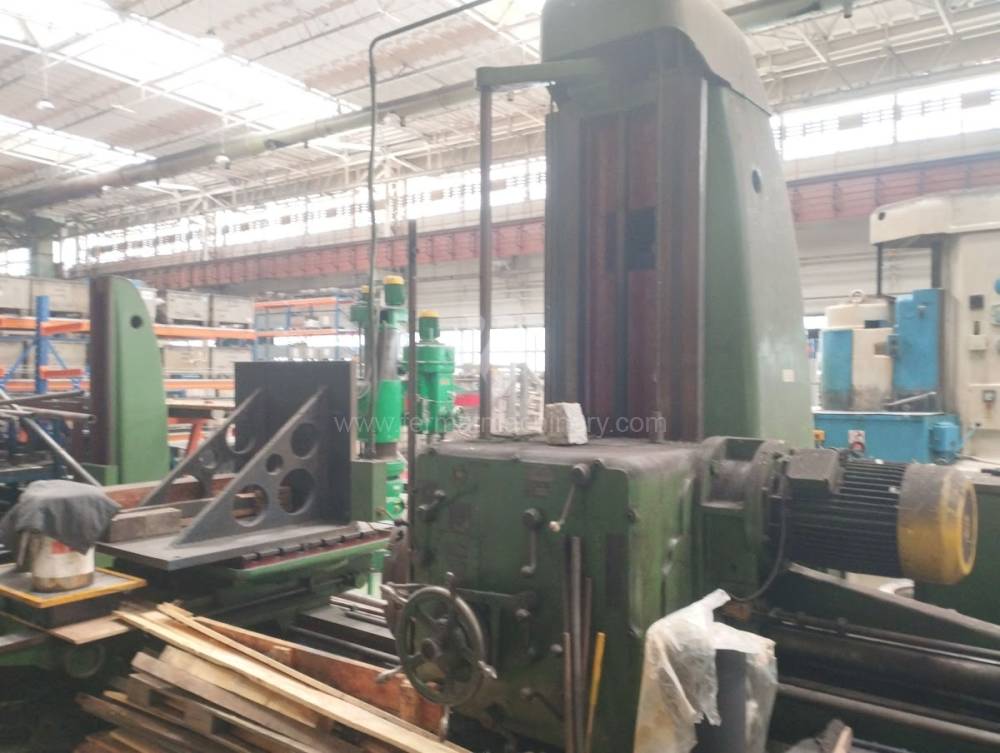
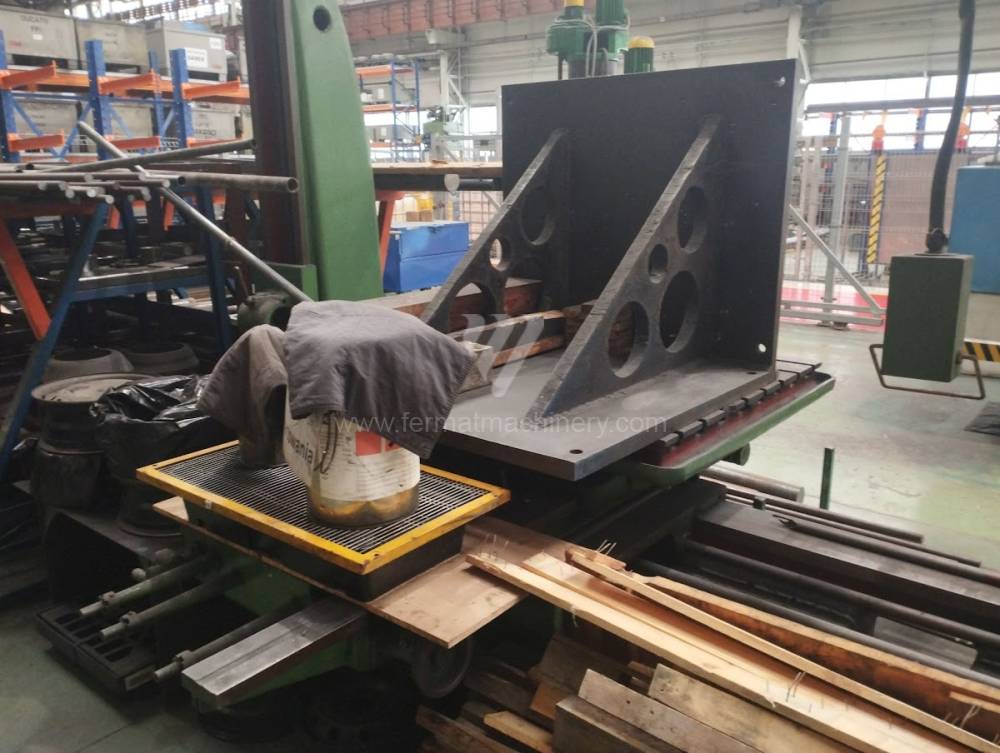







Année de production:1957
Diametre de travaille de broche: 110 mm
Course X: 1200 mm
Course Y: 1150 mm
Vitesse de broche: 8 - 1250 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 850 mm
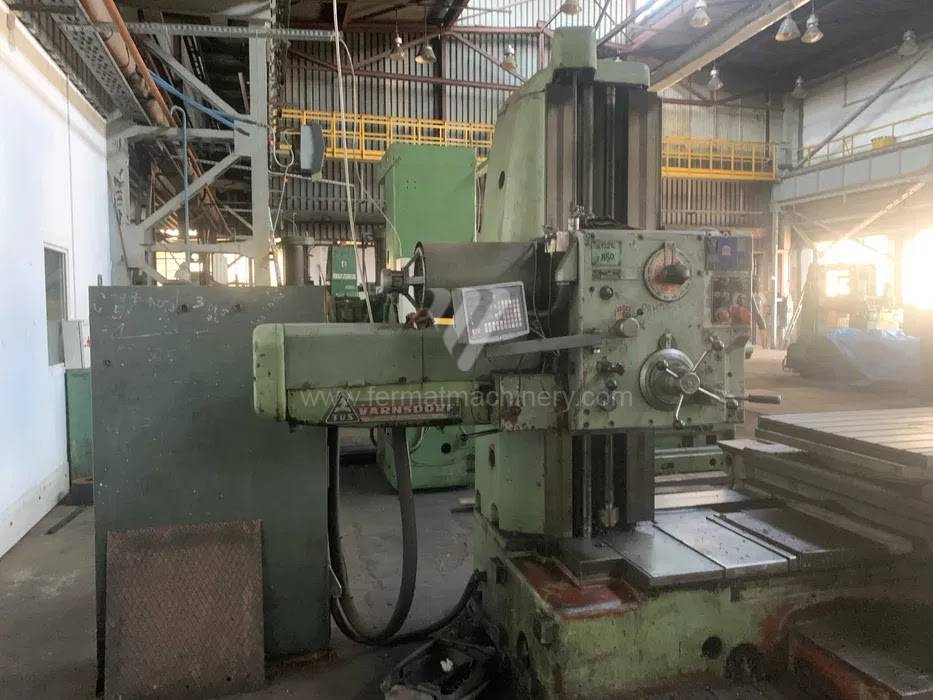




Année de production:1971
Diametre de travaille de broche: 80 mm
Course X: 1250 mm
Course Y: 900 mm
Vitesse de broche: 18 - 1800 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 710 mm
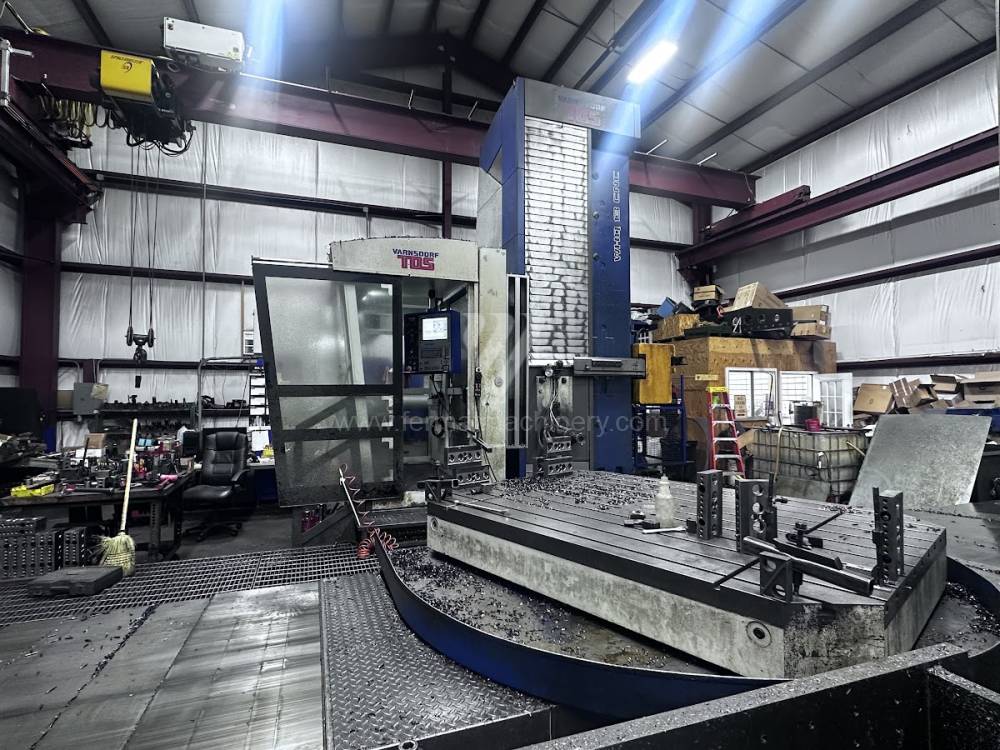
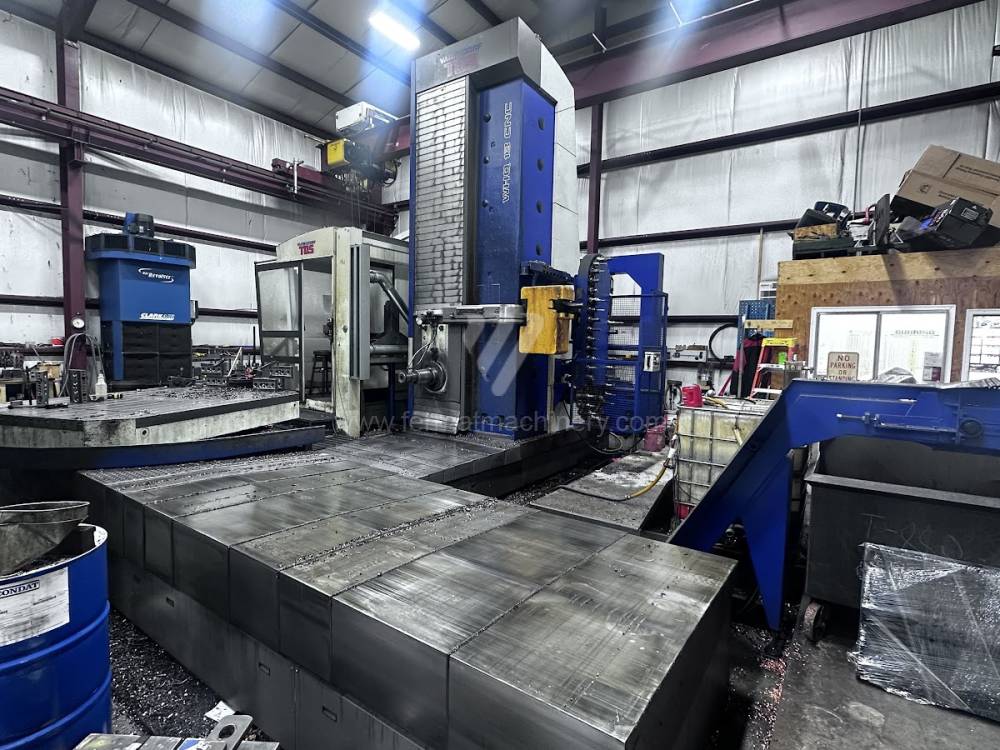
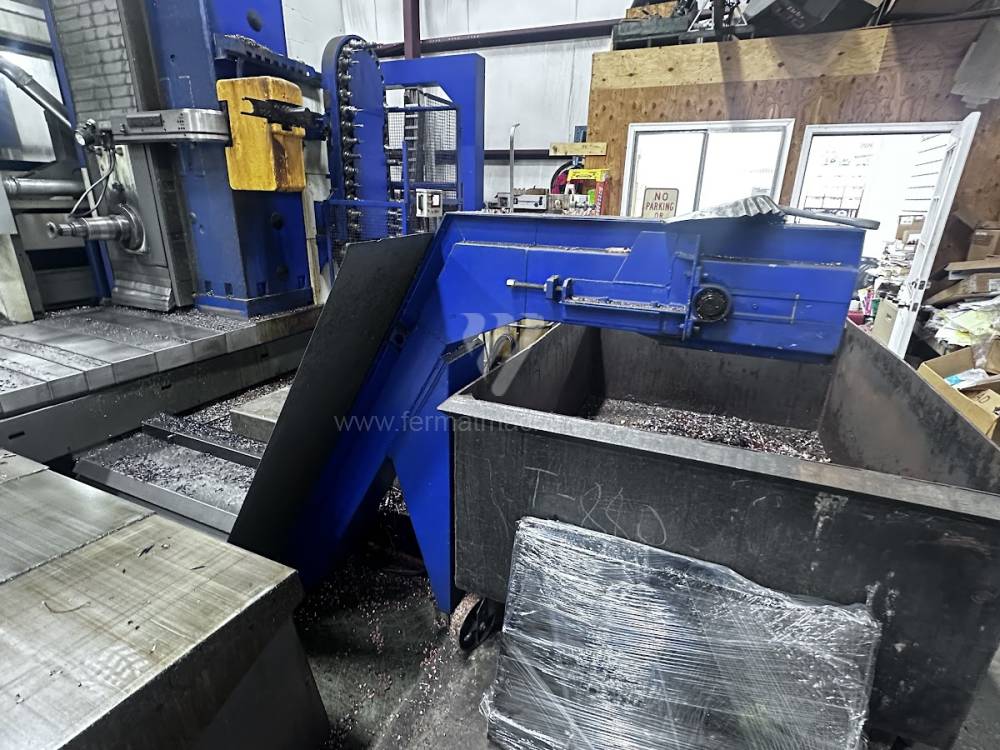
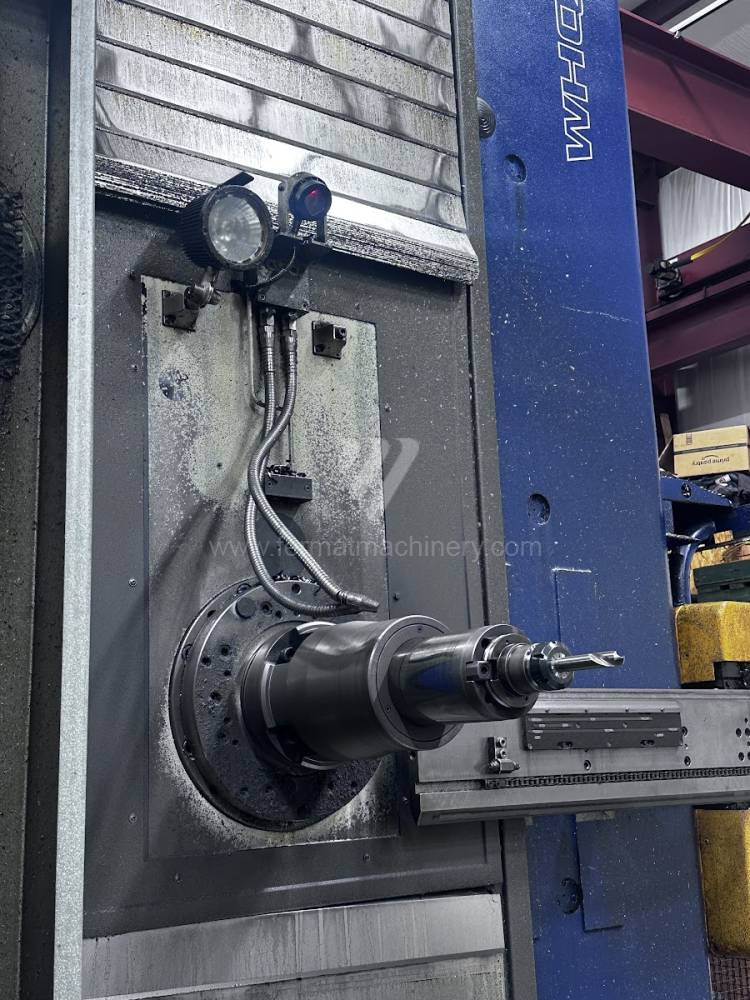
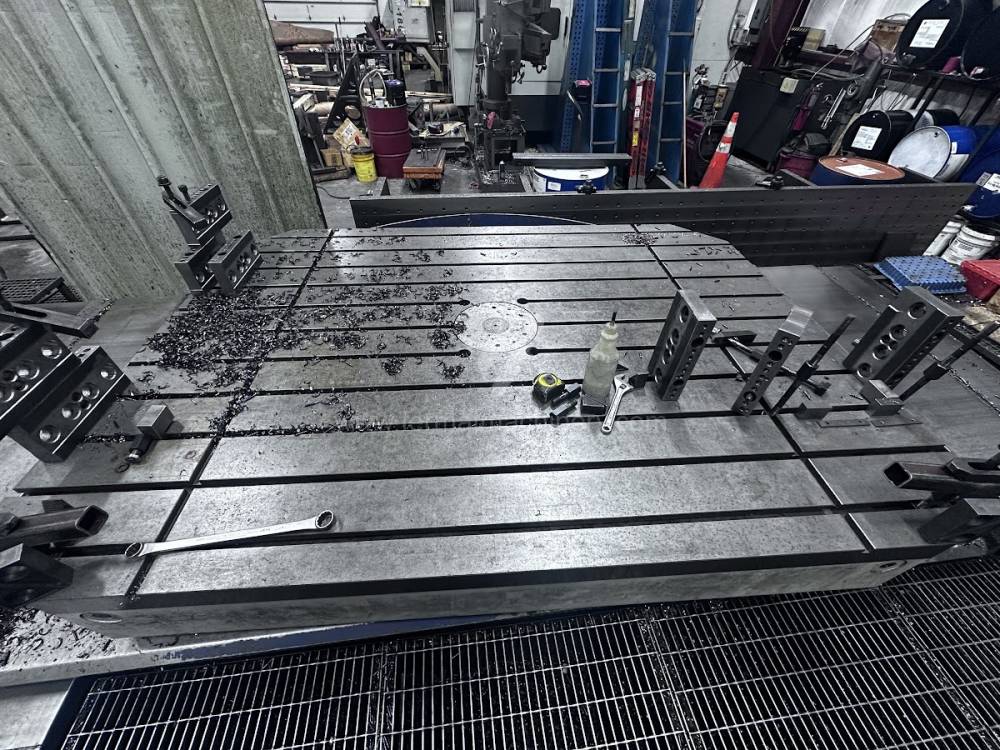
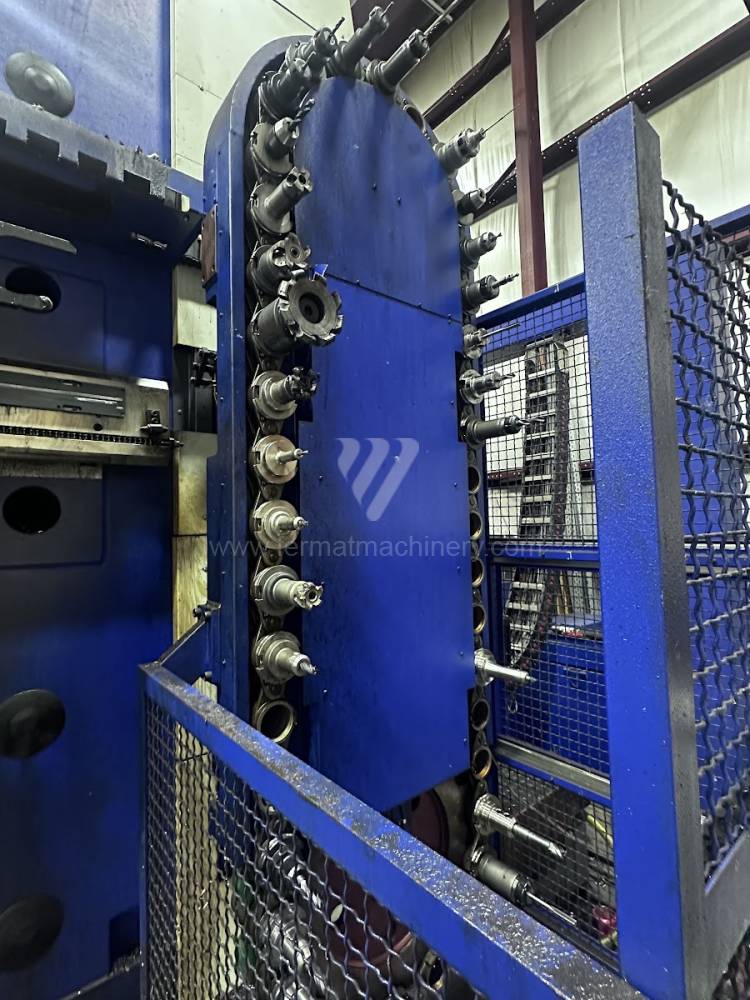








Année de production:2012
Système de contrôle Heidenhain: TNC 530
Diametre de travaille de broche: 130 mm
Course X: 5000 mm
Course Y: 3000 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 3000 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: OUI
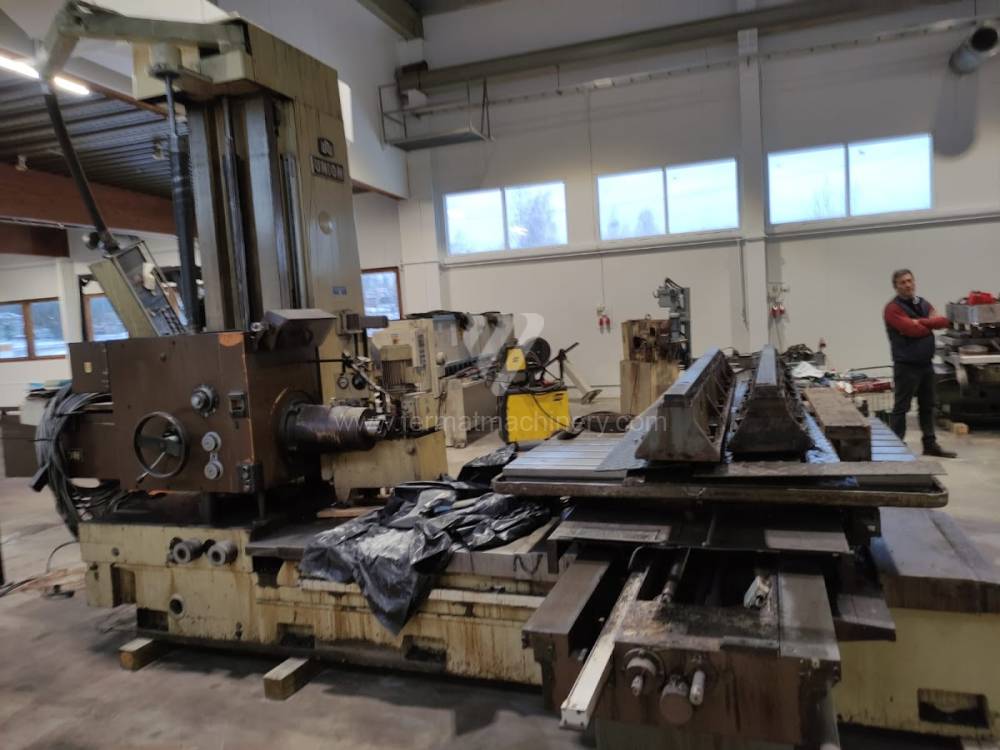
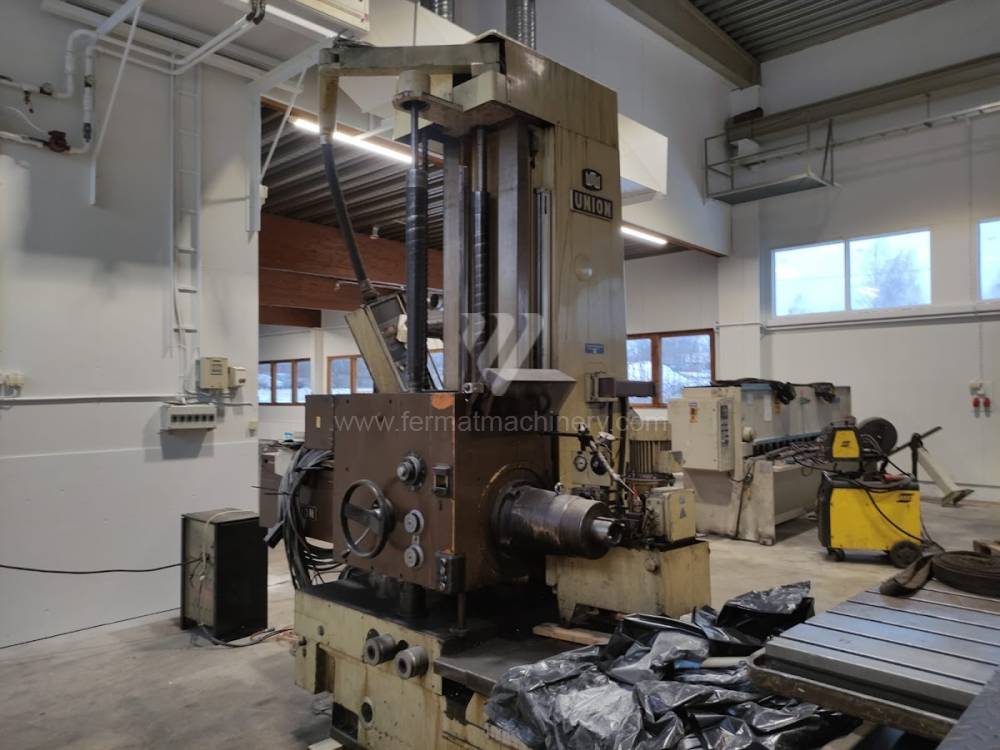
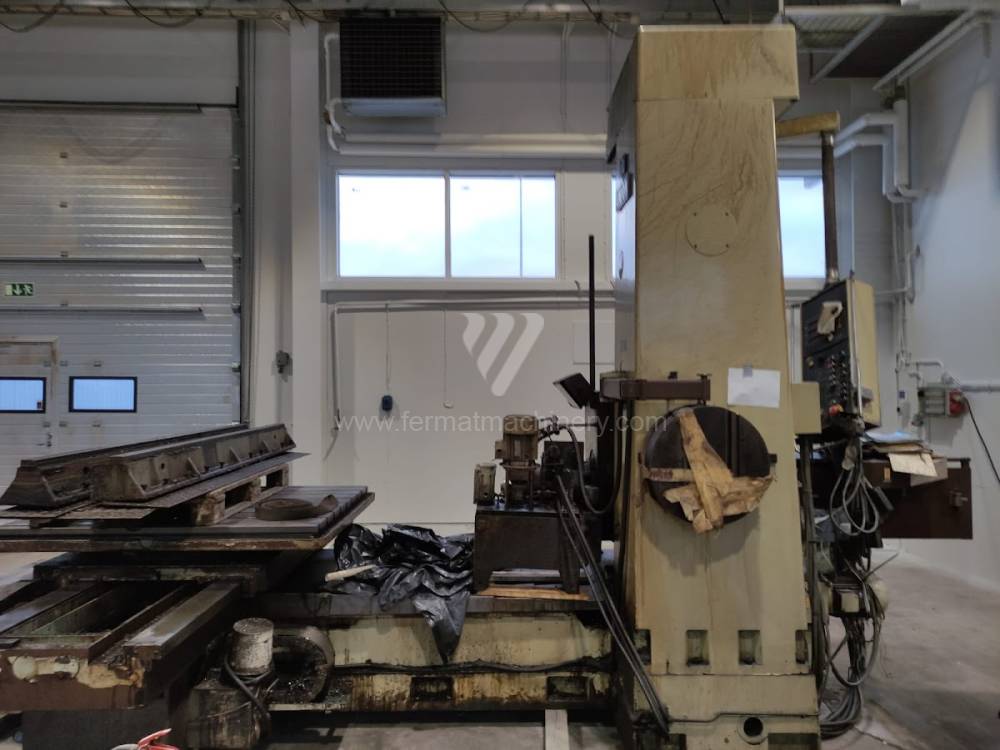




Année de production:1990
Diametre de travaille de broche: 102 mm
Course X: 1600 mm
Course Y: 1250 mm
Vitesse de broche: 8 - 1600 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 710 mm
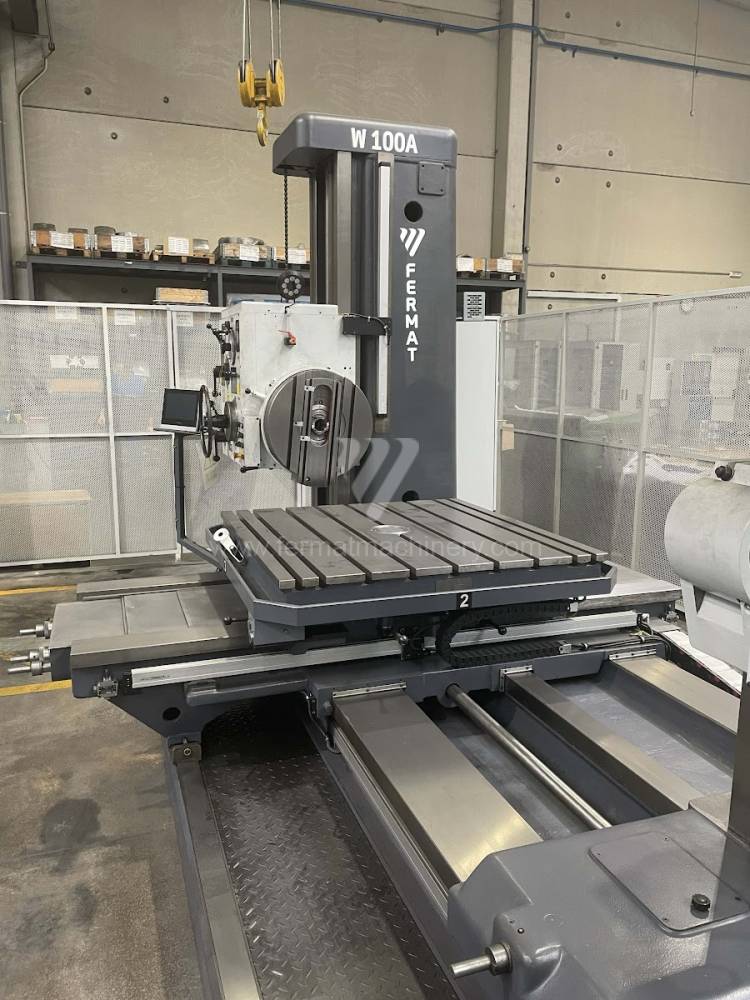
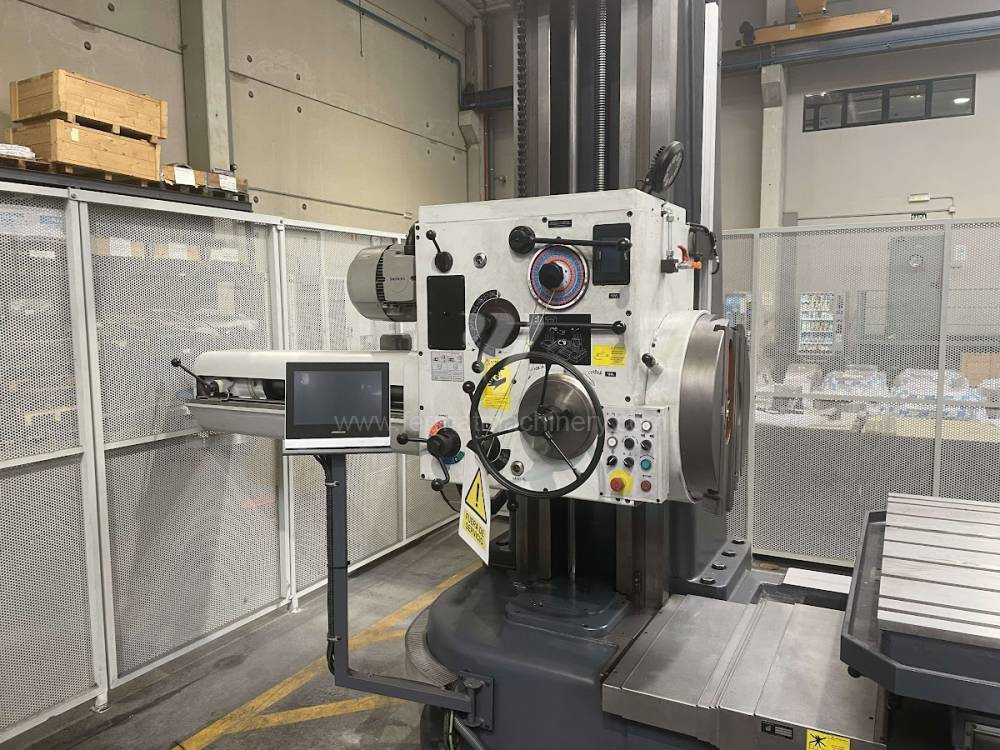
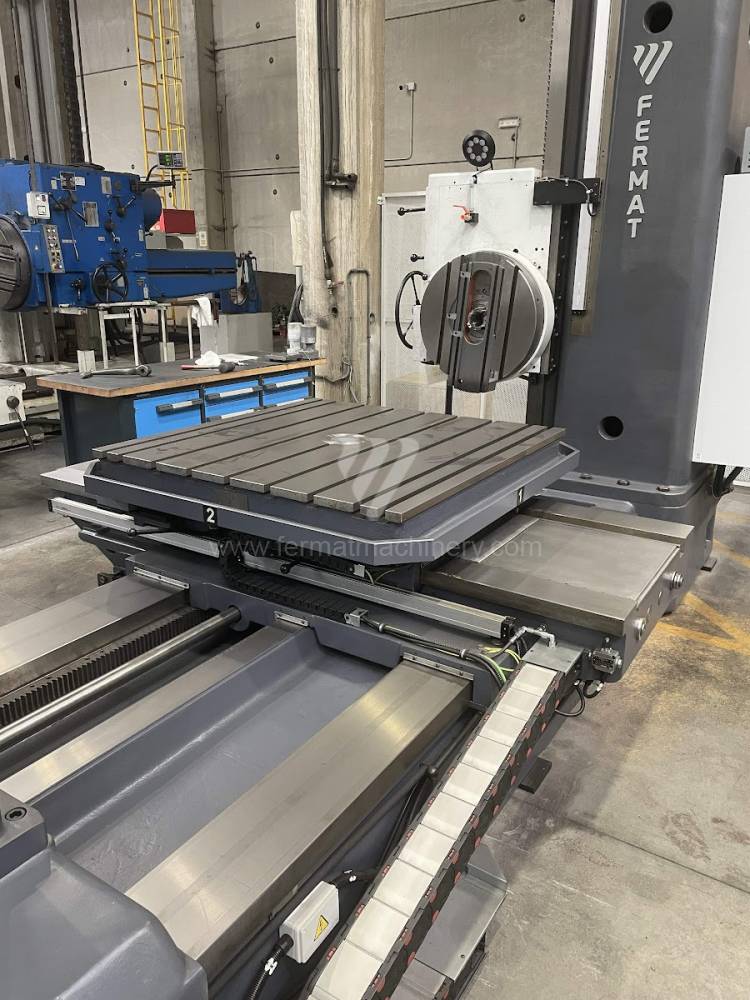



Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1600 mm
Course Y: 1120 mm
Vitesse de broche: 7 - 1120 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 900 mm

Année de production:1967
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1500 mm
Course Y: 1200 mm
Vitesse de broche: 15 - 1550 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 600 mm
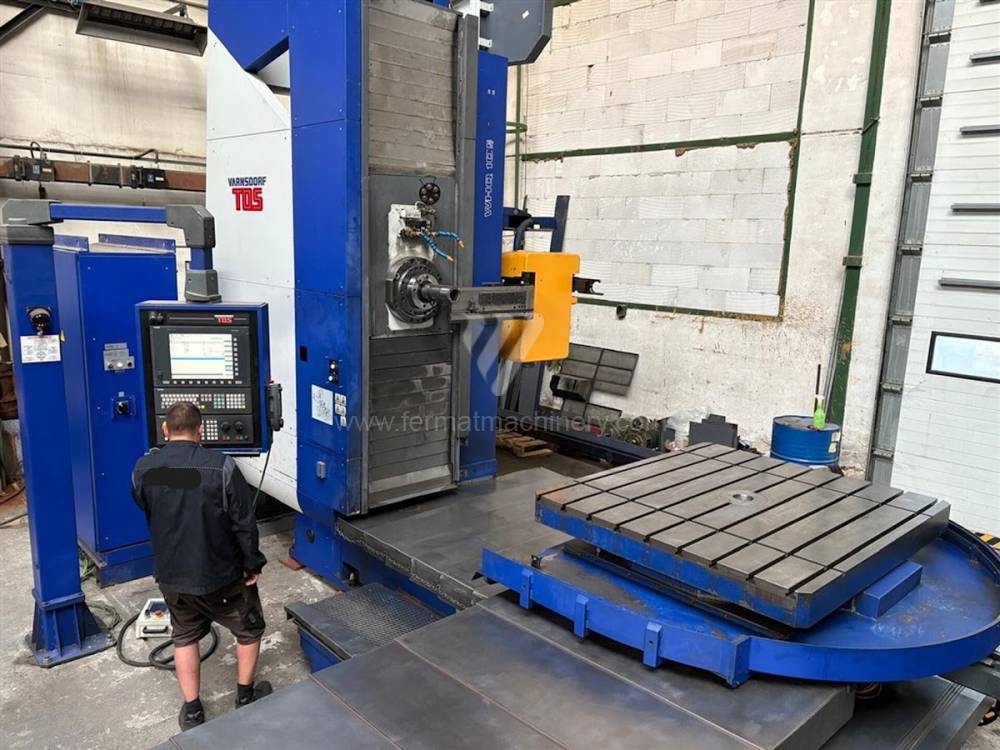
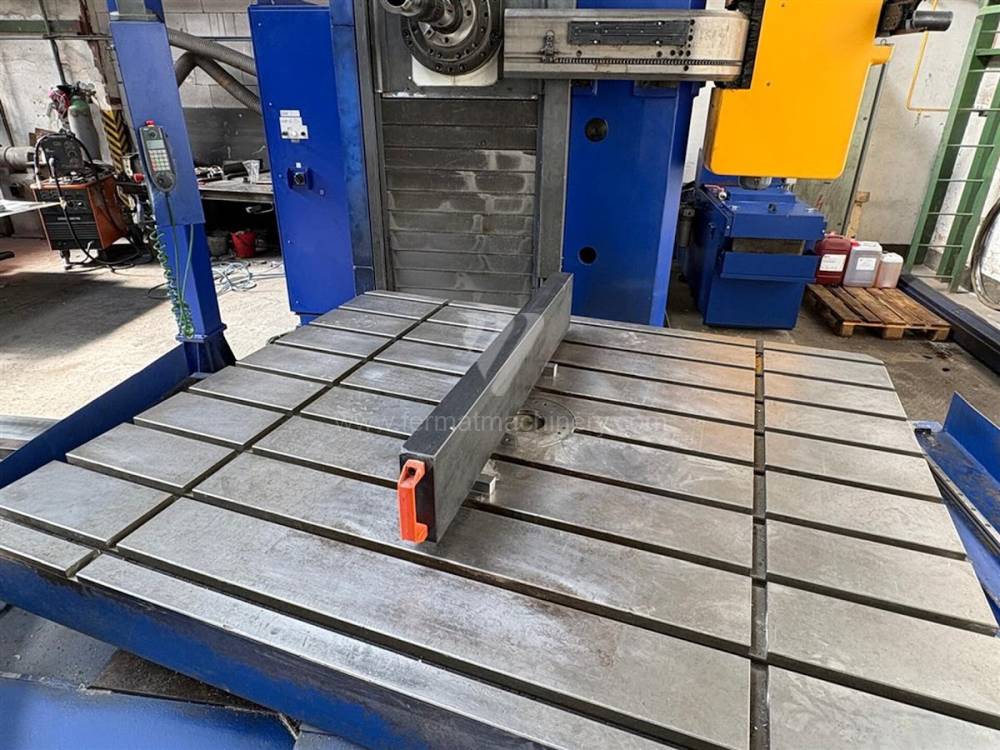
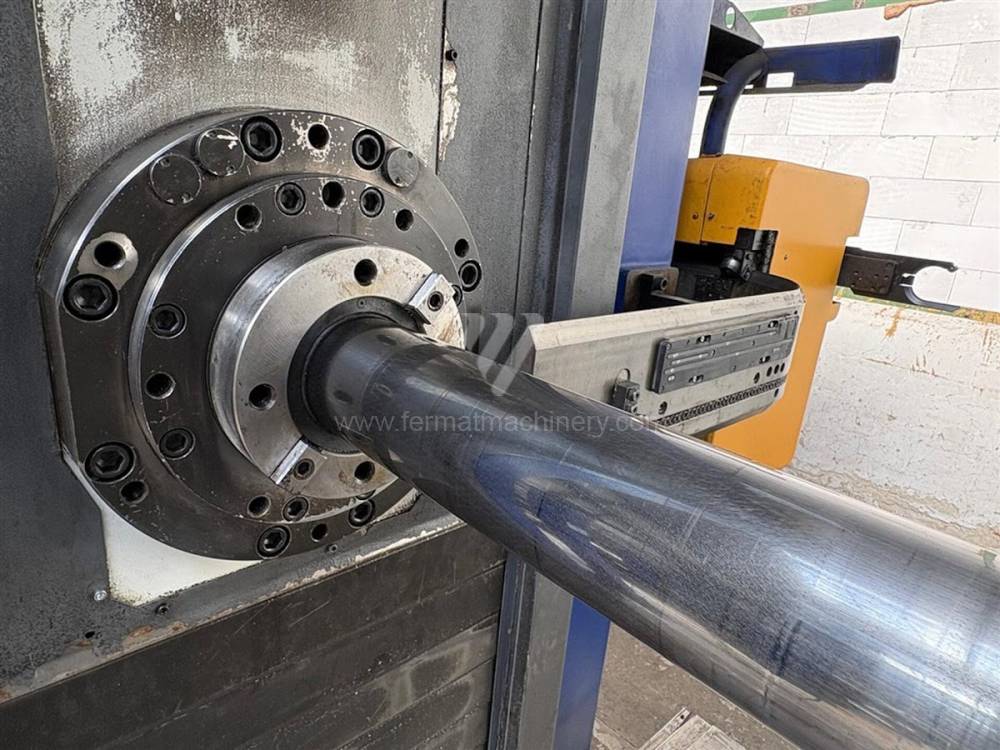
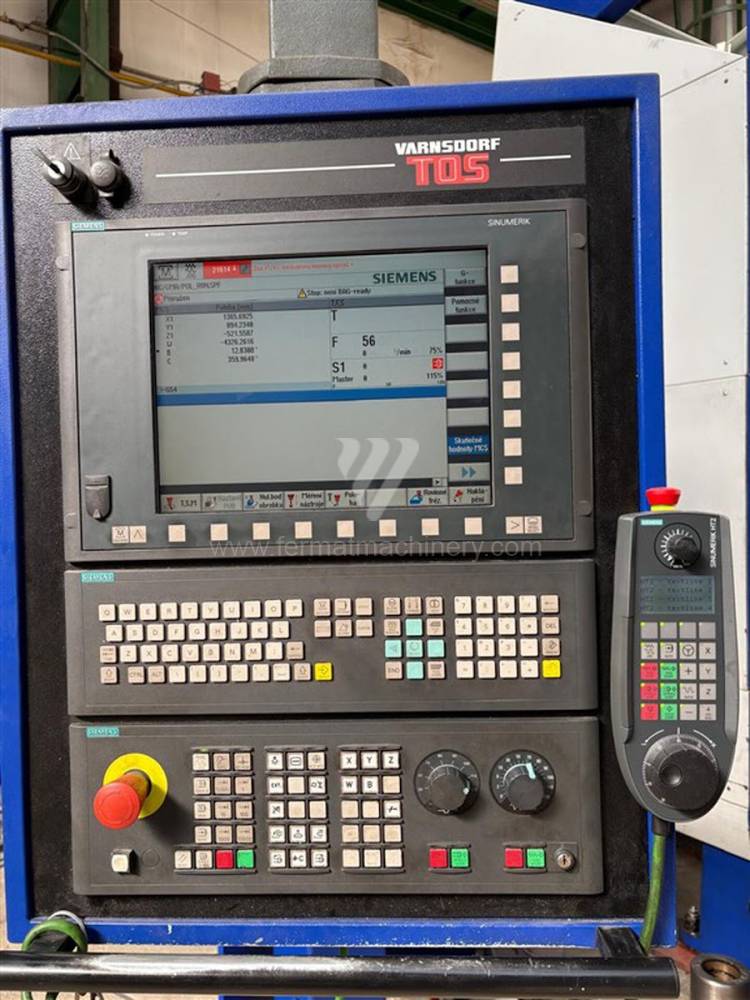
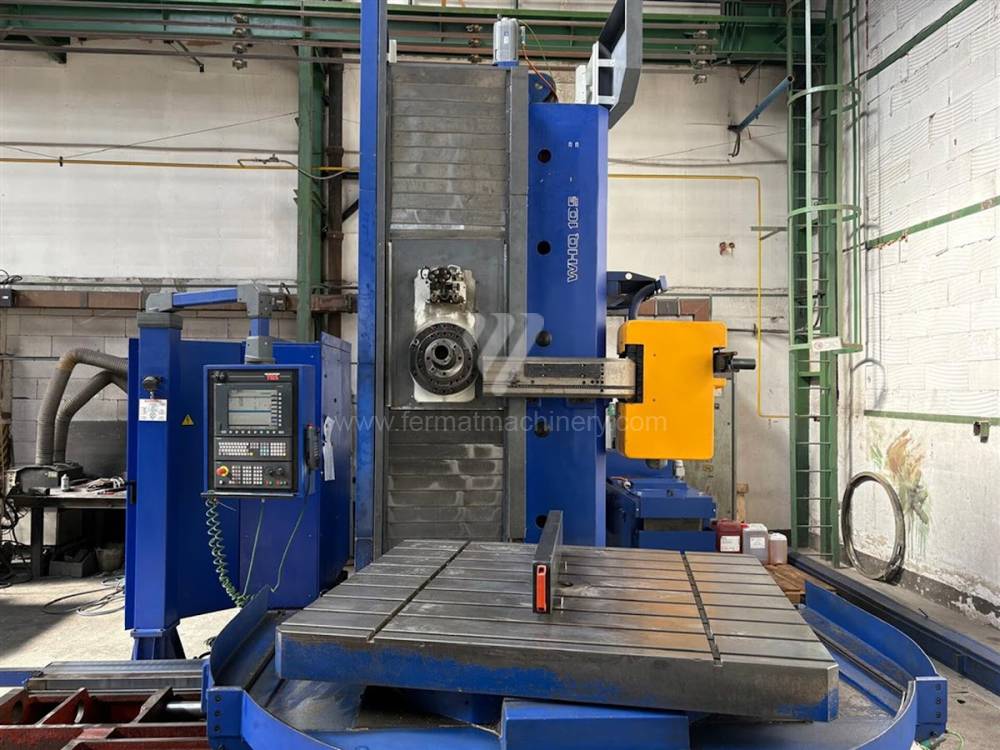
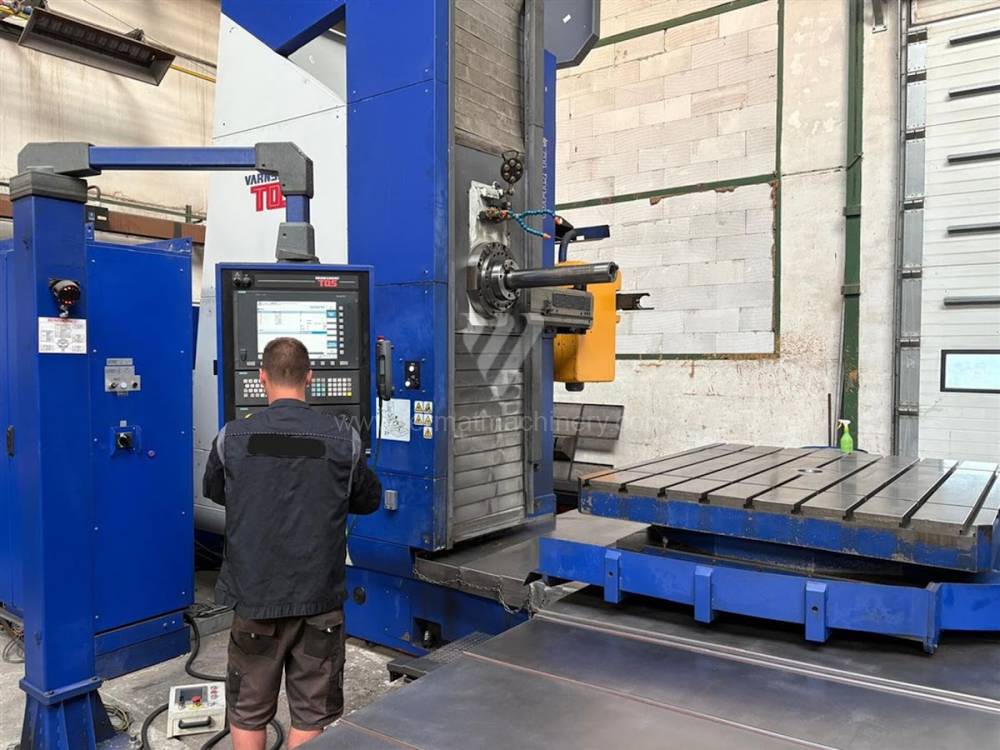



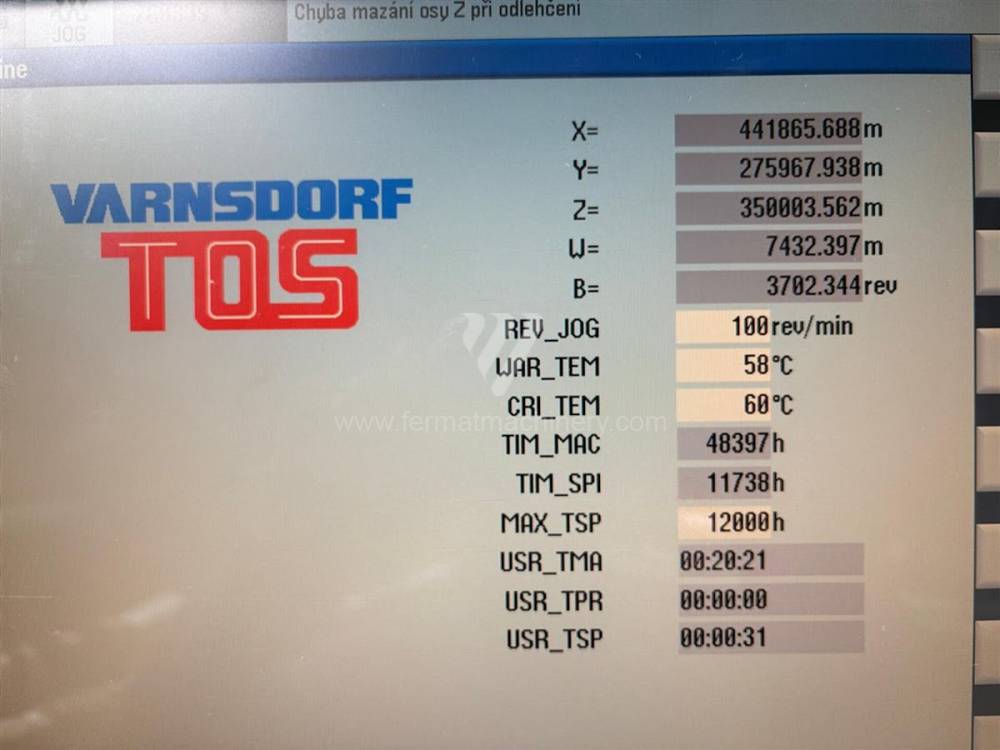



Année de production:2015
Système de contrôle Siemens: Sinumerik 840 D
Diametre de travaille de broche: 105 mm
Course X: 1800 mm
Course Y: 1600 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 3300 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: OUI
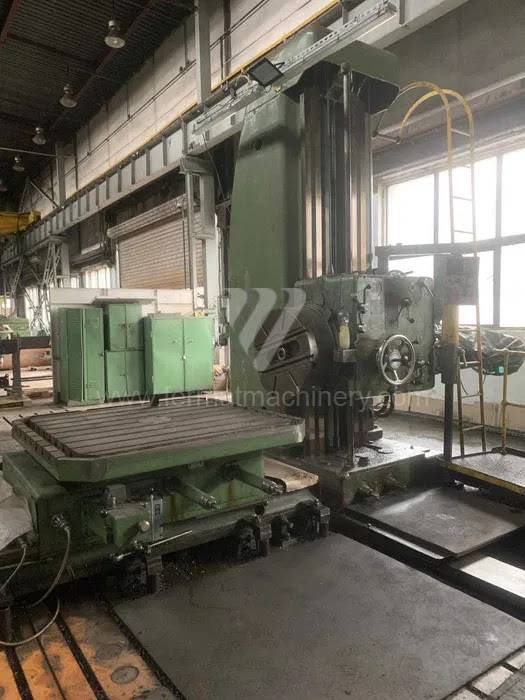
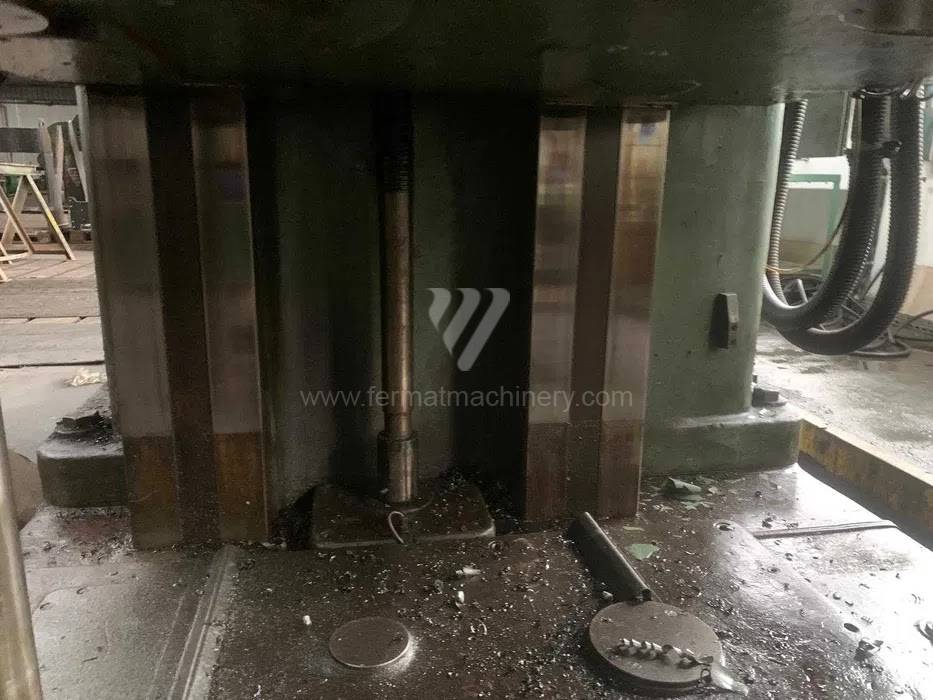
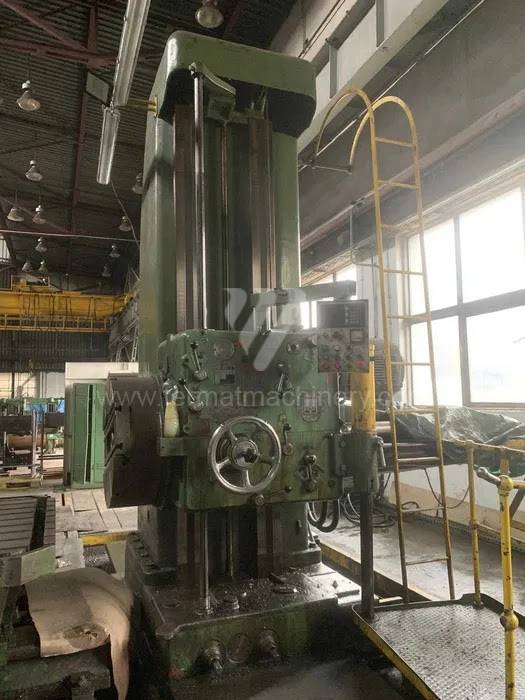







Année de production:1967
Diametre de travaille de broche: 110 mm
Course X: 2400 mm
Course Y: 1750 mm
Vitesse de broche: 10 - 300 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 800 mm
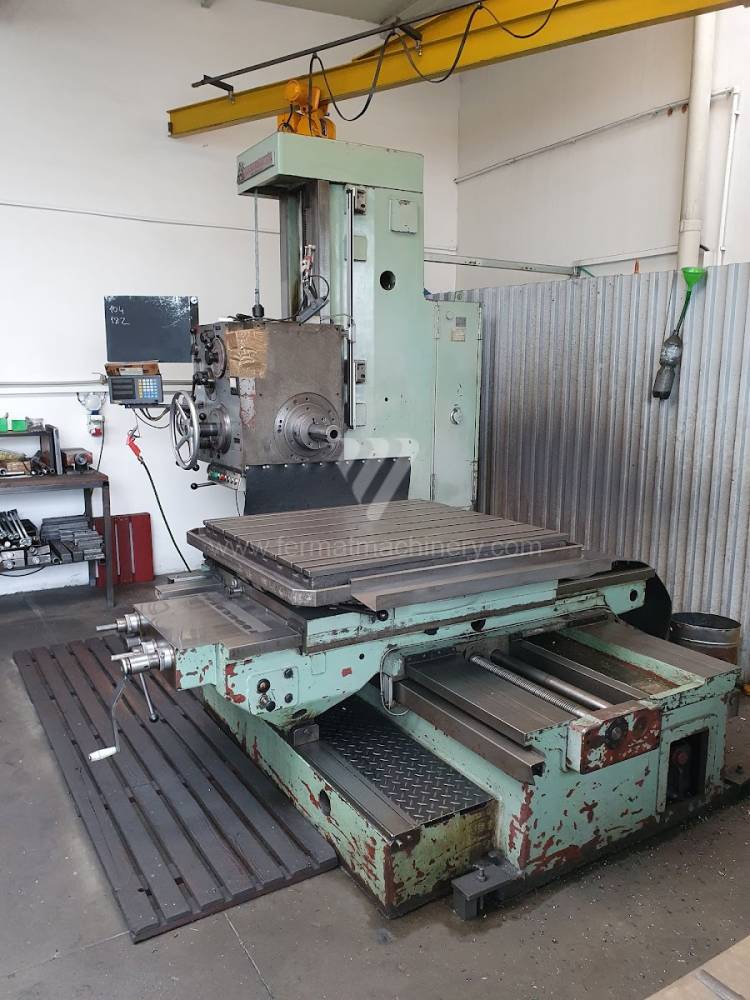
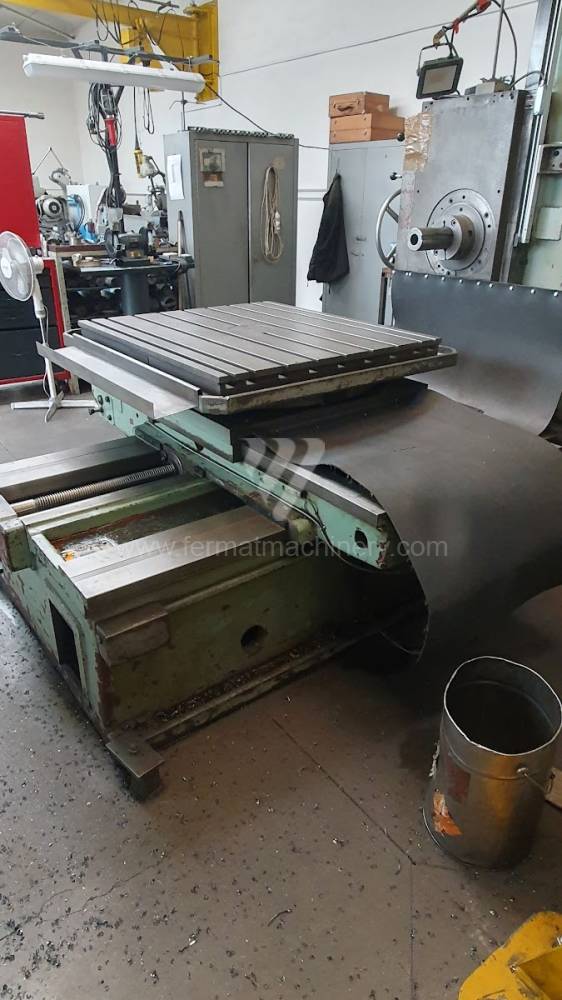
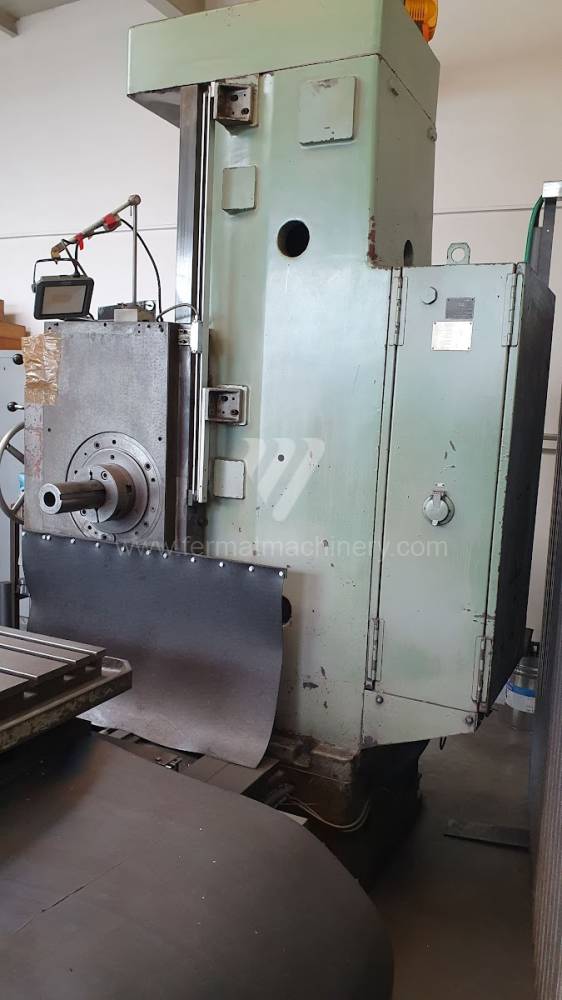
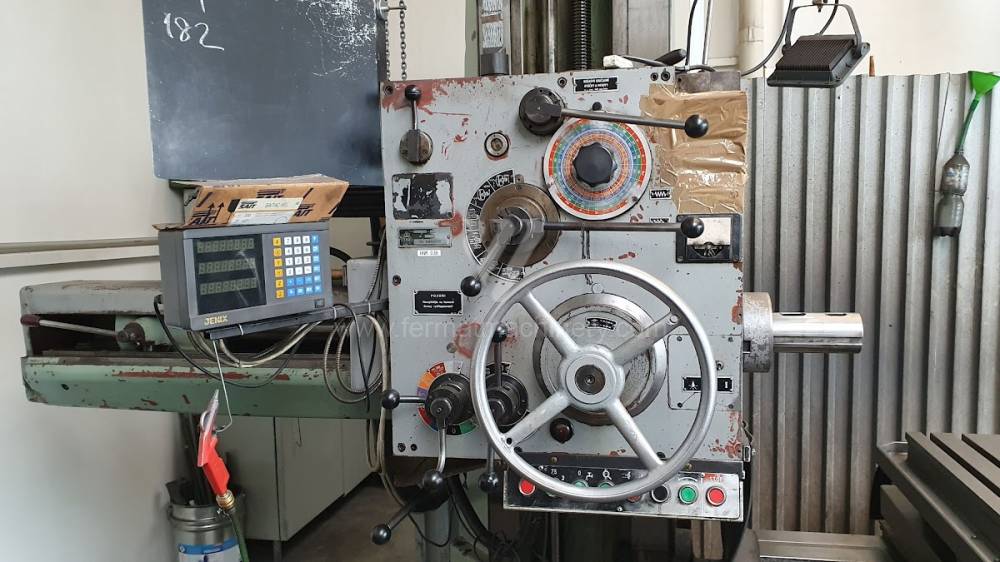
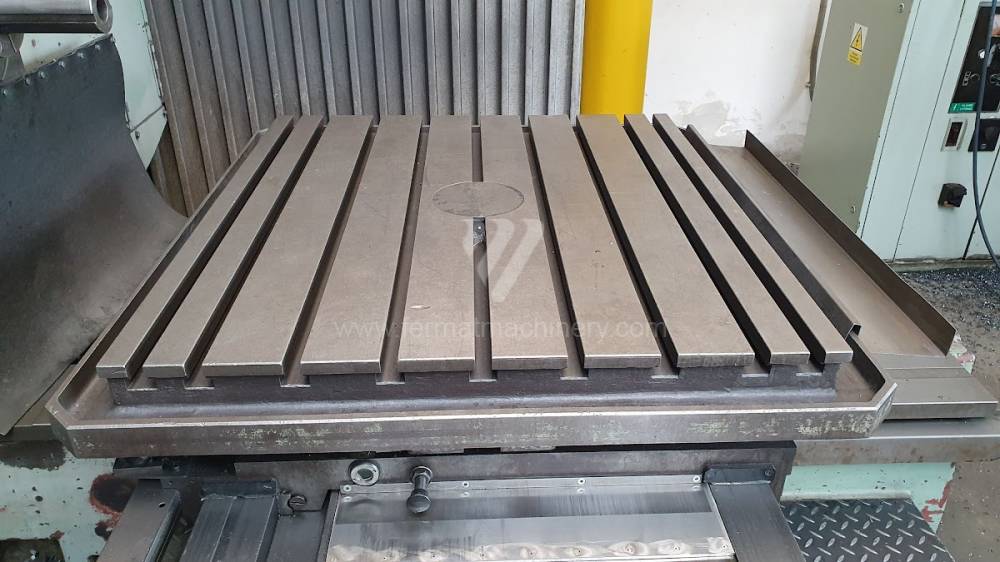
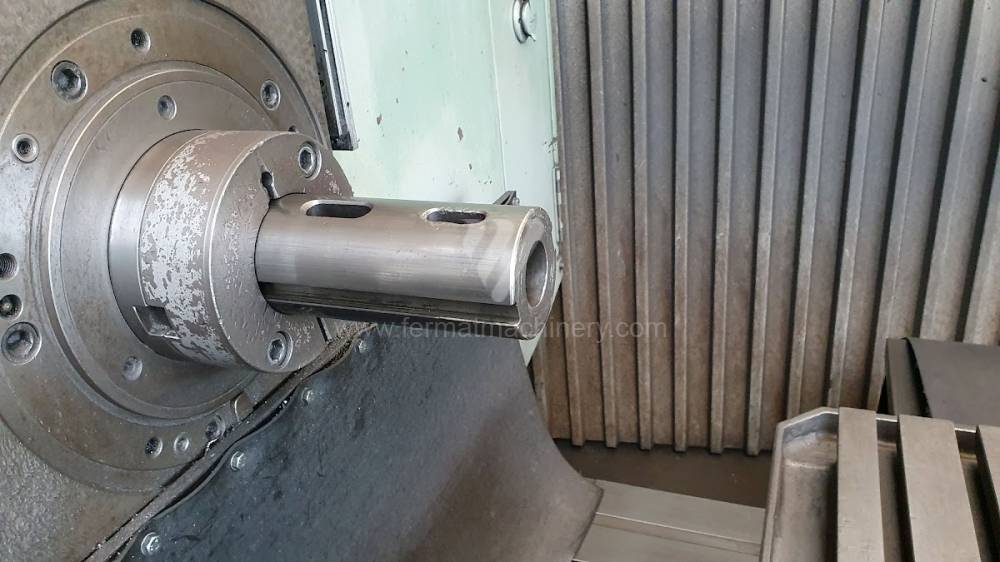









Année de production:1975
Diametre de travaille de broche: 90 mm
Course X: 1000 mm
Course Y: 900 mm
Vitesse de broche: 0 - 1400 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 710 mm
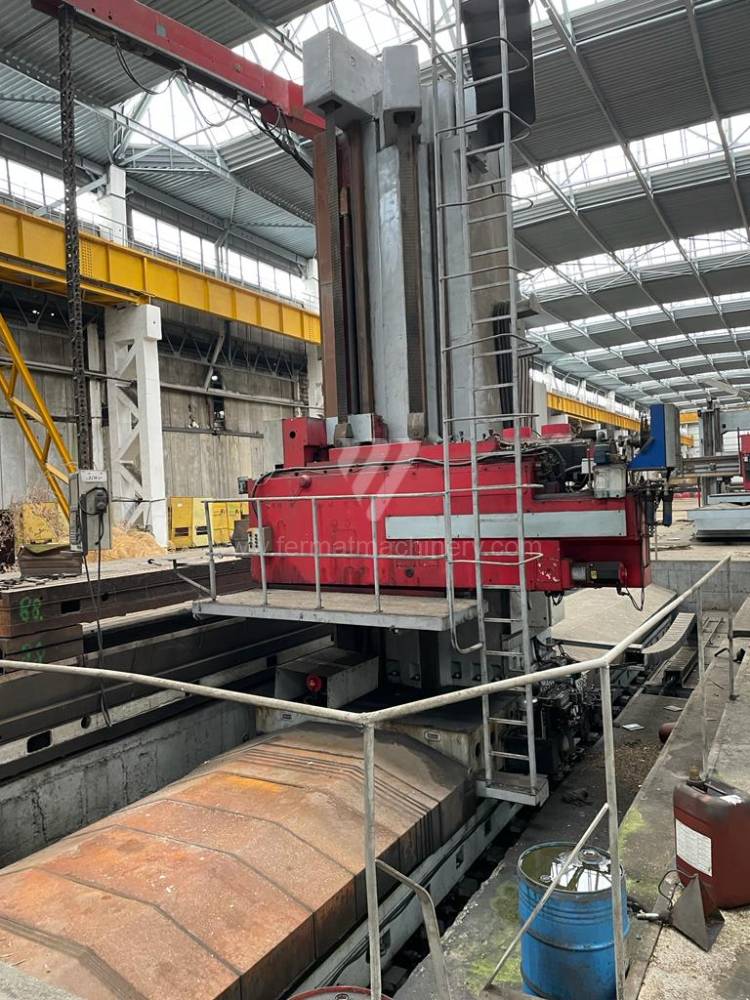
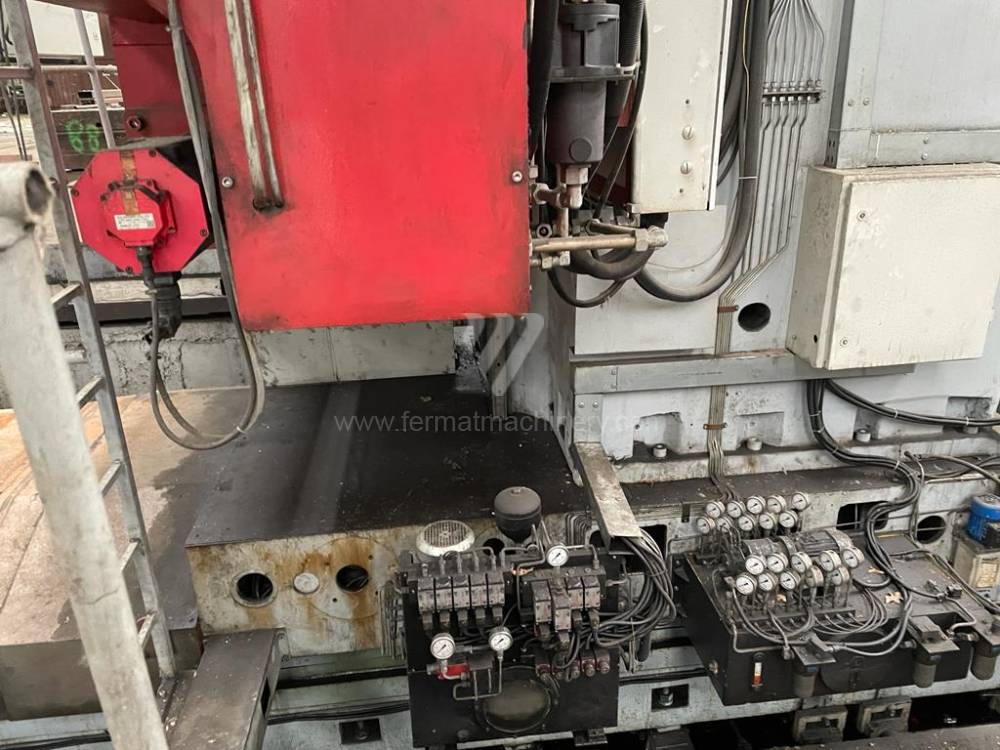
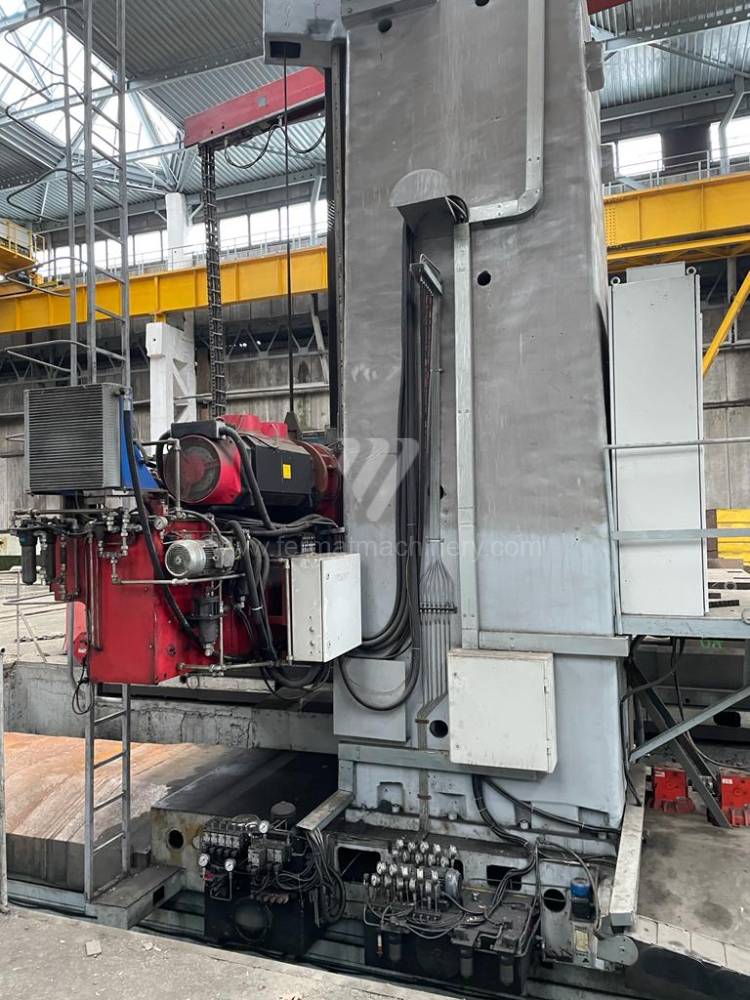
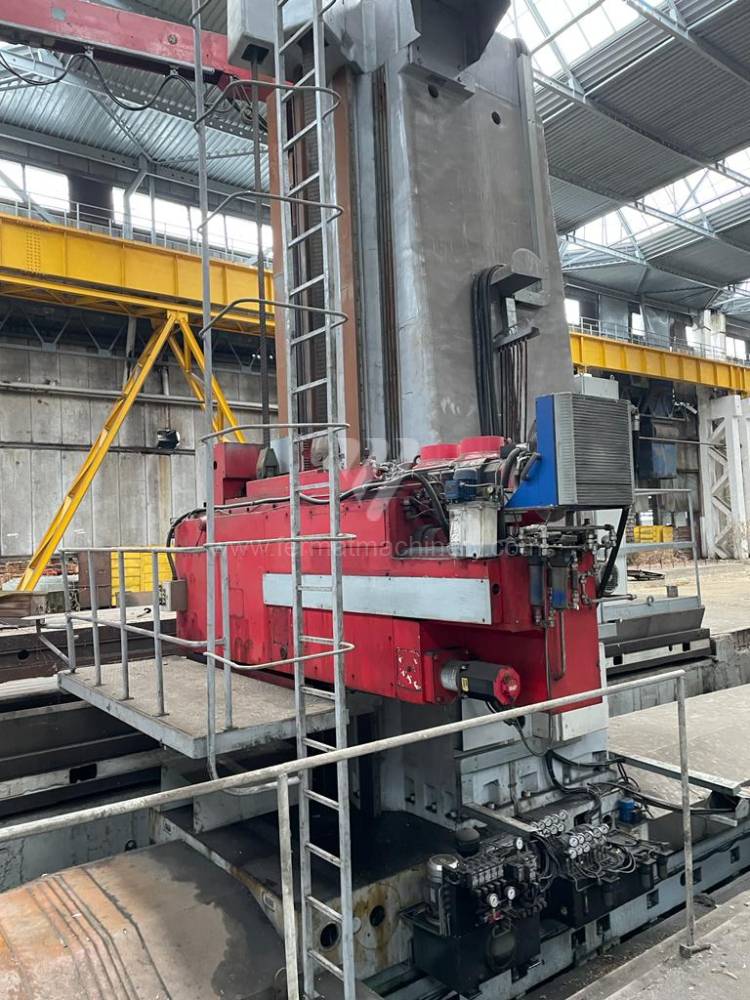
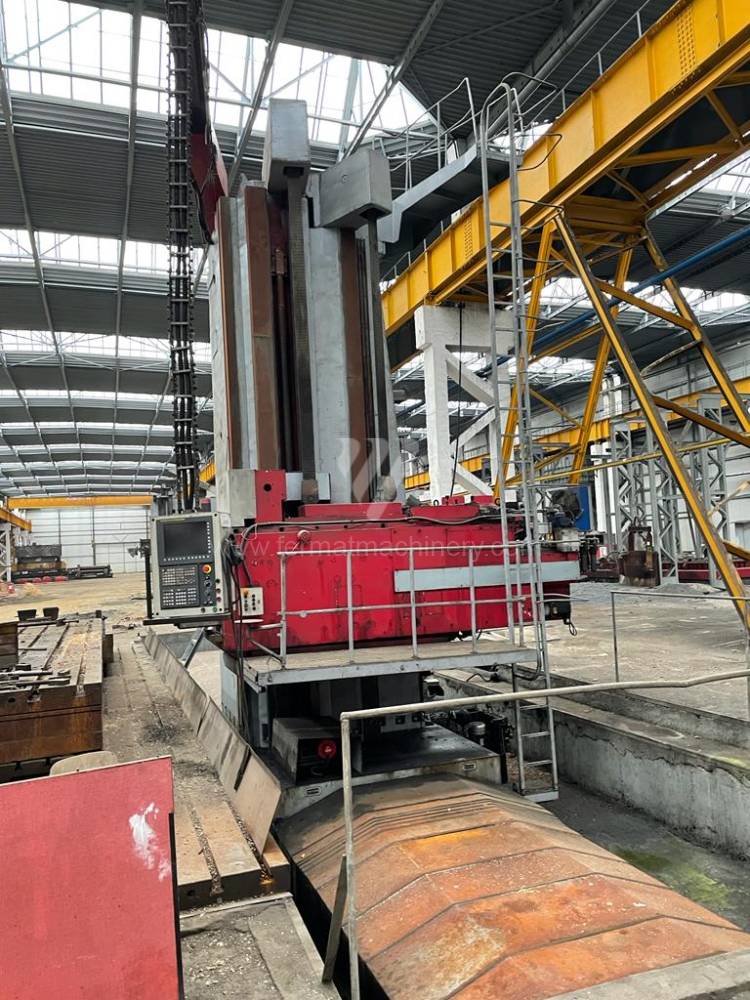
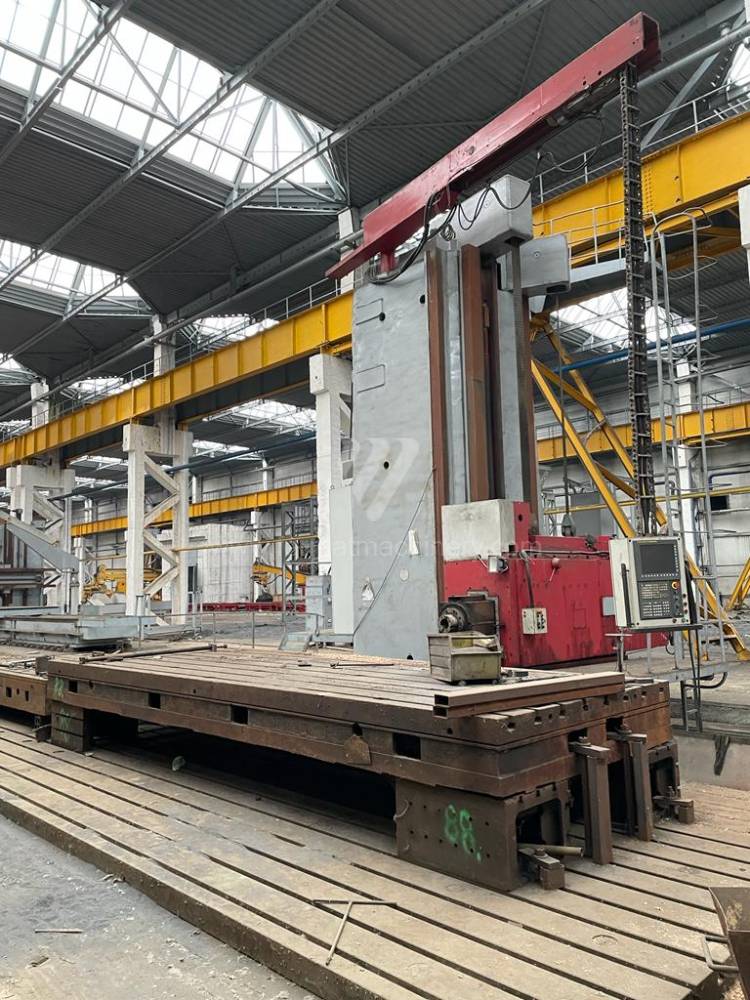






Année de production:2009
Système de contrôle Fanuc: Fanuc 32i
Diametre de travaille de broche: 180 mm
Course X: 9130 mm
Course Y: 3980 mm
Déplacement de travaille Z: 1900 mm/min
Axe W: 1200 mm
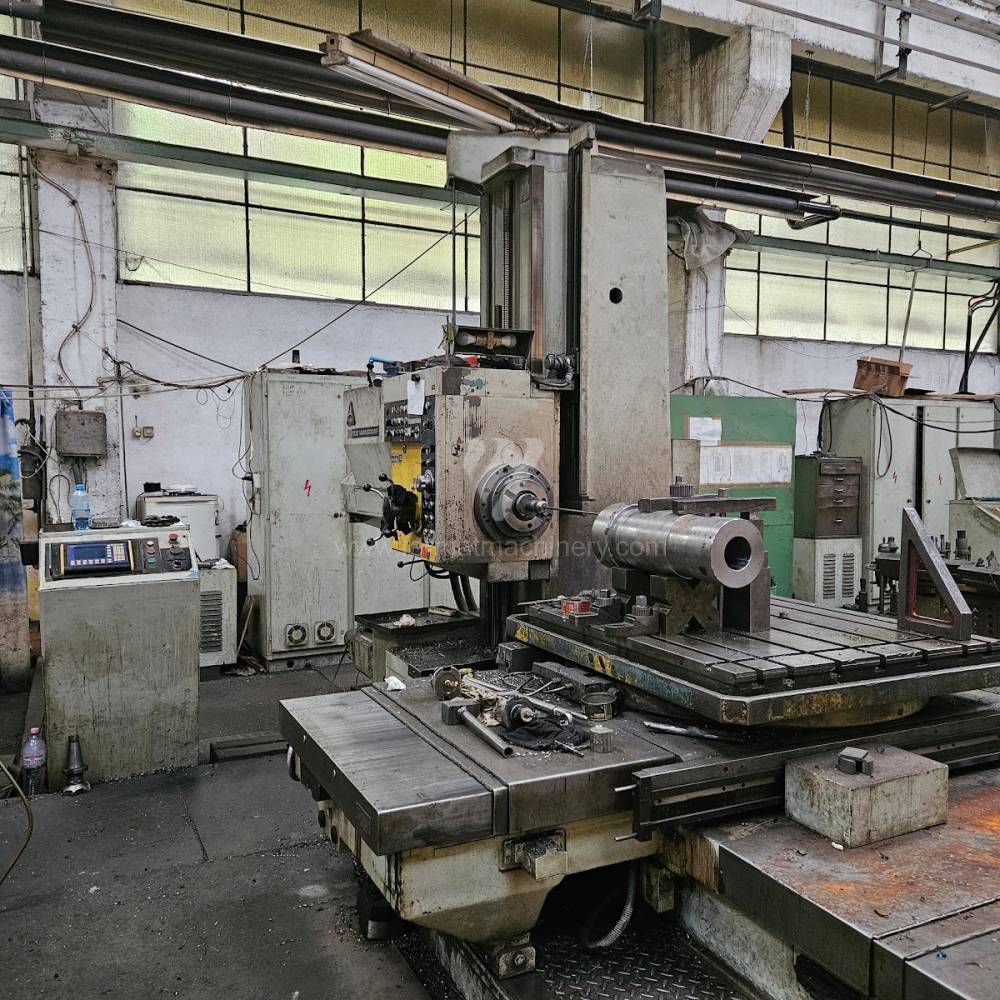
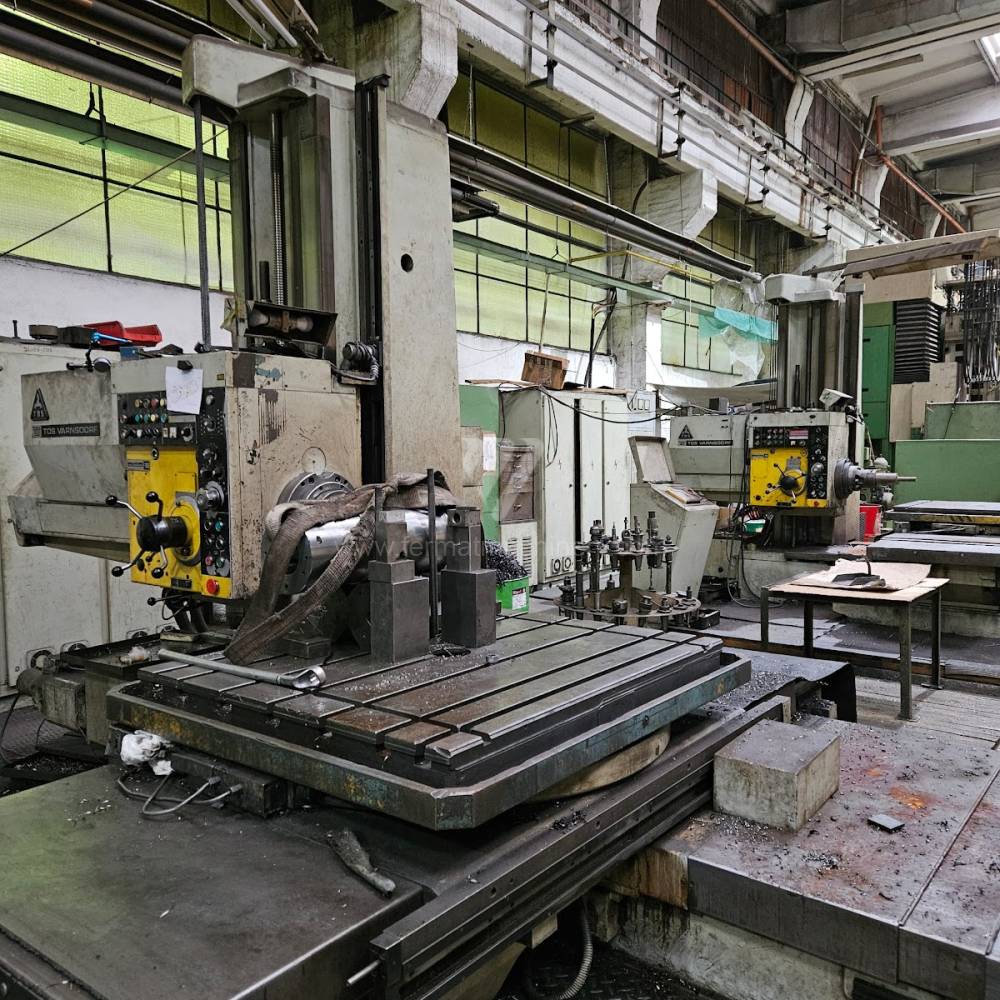




Année de production:1987
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1130 mm
Course Y: 1250 mm
Vitesse de broche: 16 - 1500 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Extension du curseur (W): 650 mm
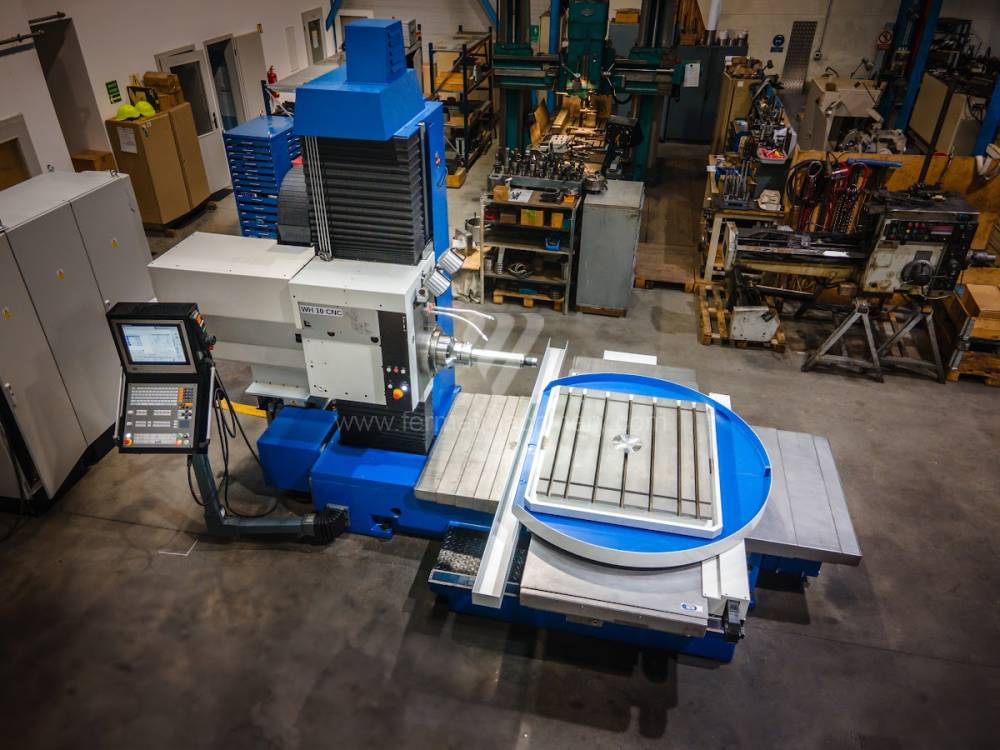
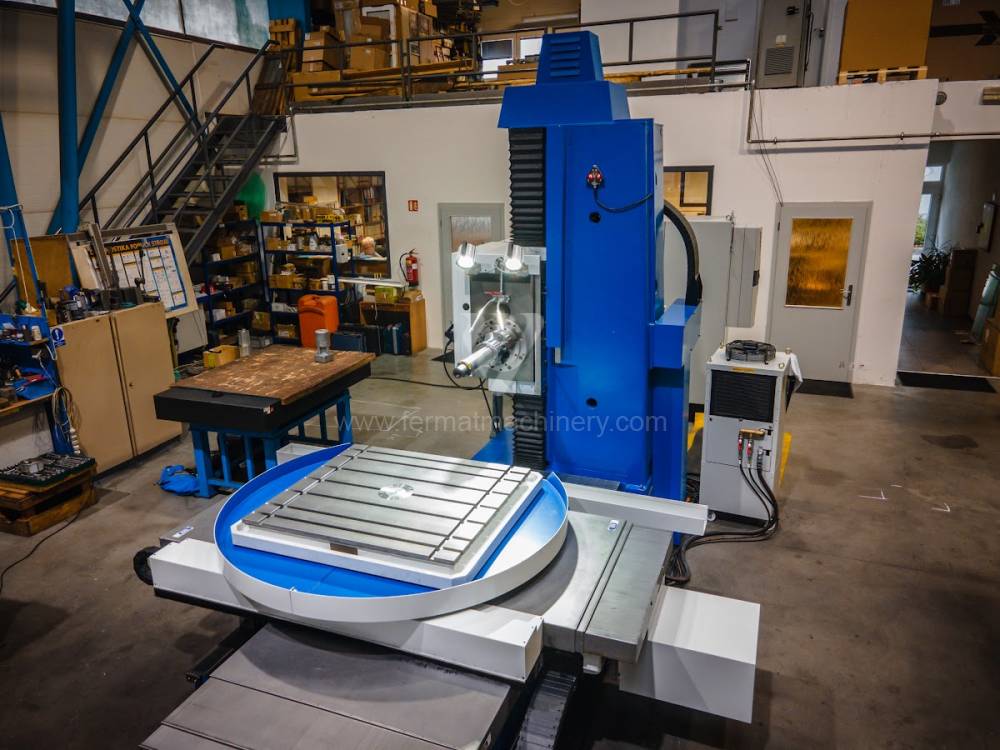
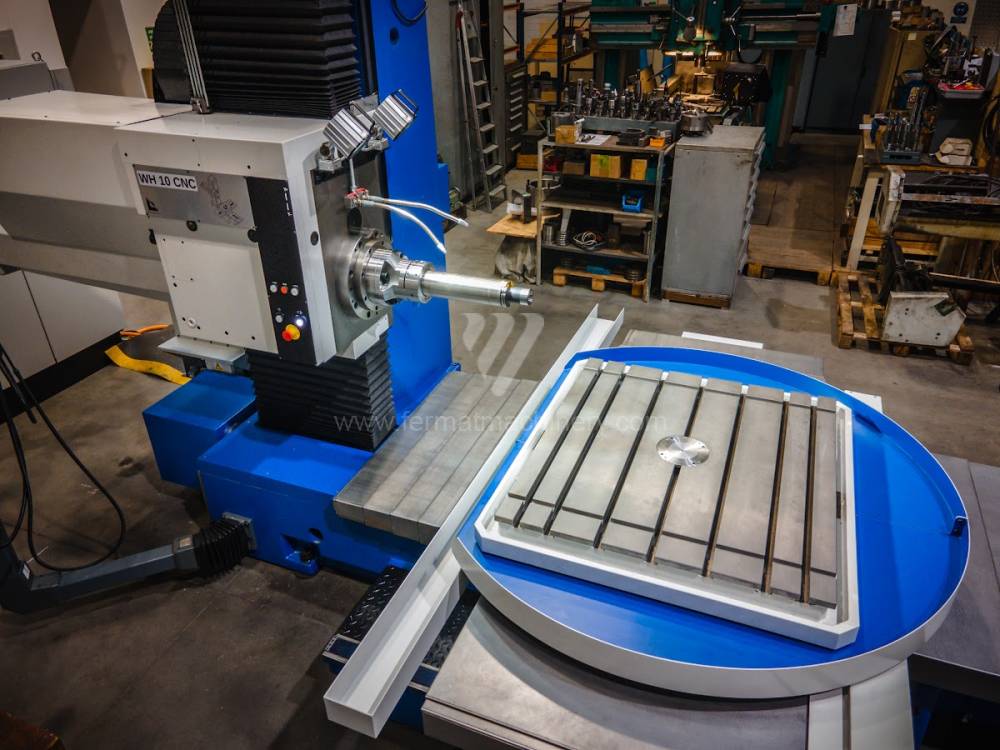
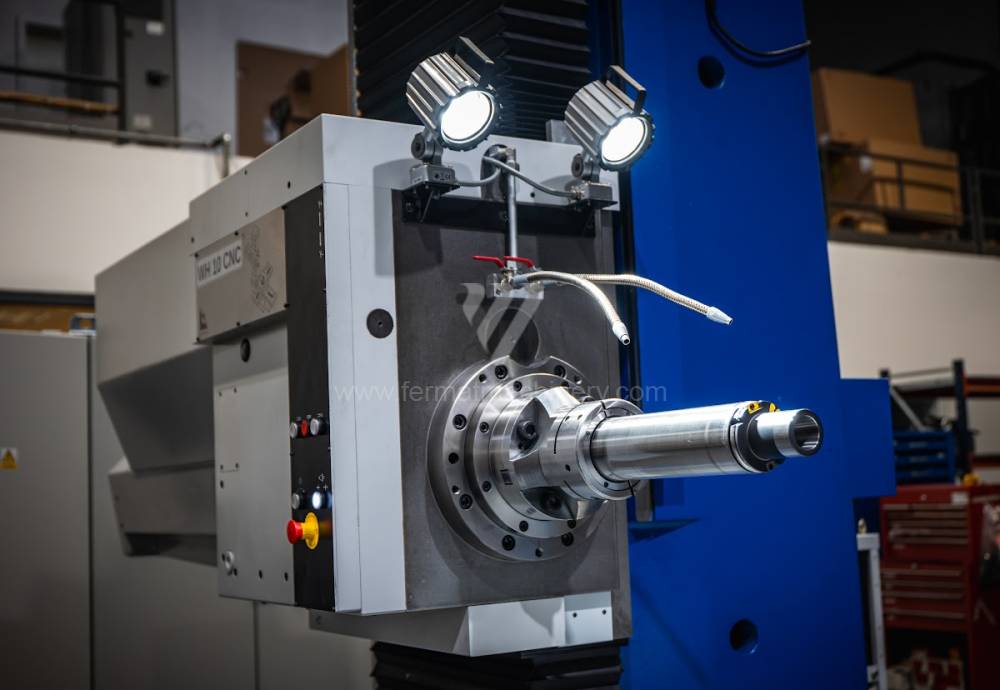
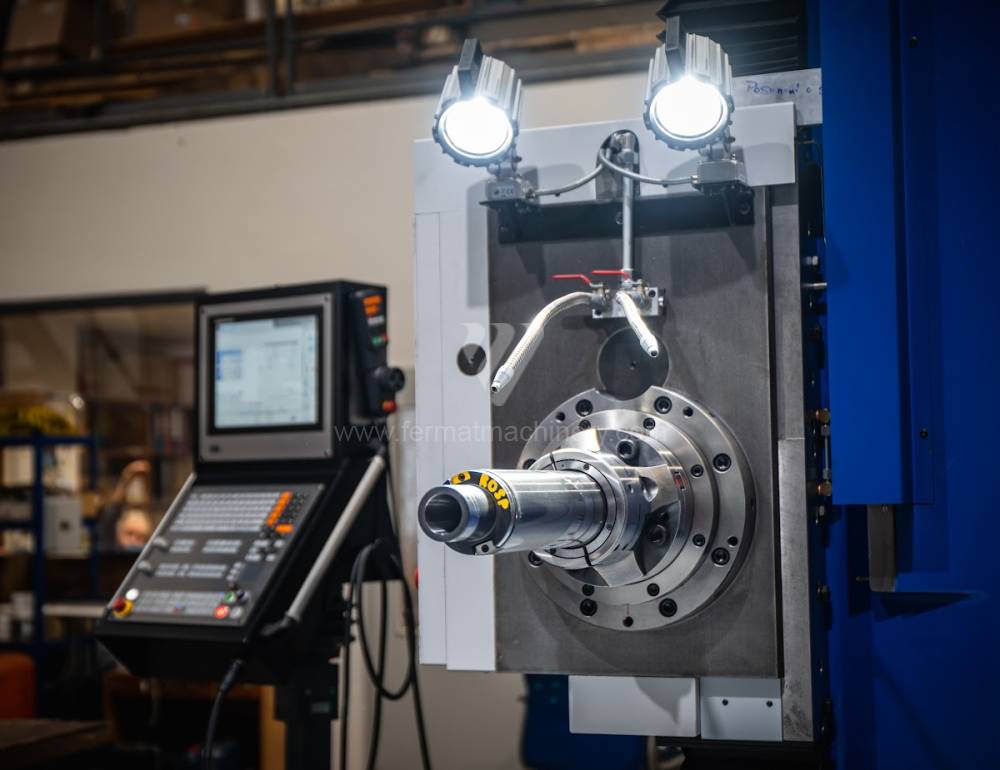
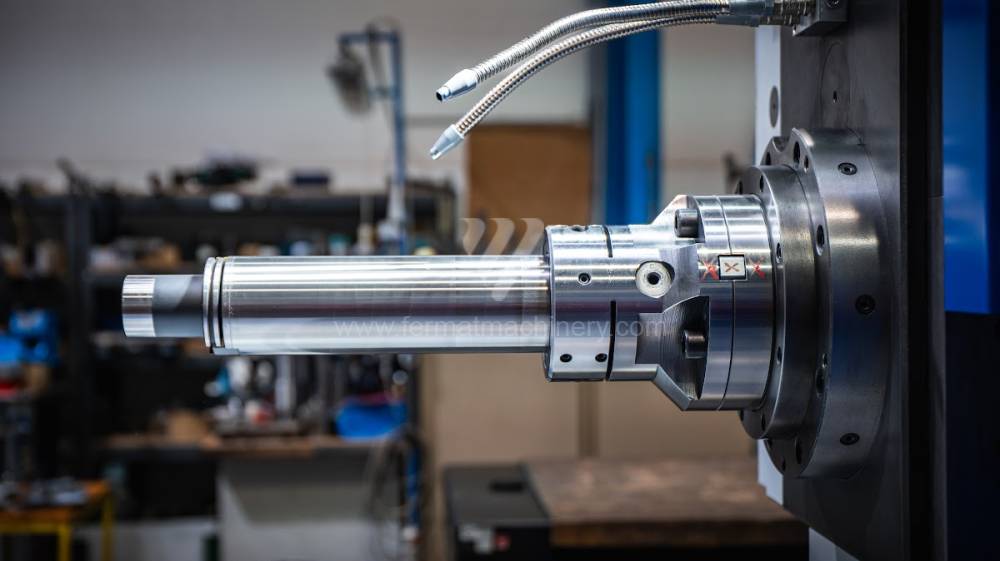
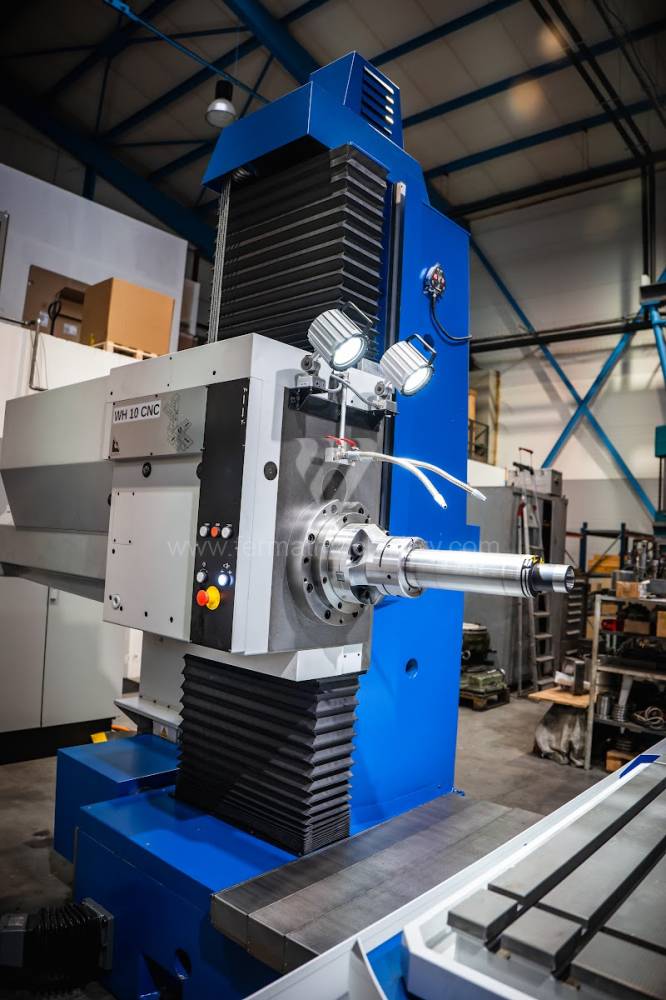
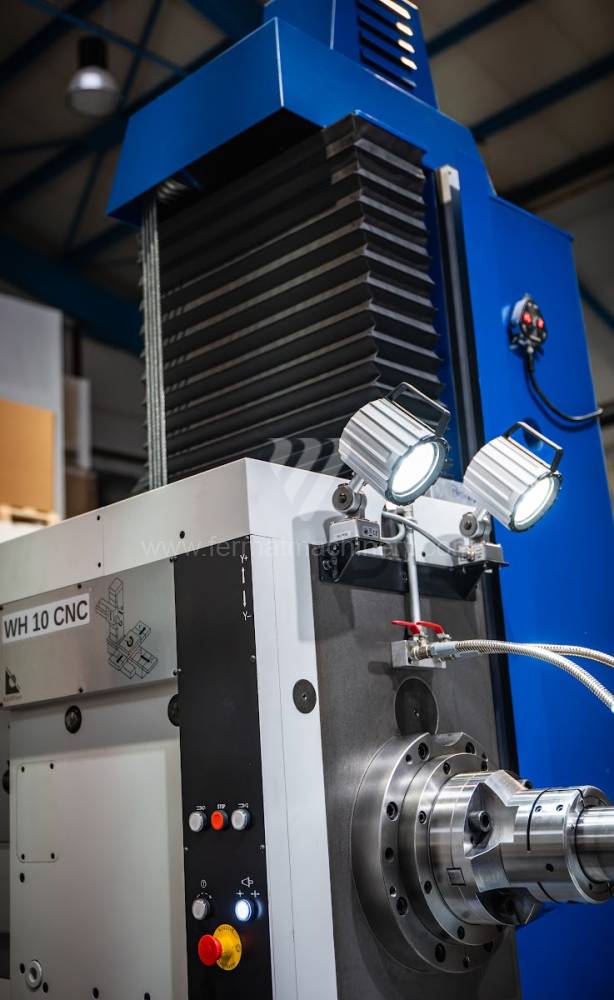
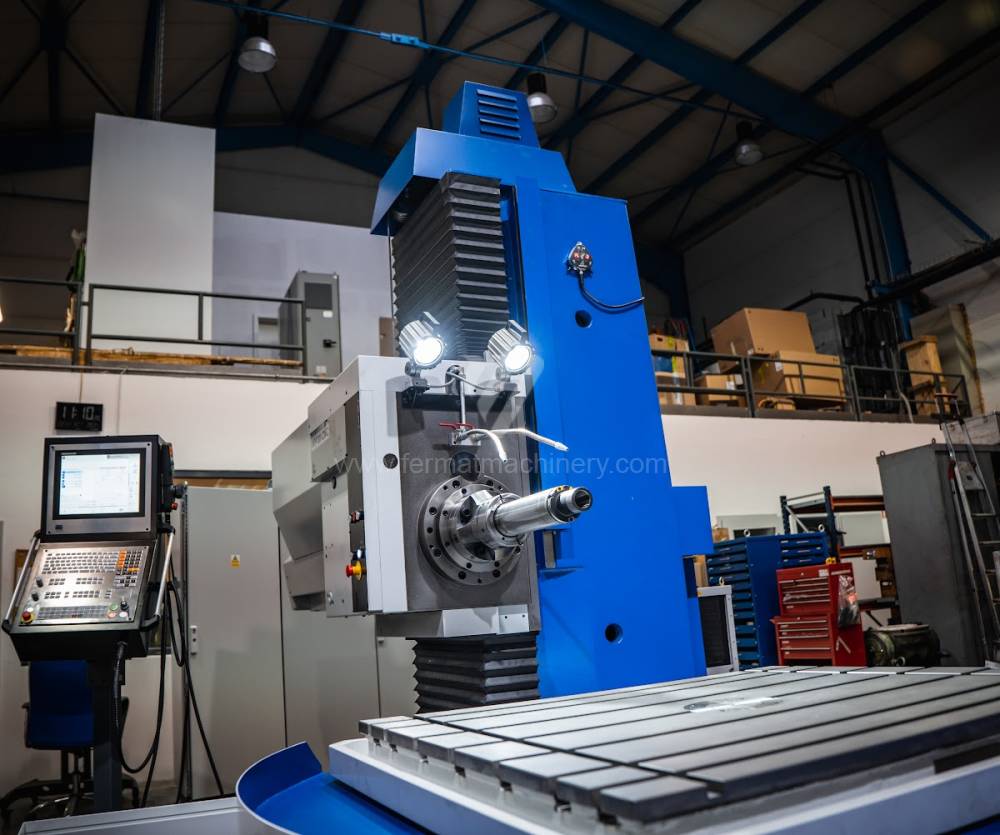
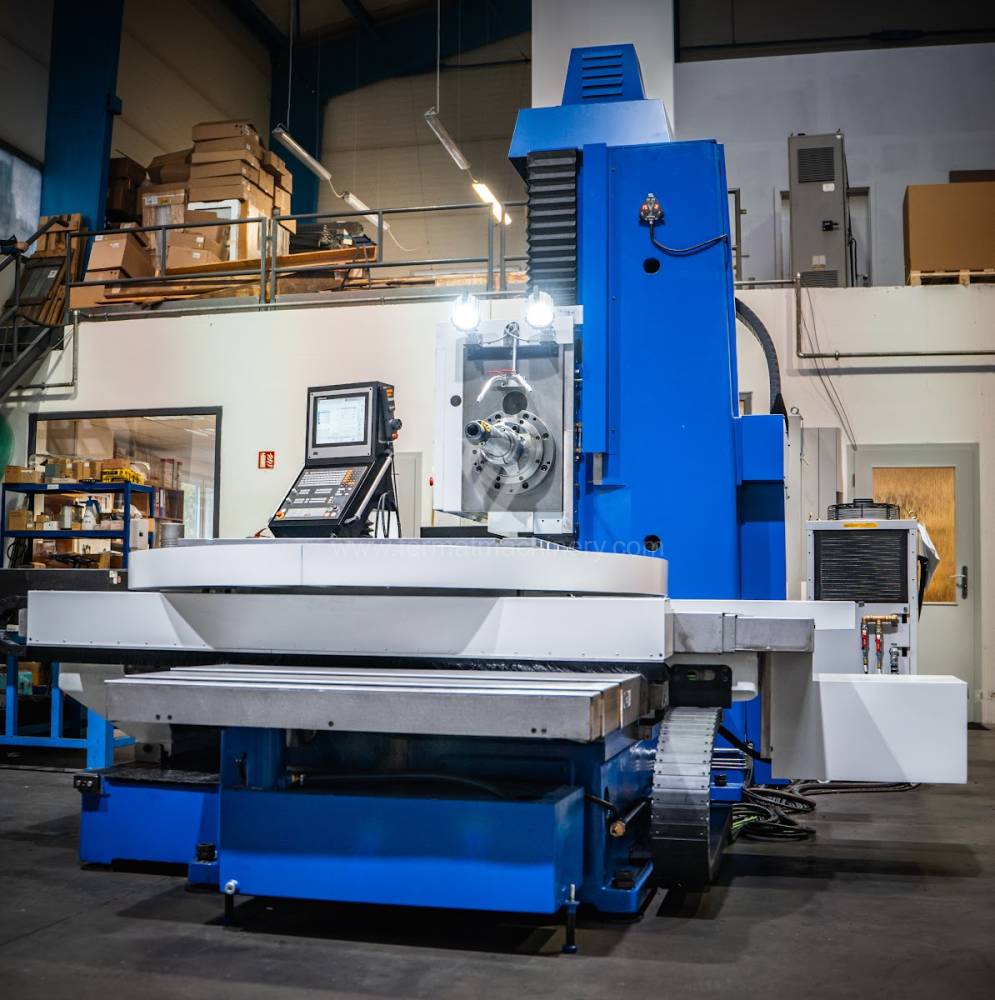

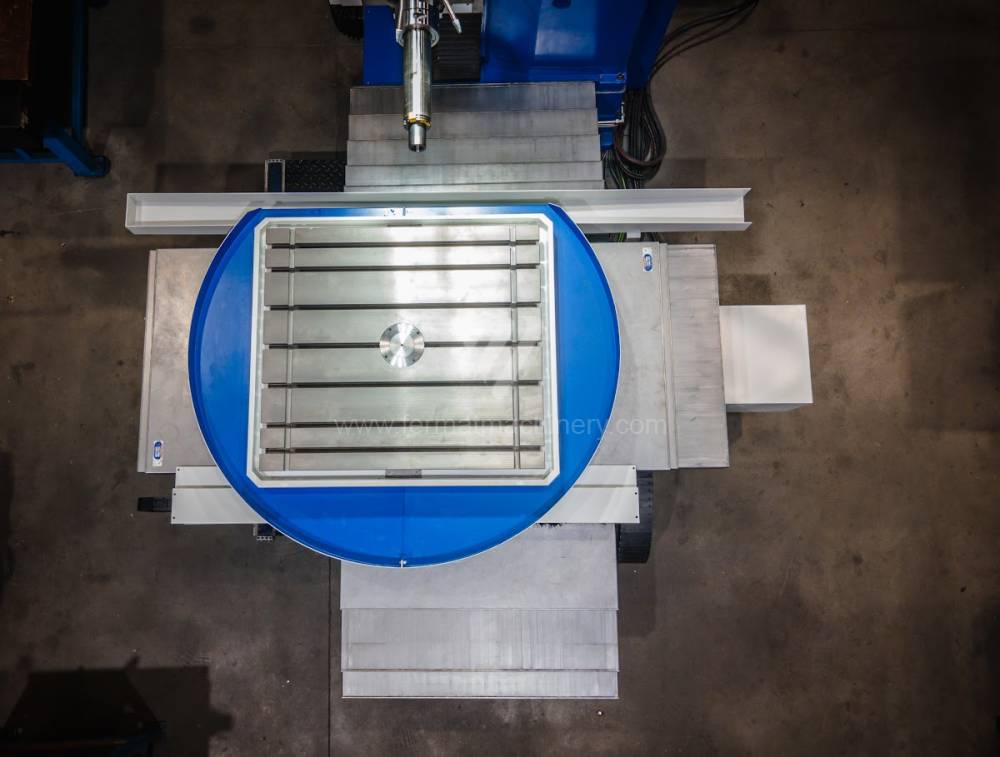








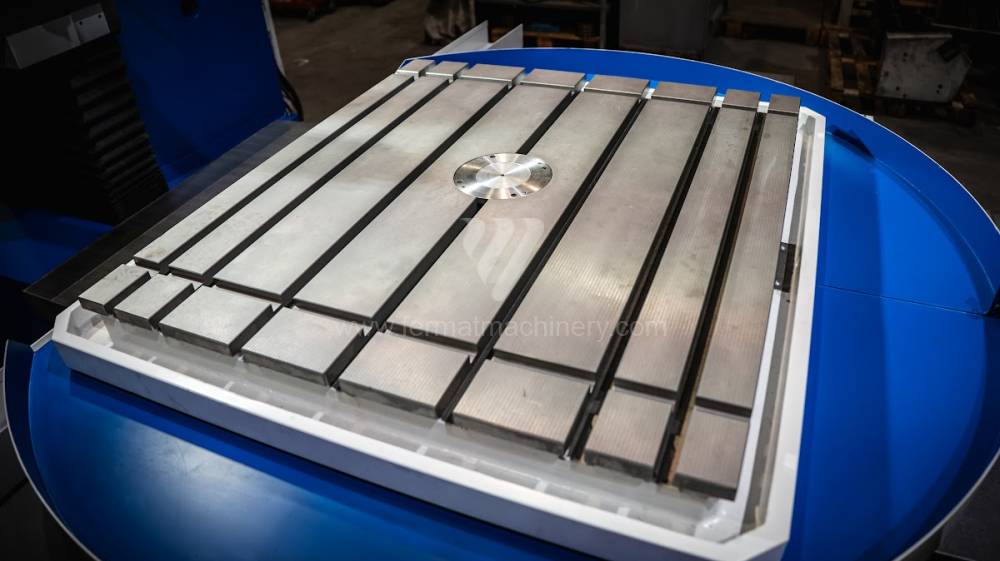







Système de contrôle Heidenhain: TNC 620
Diametre de travaille de broche: 100 mm
Course X: 1250 mm
Course Y: 1030 mm
Vitesse de broche: 16 - 2500 /min.
Refroidissement par axe: NON
Horizontal boring machines are universal machines used for machining of complex products. These borers are mainly used for small batch production. For one workpiece clamping, the operation can be performed from up to five sides, either simultaneously or sequentially. A large number of standard and special accessories are available for horizontal boring machines. This makes boring machines suitable not only for boring, but also for drilling, turning, milling and other operations.
Horizontal boring machines can be divided into several types, such as: table, cross, plate, coordinate. Can be divided also according to the type of control - conventional (without system), or CNC controlled.
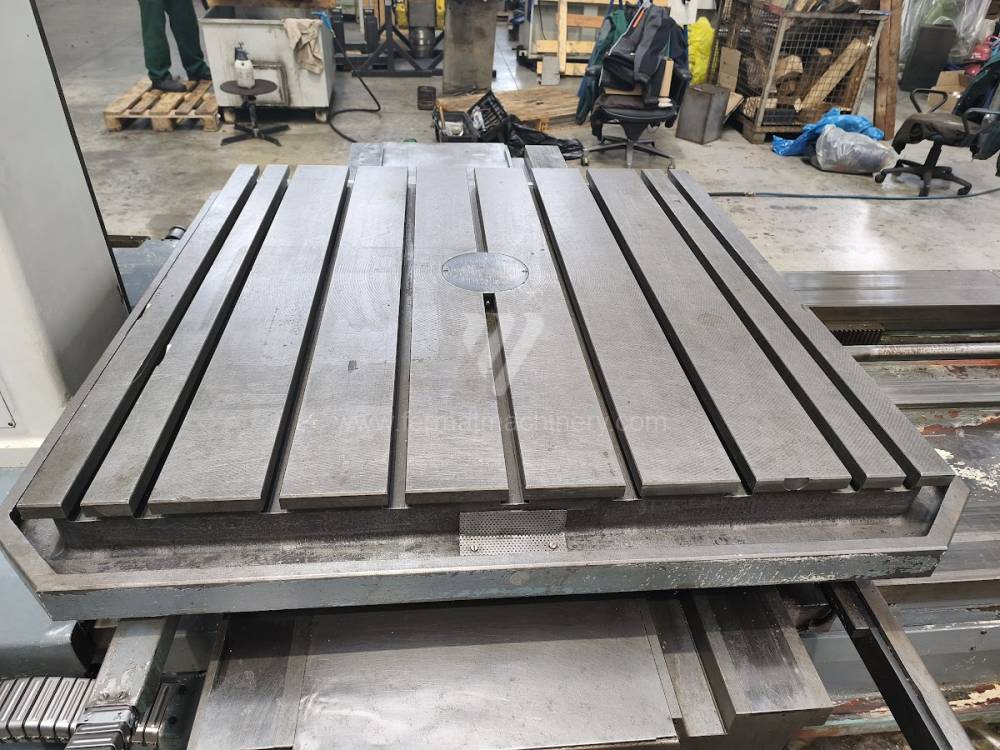
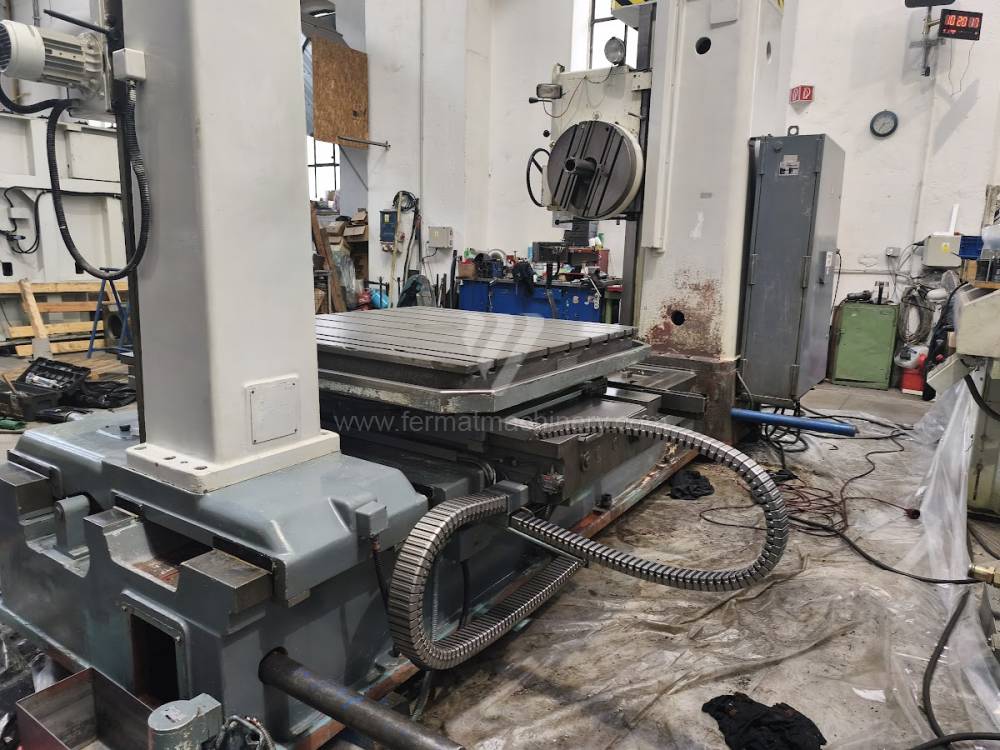
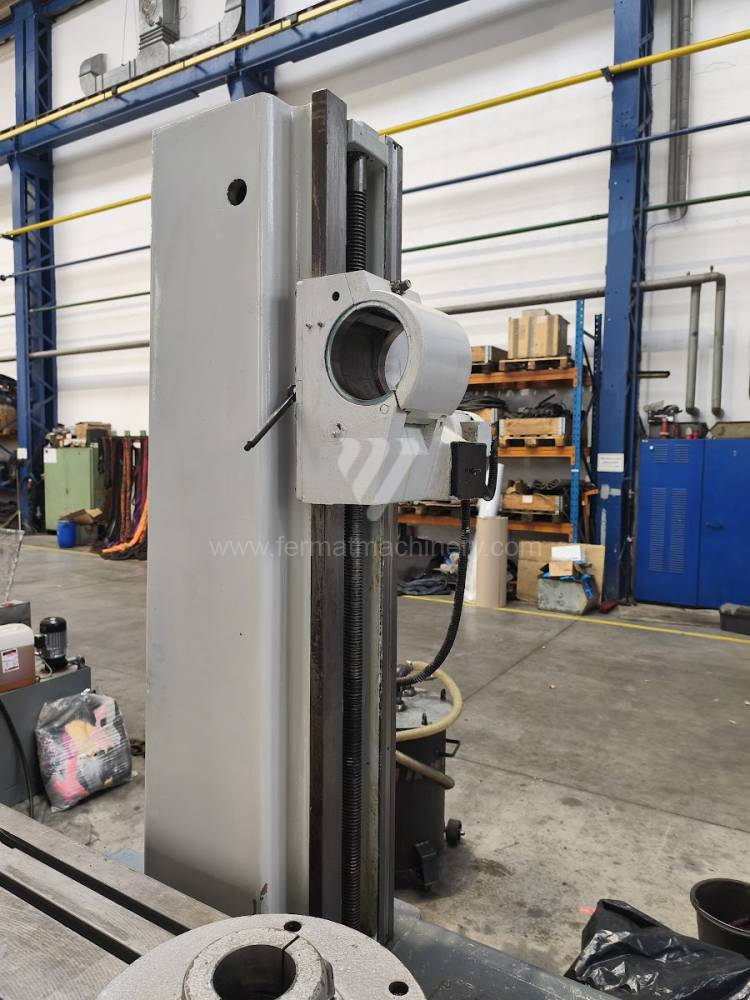
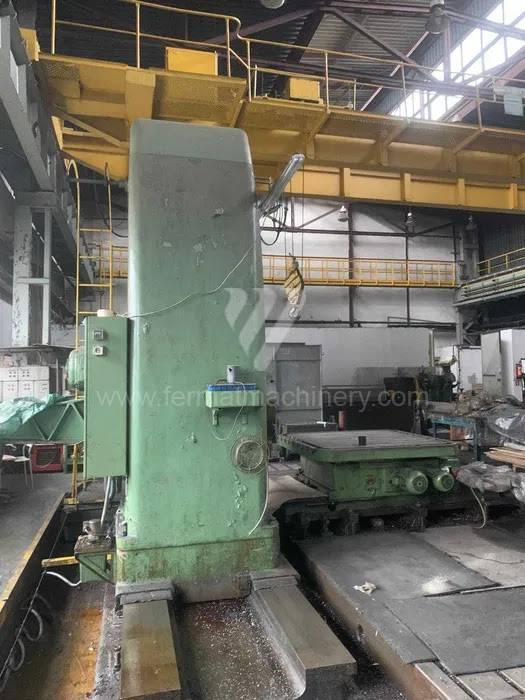
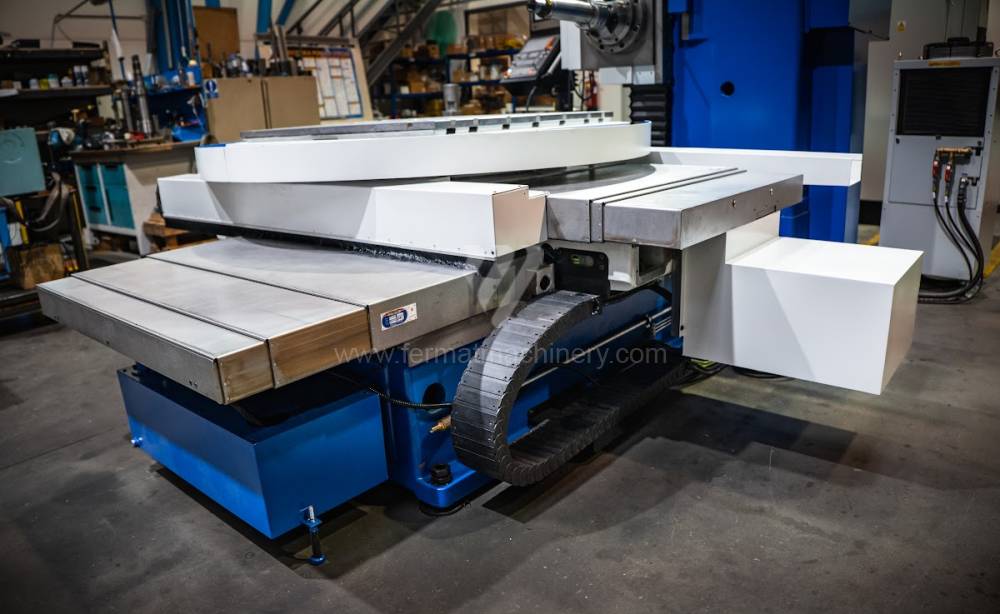
Table boring machines are equipped with a movable table that moves in one or two axes. Depending on this, boring machines are further divided into cross-construction or T-construction. The table is usually rotary (B axis), which allows four sides of the workpiece to be machined in one clamp. However, if the machine is equipped with an angle head (A and C axes) and the workpiece does not exceed the dimensions of the machine, five sides can be machined in one clamp. The boring milling machines differ from the table milling machines in particular by the extendable spindle (W axis). Higher series often also have a movable headstock (V axis).
These kinds of boring machines are suitable and used for machining of the largest workpieces. Headstock is moving along the vertical guide of the column and column itself is moving along the bed perpendicular to the axis of the spindle. The workpiece is clamped immovably on a cast-iron floor plate equipped with T-slots. If this floor type boring machine is equipped with a rotary table which is movable in the direction of the spindle axis, the number of controlled axes increases. Such boring machines mainly have a boring spindle diameter of 130-315 mm.
So-called coordinate boring machines are used for machining precise holes. Its design is affected by the requirements for very high accuracy of all movements, good dynamics and the best possible temperature stability. There are two types of these machines. One-column borer with horizontal or vertical spindle axis (this is for smaller sizes of workpieces that are clamped on a cross table) and two column borer with one or more vertical spindles. Workpiece is clamped on a longitudinal table, which is in between two columns along which the crosspiece carrying the work headstock moves. An optical system is usually used for measuring. More modern machines are then equipped with a CNC control system.
All types of horizontal boring machines are conventional or CNC controlled. Among the most popular producers of CNC systems are Heidenhain, Siemens, Fanuc, Fagor.
Horizontal boring machines can be also equipped with automatic tool change which is primarily used for storage of tool holders, its manipulation and positioning without participation of human factor.
Among the main and most popular manufacturers of boring mills we have to mention: FERMAT, TOS, ŠKODA, PAMA, UNION, JUARISTI, SCHARMANN, KURAKI, WOTAN.