Közel






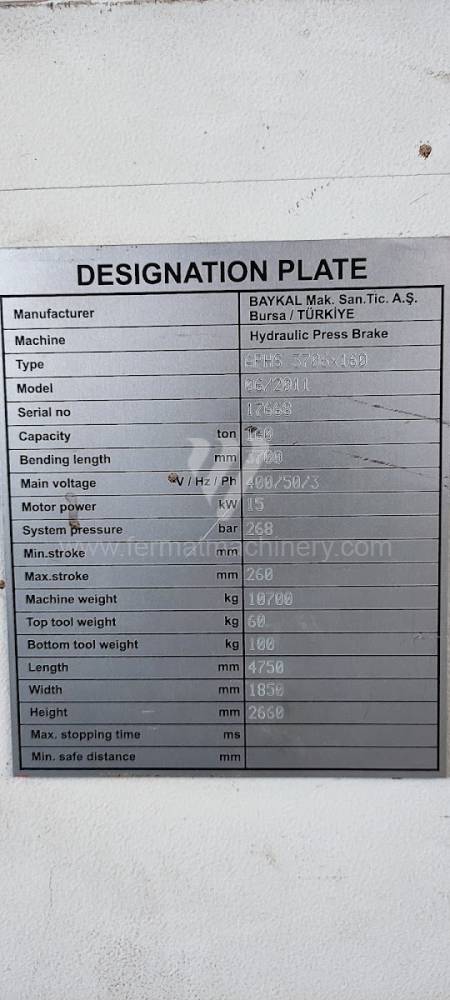







Gyártás éve:2011
Delem vezérlőrendszer: DA - 56 s
Hajlítási erő: 160 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3700 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
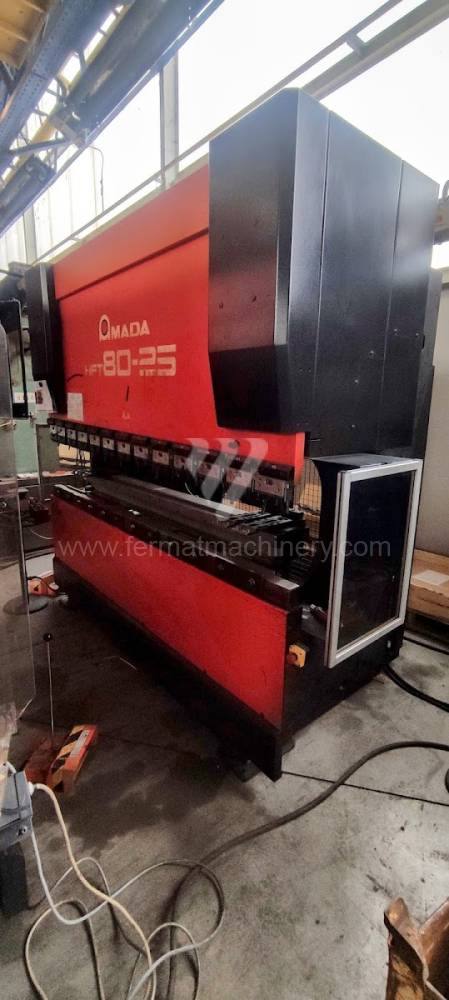



















Gyártás éve:2001
Hajlítási erő: 80 t
Hajlítási hossz: 2620 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung:
A medve lökete: 200 mm
A gép súlya: 5750 kg
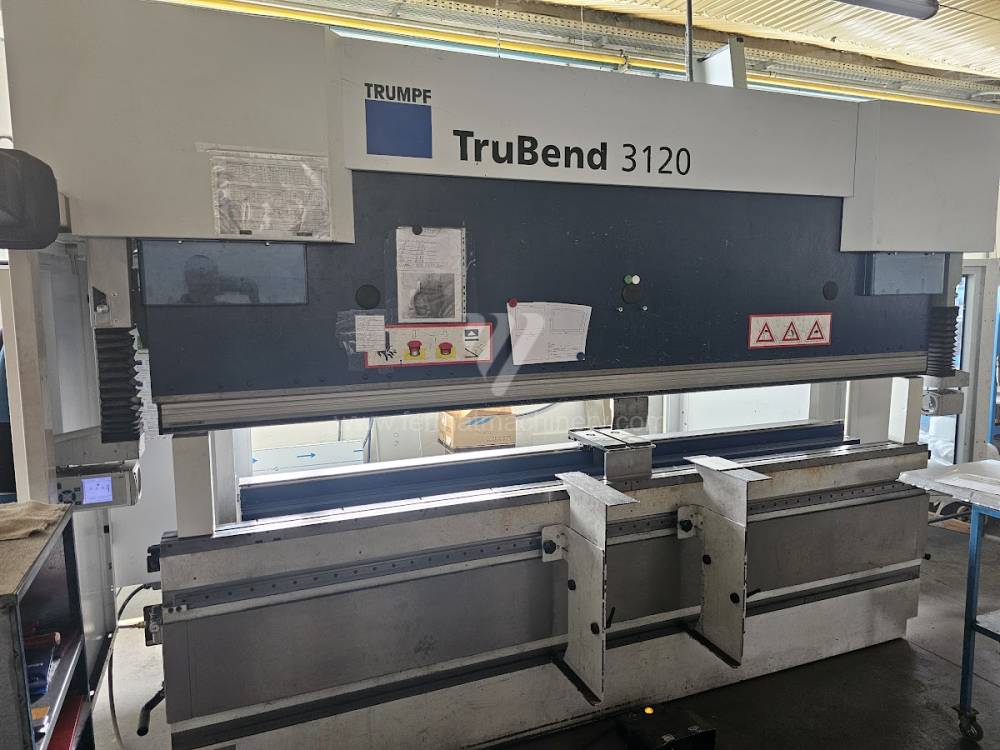
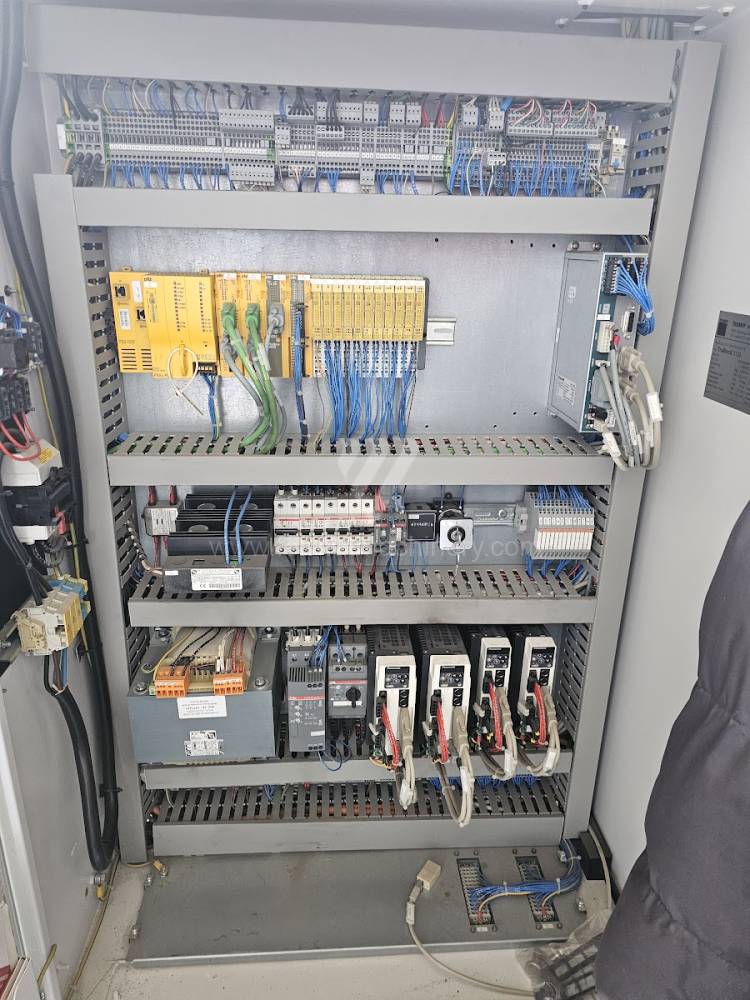
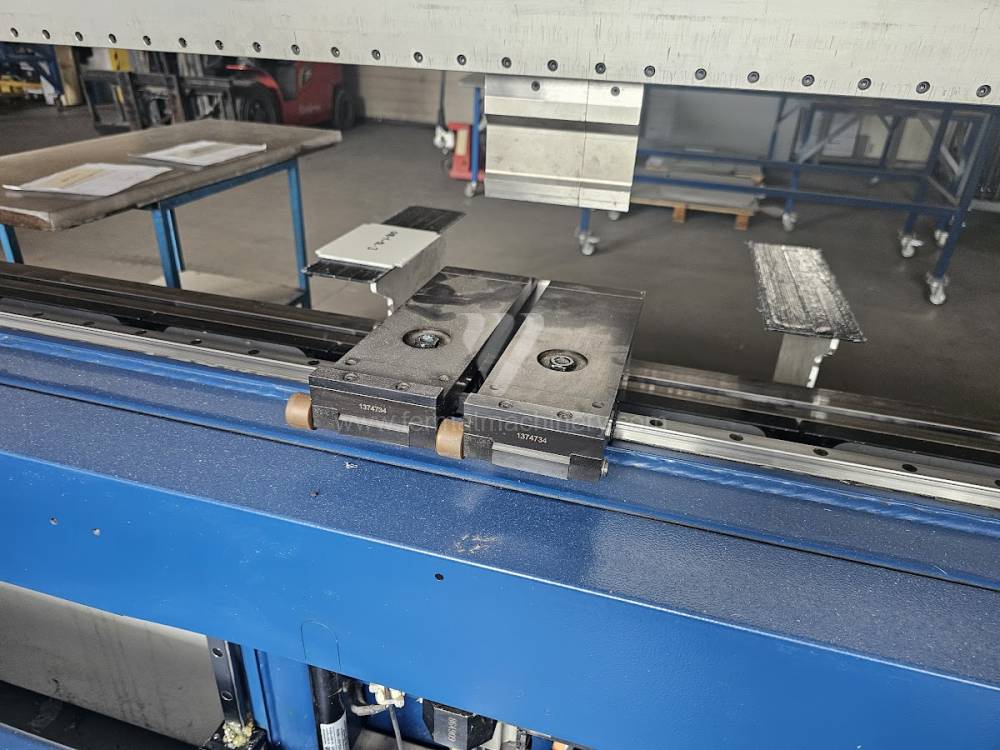
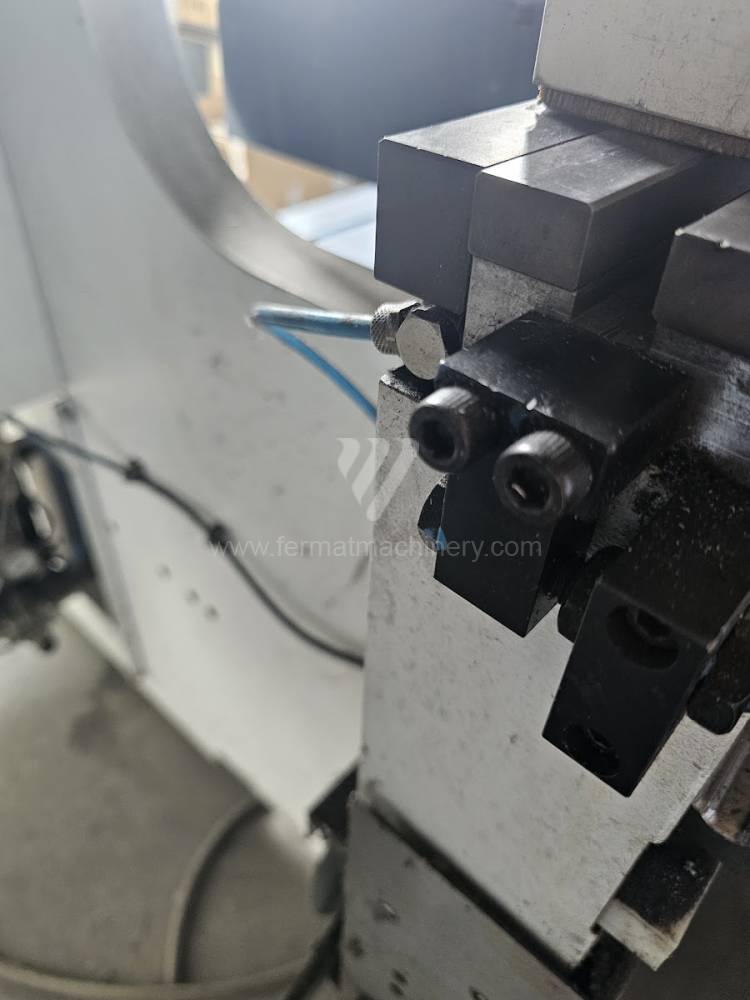








Gyártás éve:2013
Hajlítási erő: 120 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A medve lökete: 200 mm









Gyártás éve:2000
Hajlítási erő: 300 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3050 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A medve max. lökete: 245 mm
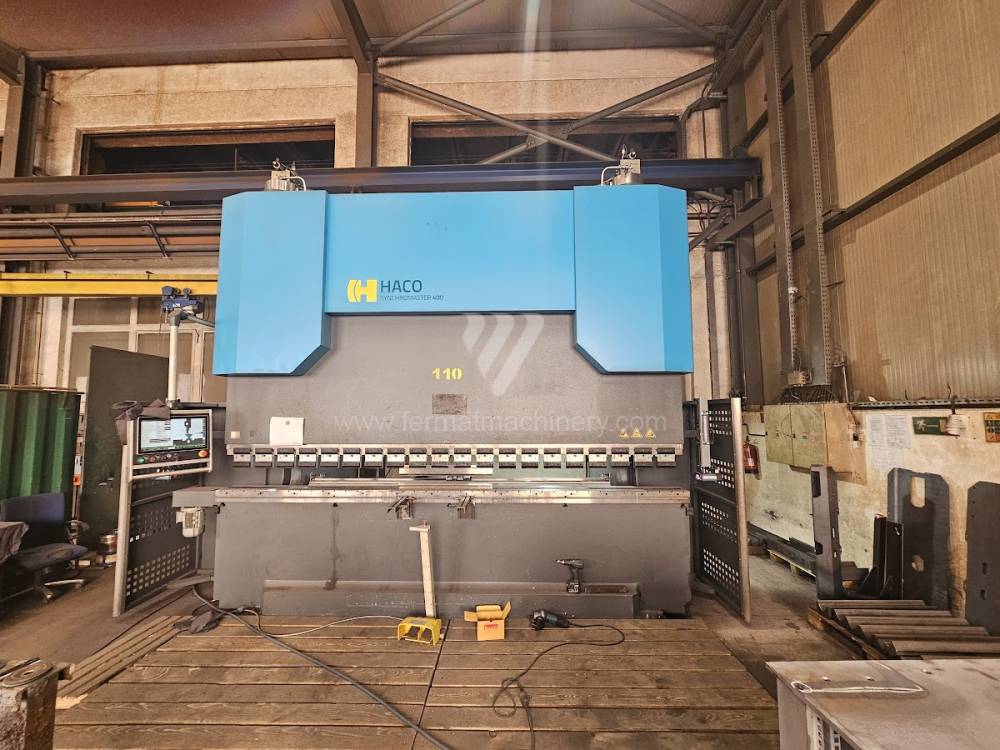







Gyártás éve:2023
Hajlítási erő: 400 t
Hajlítási hossz: 4100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 2
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
Méretek hossz.×szél.×mag.: 6000 x 2852 x 3933 mm
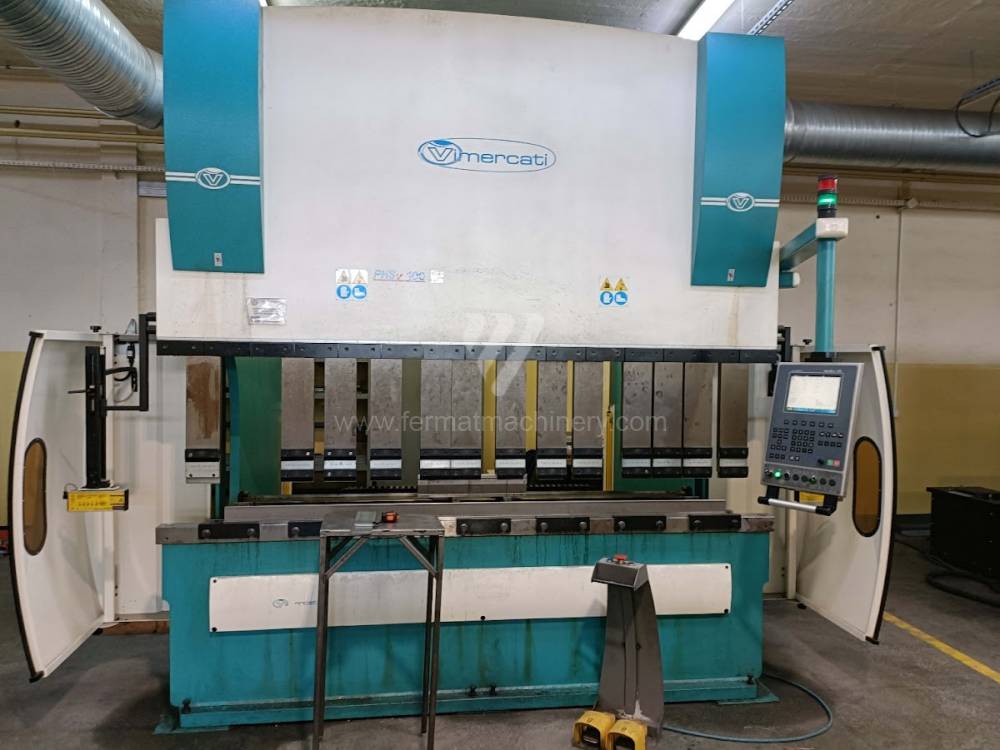
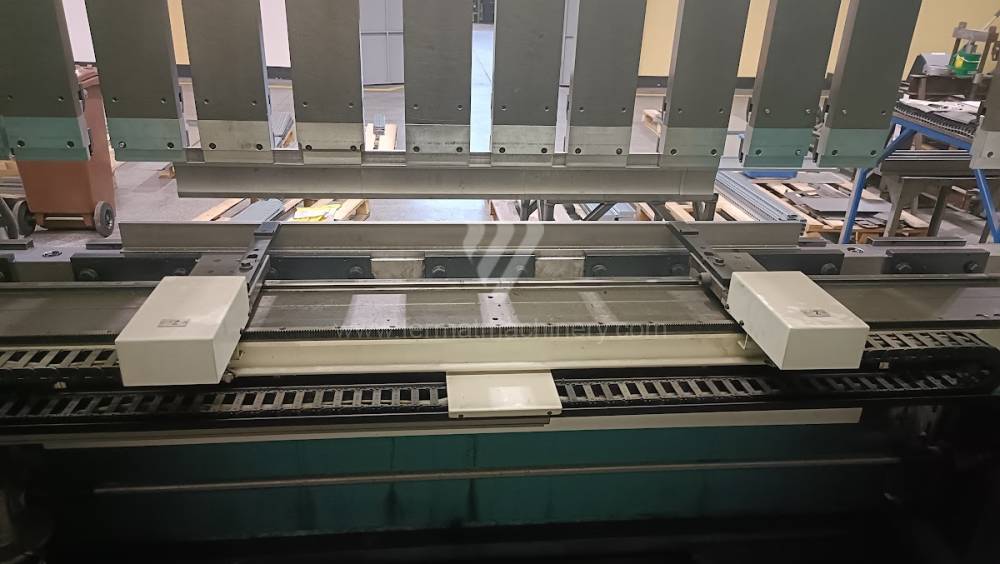
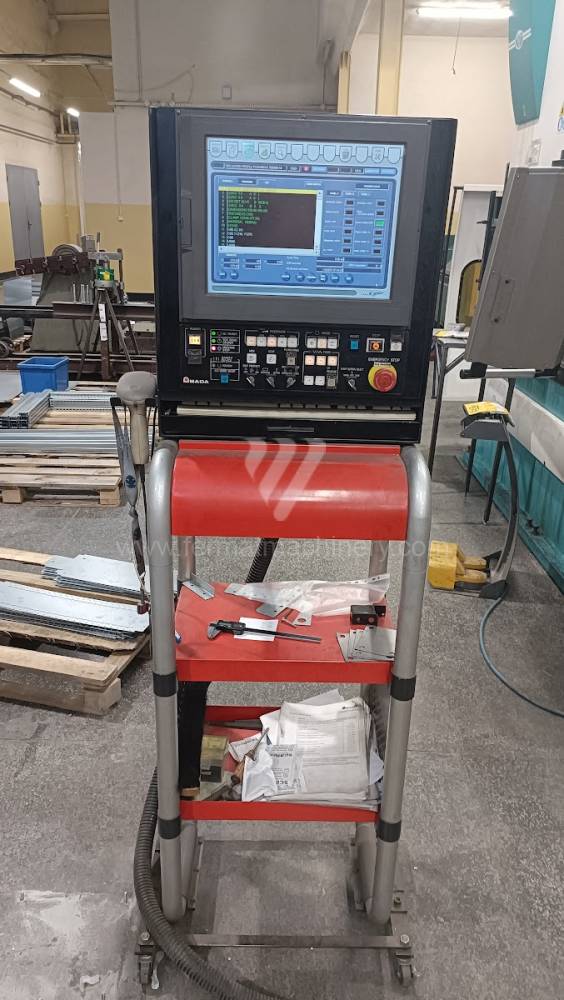
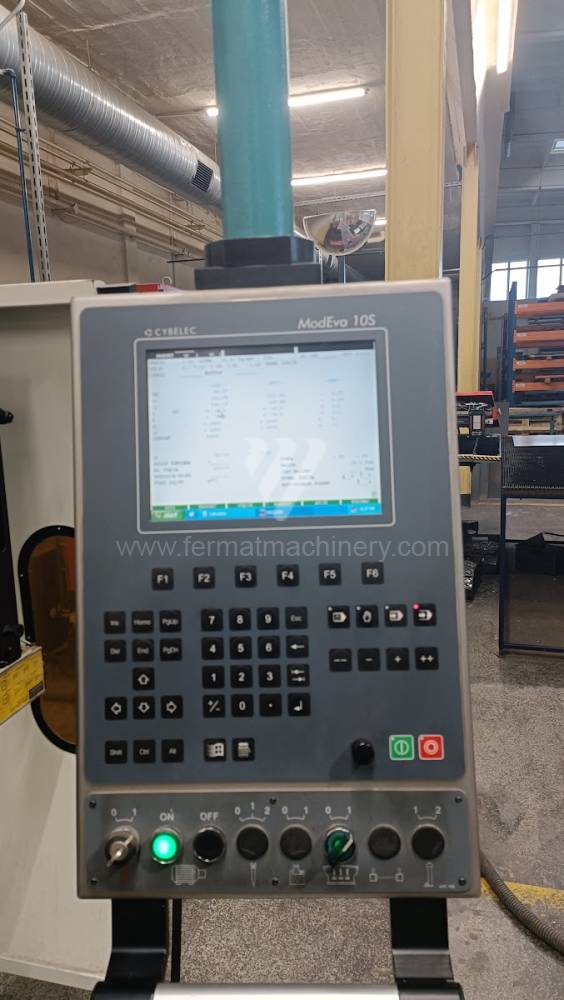
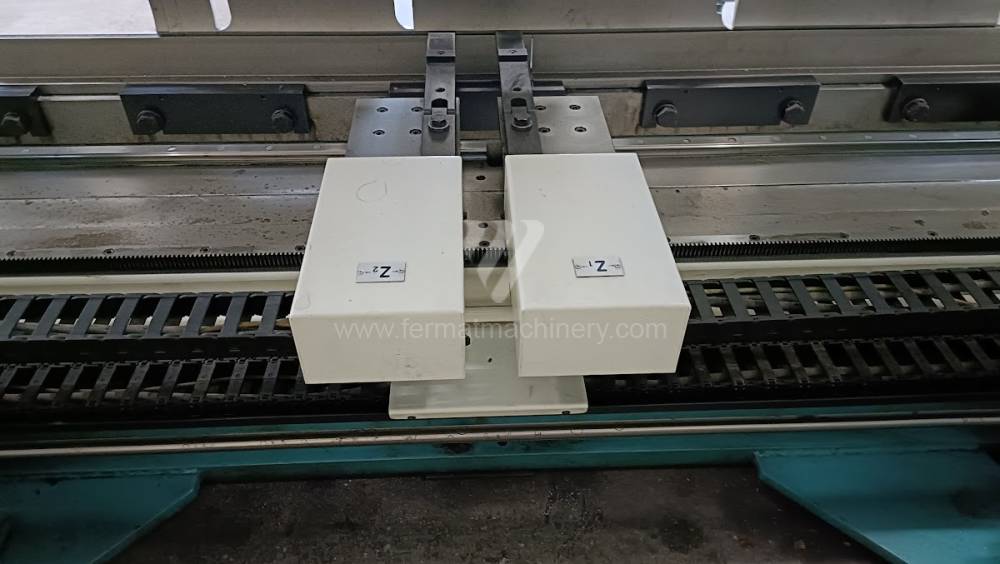








Gyártás éve:2007
Cybelec vezérlőrendszer:
Hajlítási erő: 100 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3050 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 6
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: nem
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
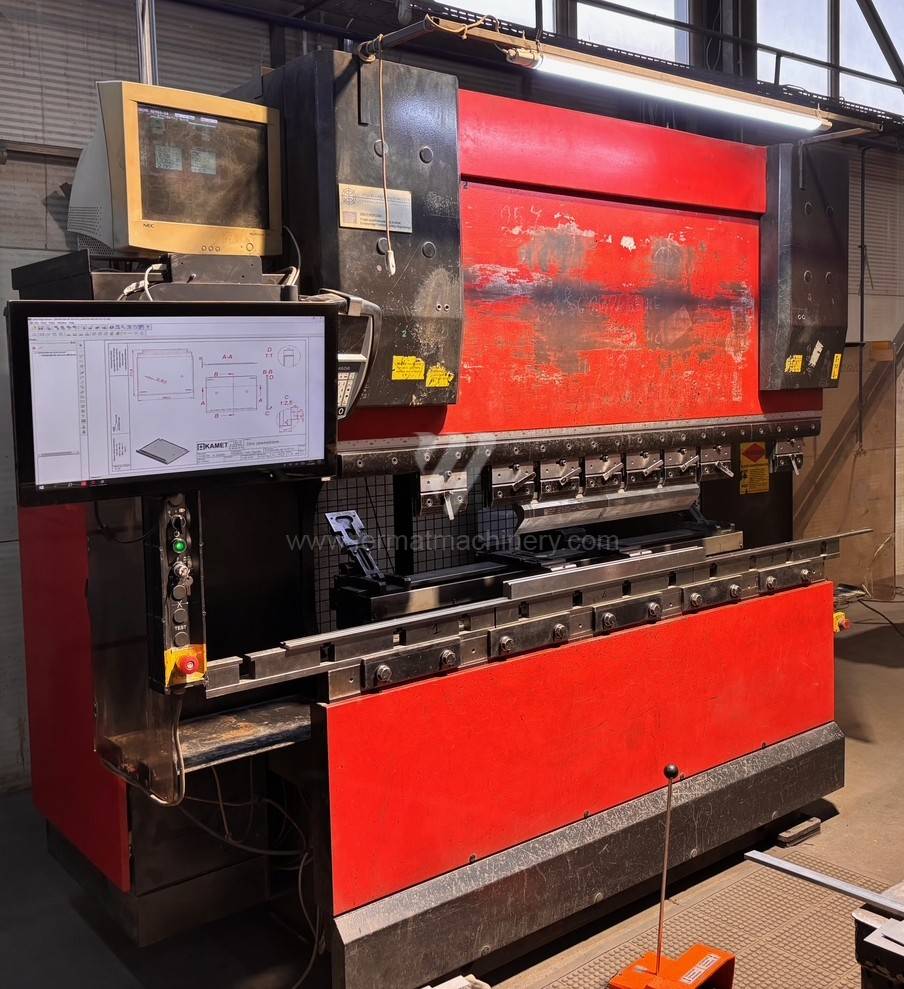
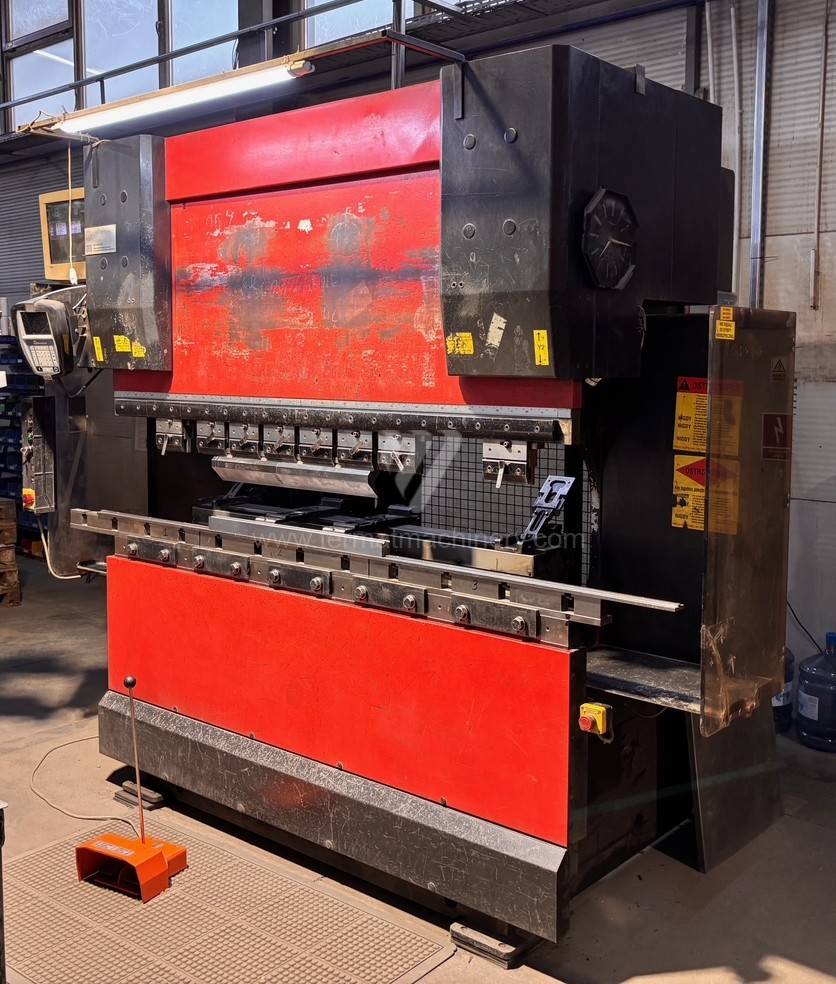




Gyártás éve:2005
Hajlítási erő: 50 t
Hajlítási hossz: 2090 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A gép súlya: 4700 kg
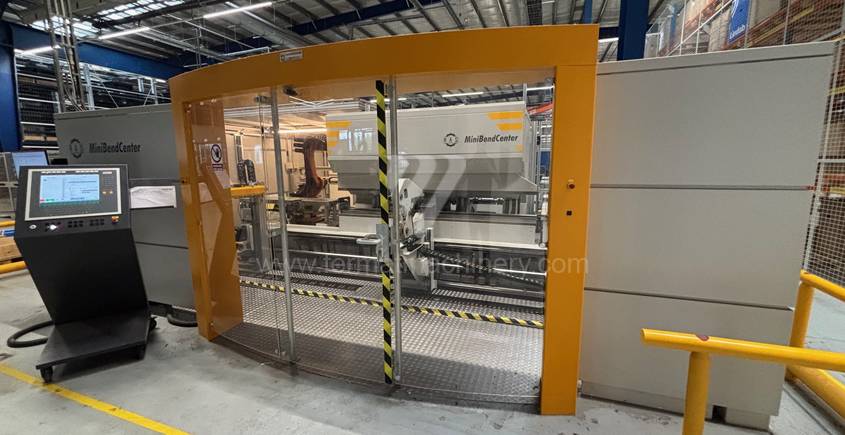

Gyártás éve:2020
Hajlítási erő: t
Hajlítási hossz: 2500 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma:
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung:
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa:
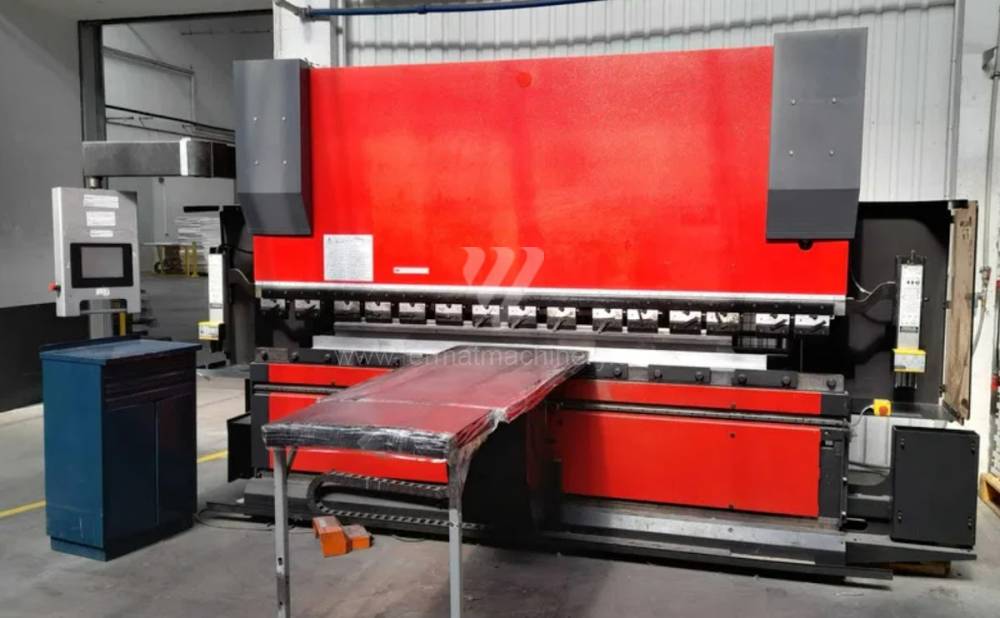
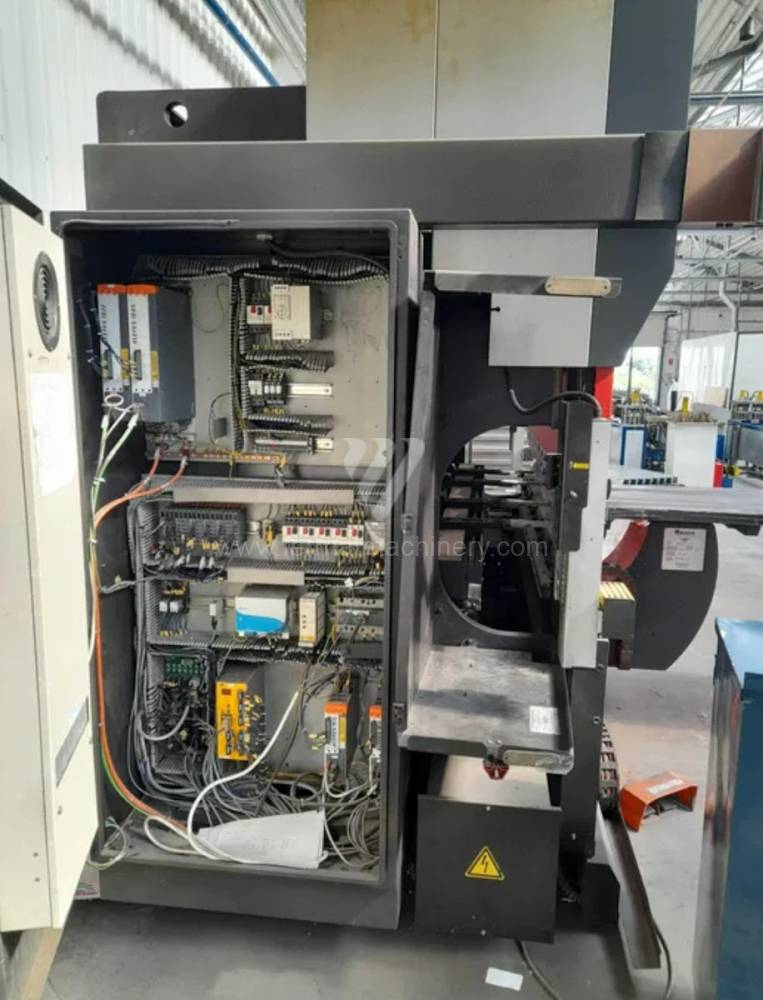
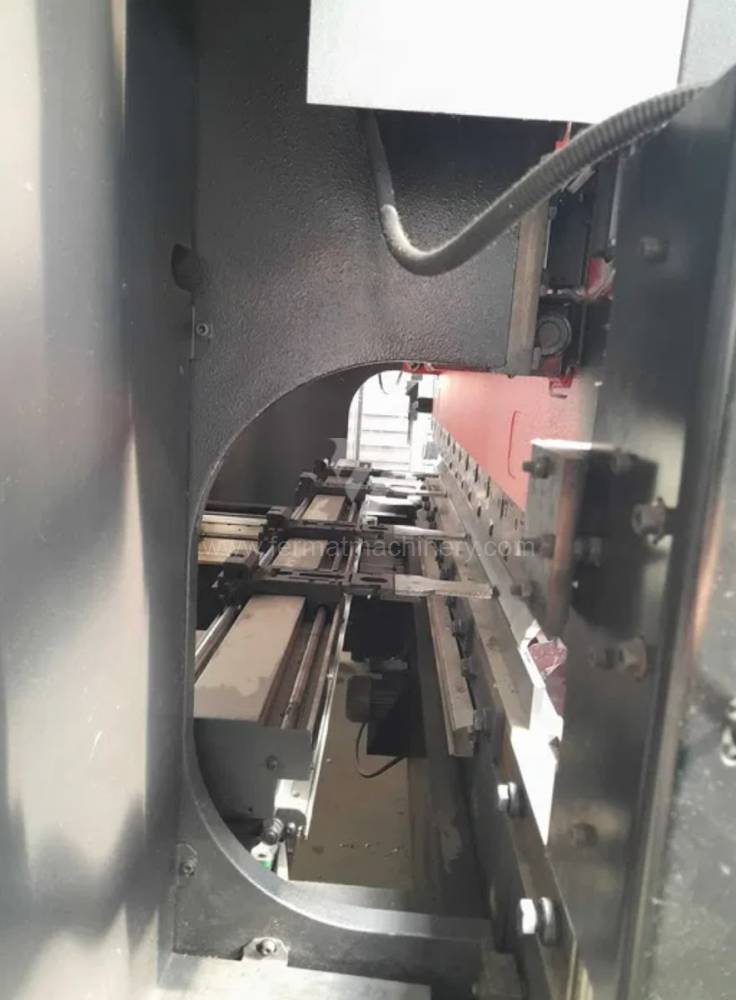
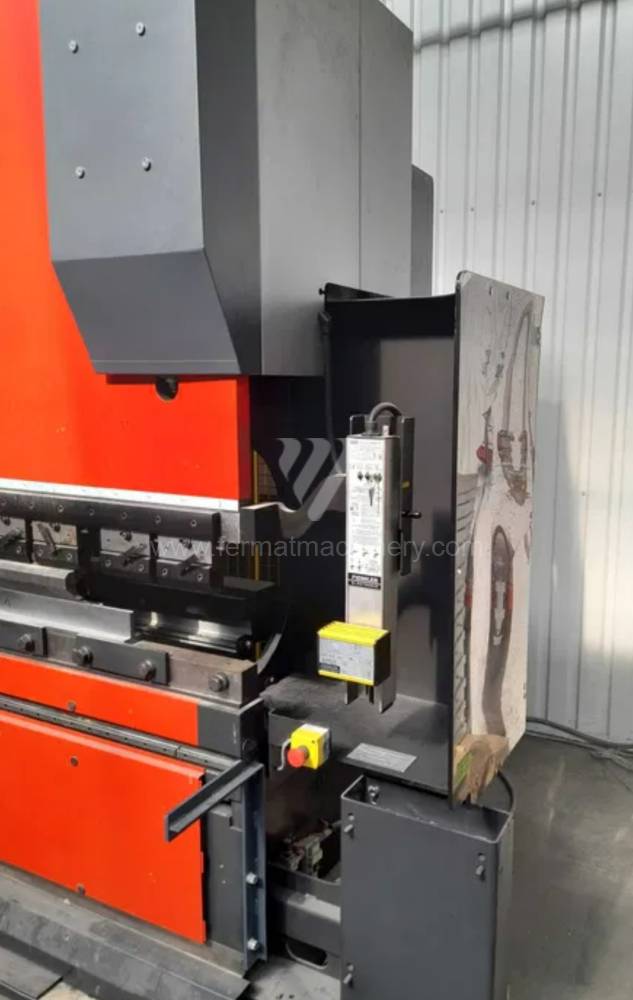
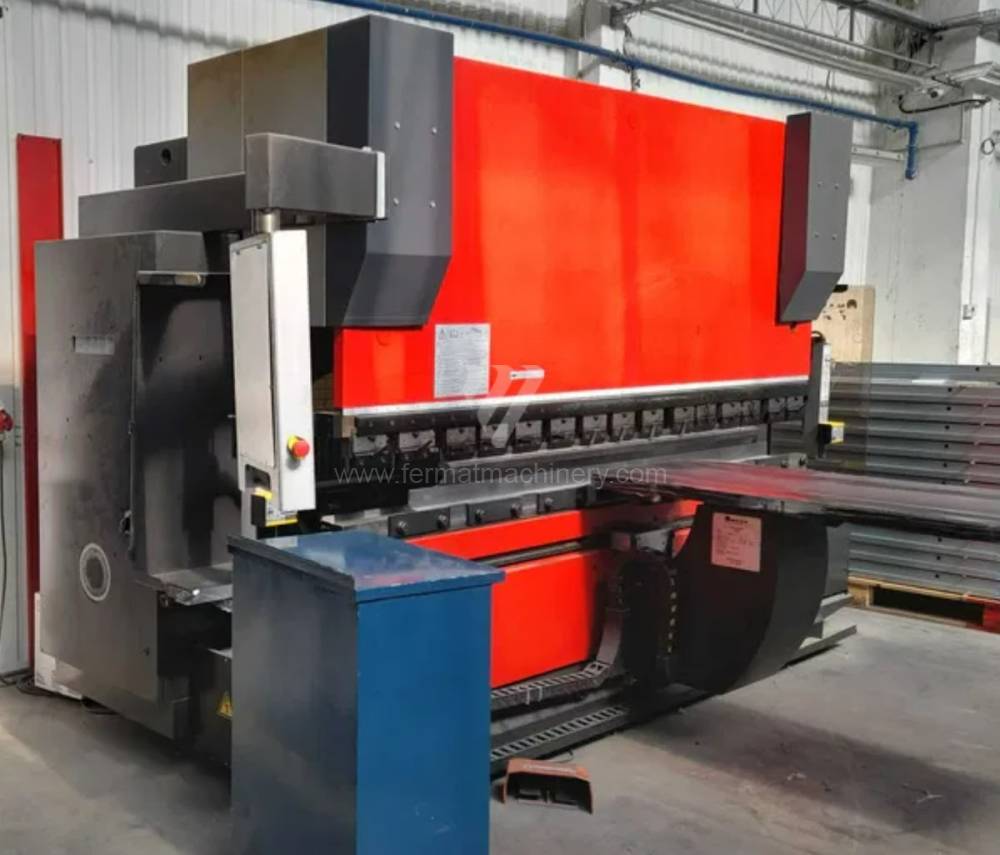





Gyártás éve:2012
Amada vezérlőrendszer:
Hajlítási erő: 100 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3110 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 7
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
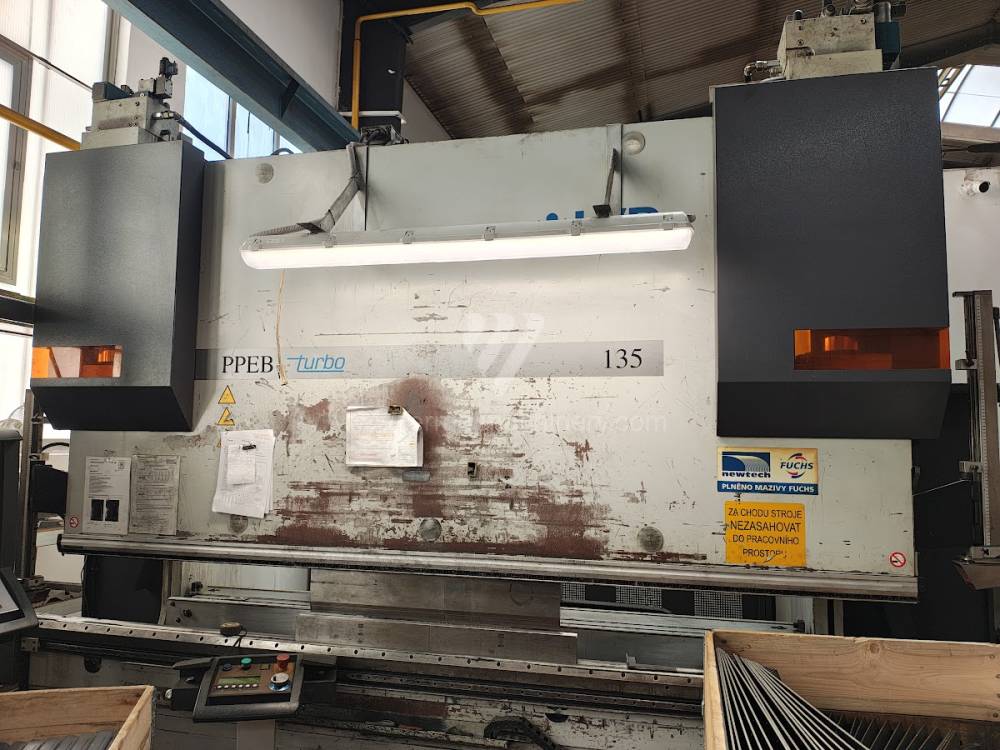
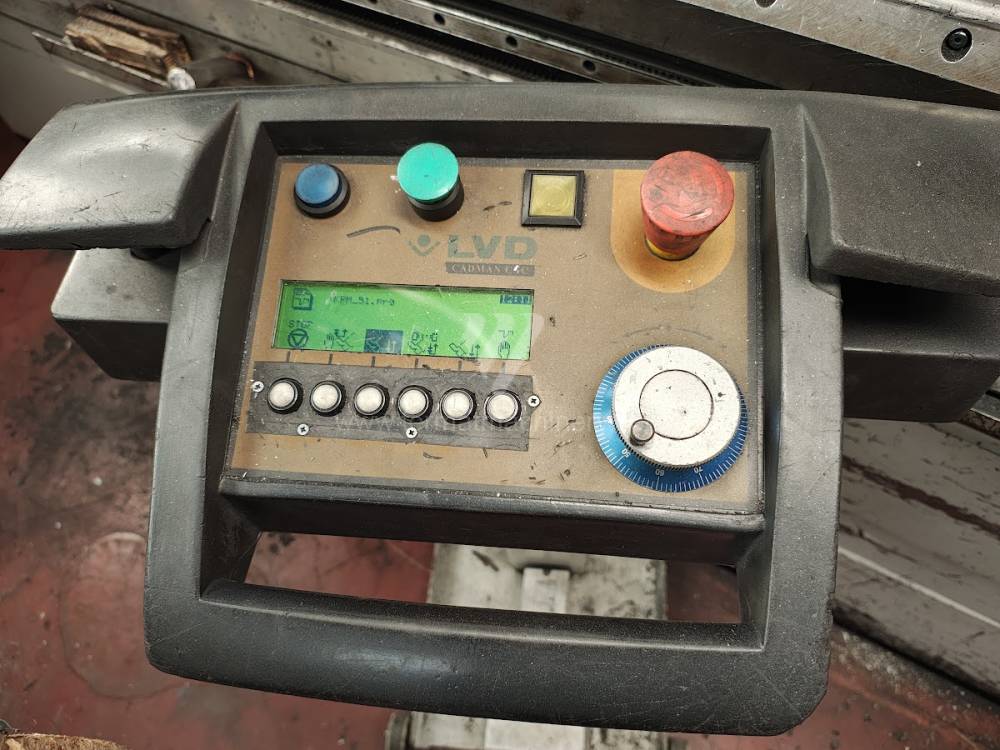
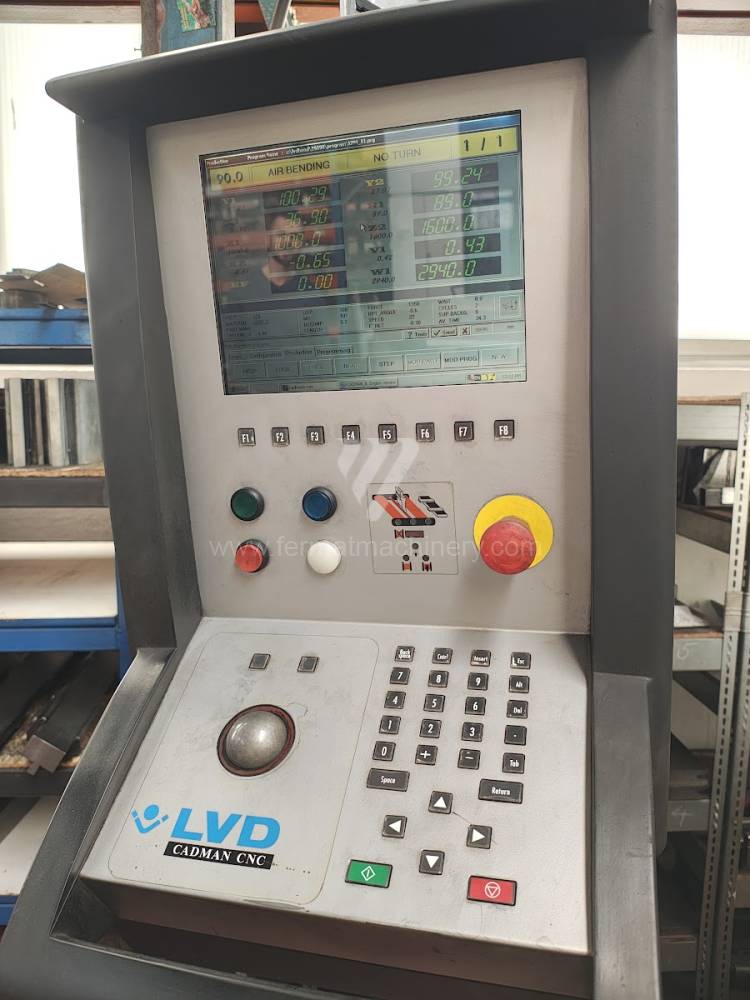






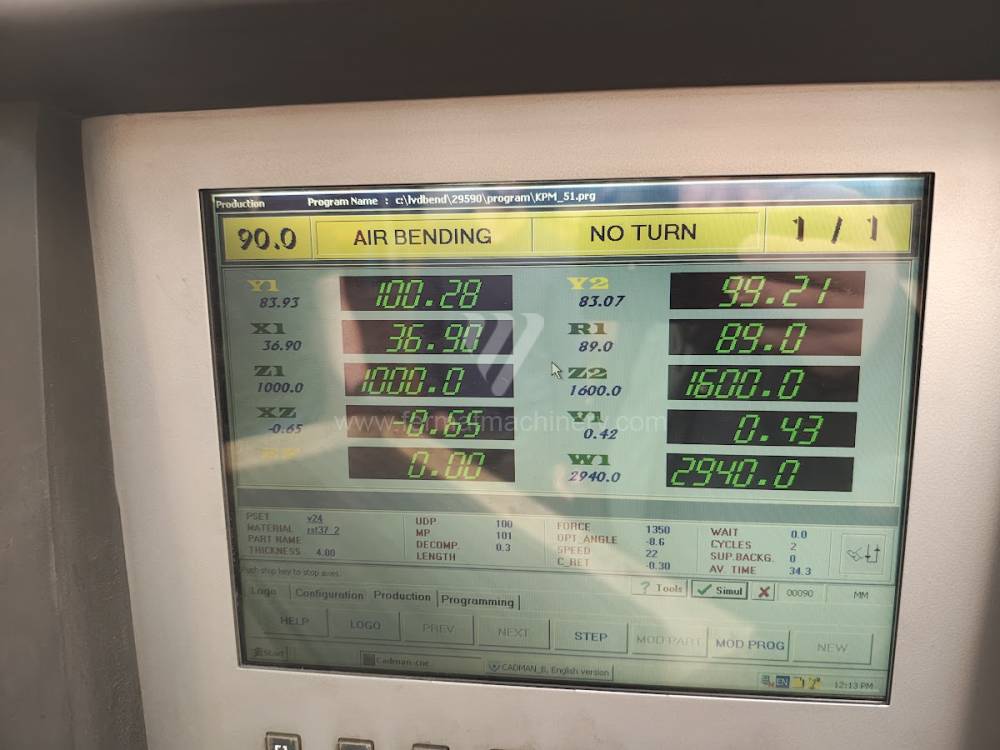








Gyártás éve:2004
LVD vezérlőrendszer: CADMAN
Hajlítási erő: 135 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3000 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 5
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
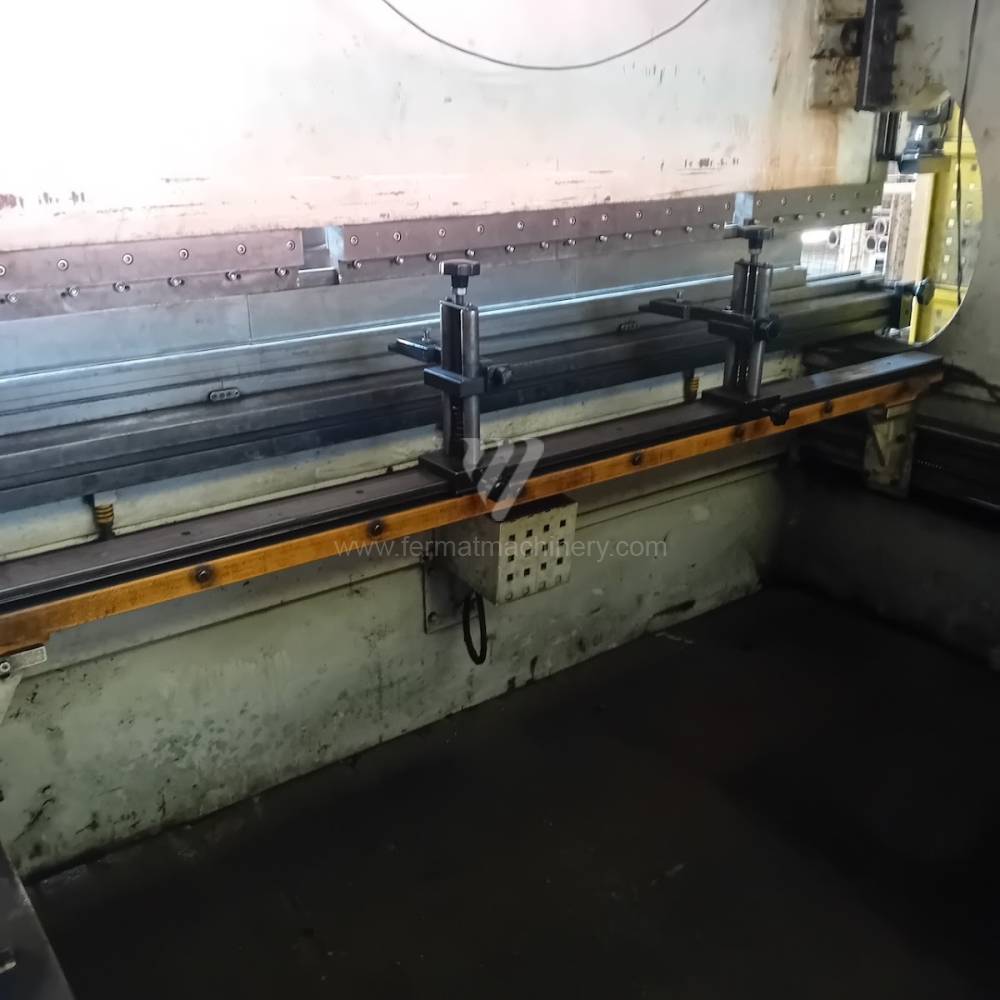
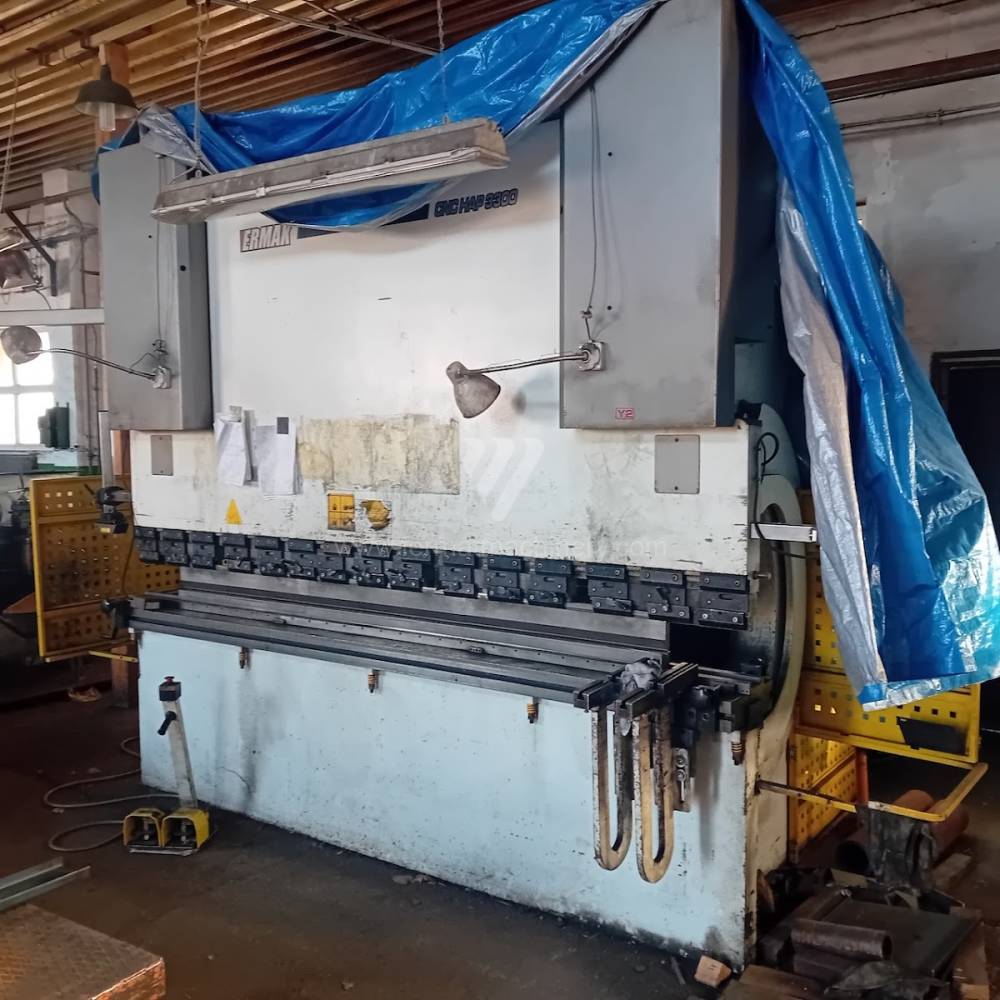
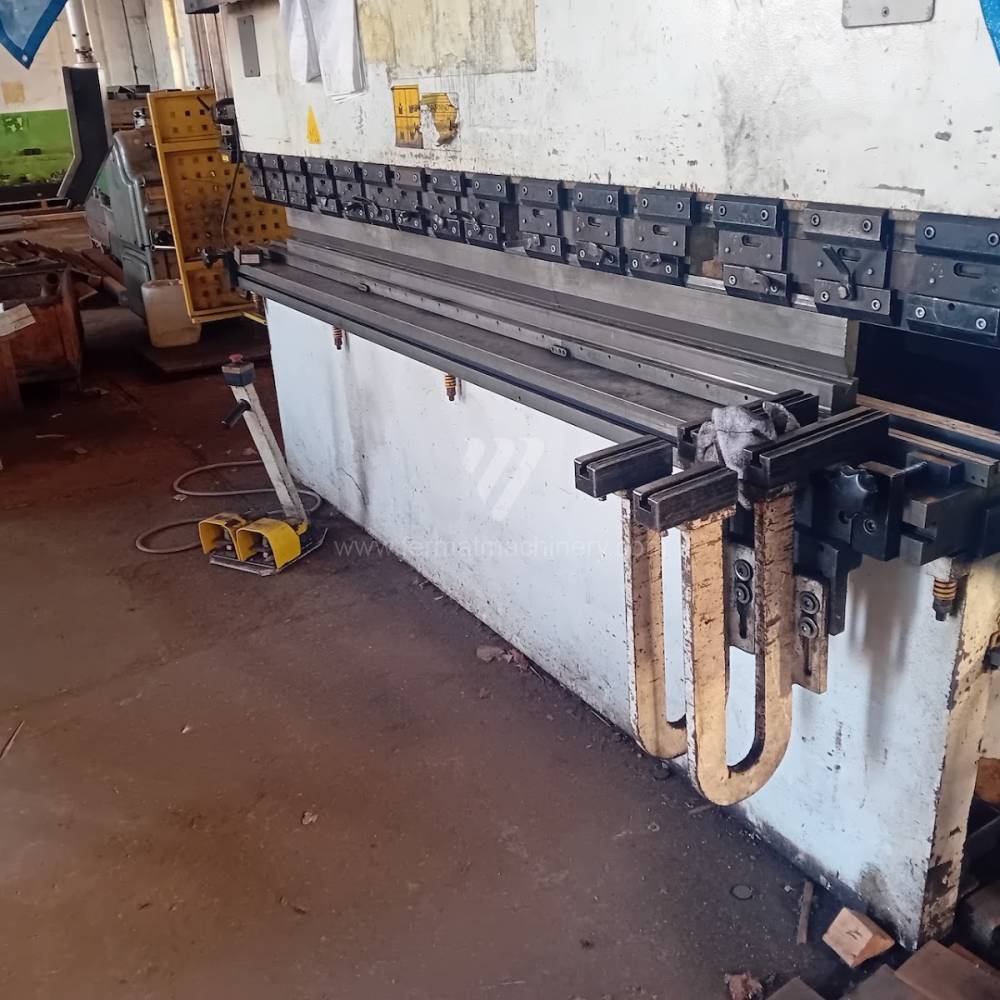





Gyártás éve:2006
Cybelec vezérlőrendszer:
Hajlítási erő: 300 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 3
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
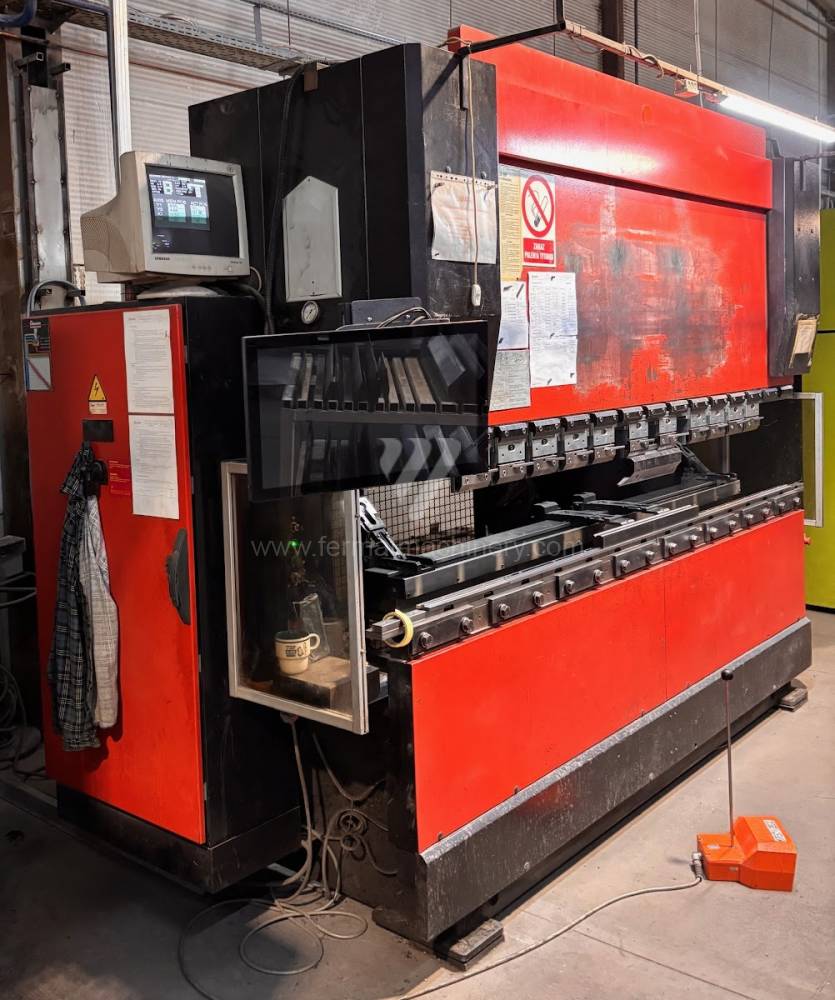
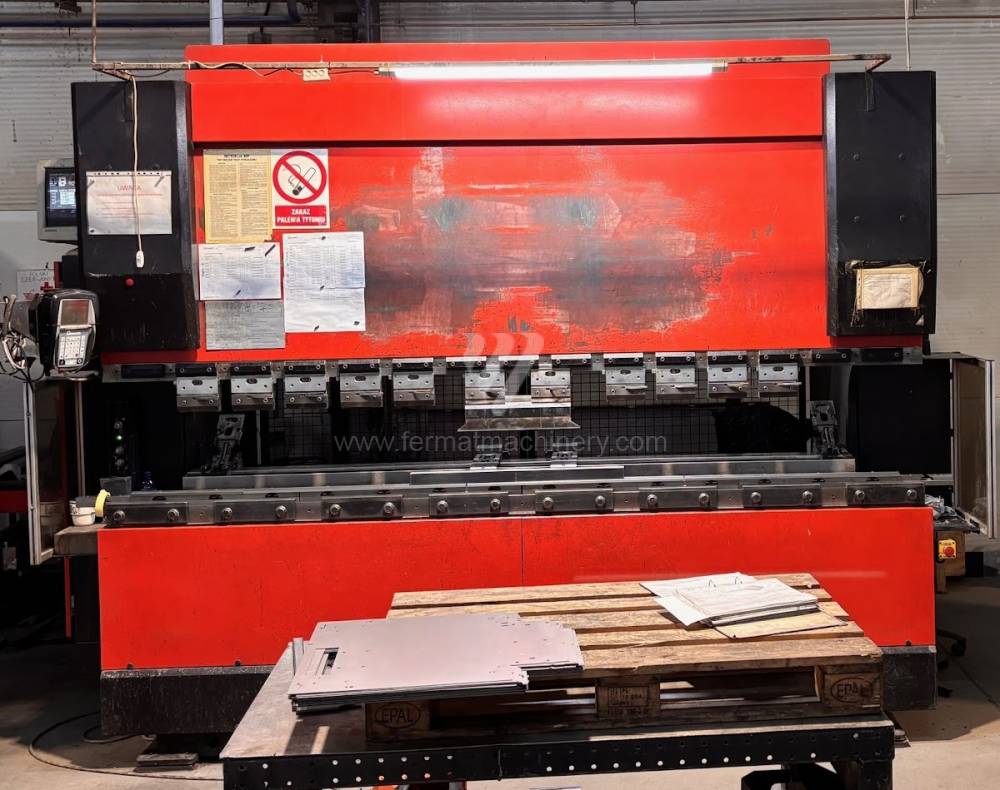
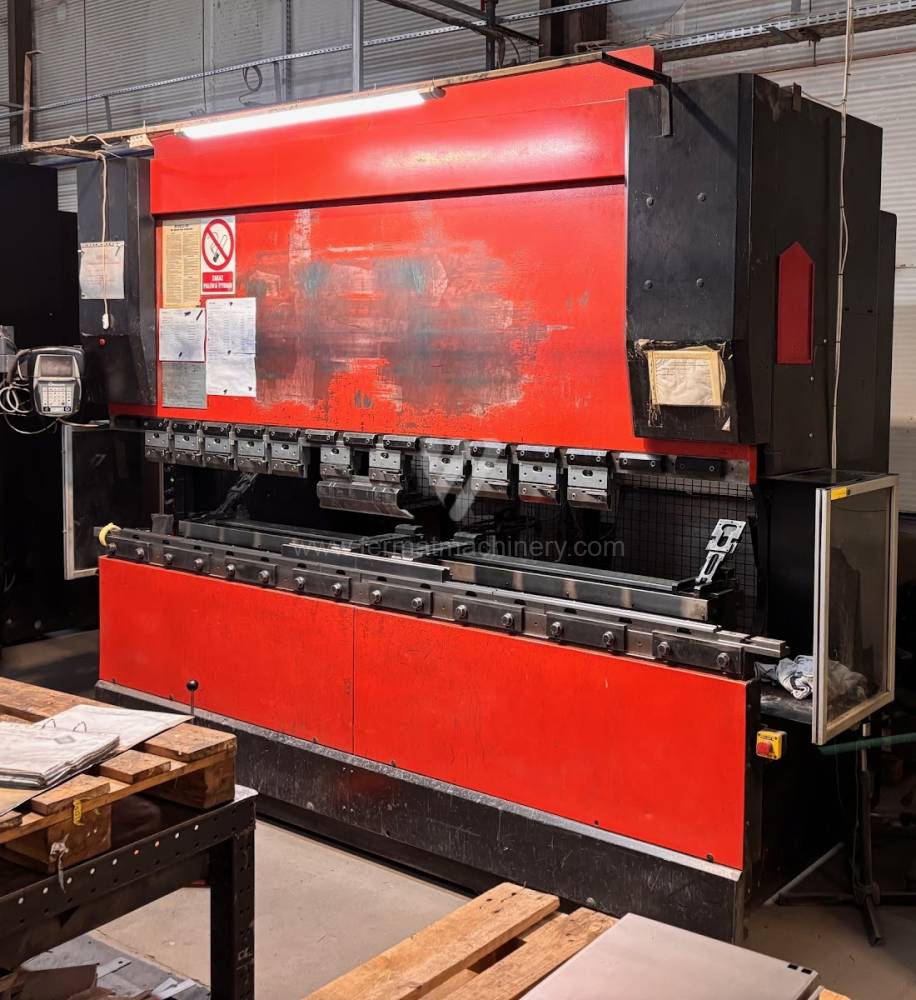



Gyártás éve:2001
Hajlítási erő: 100 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3110 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: nem
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A gép súlya: 6750 kg
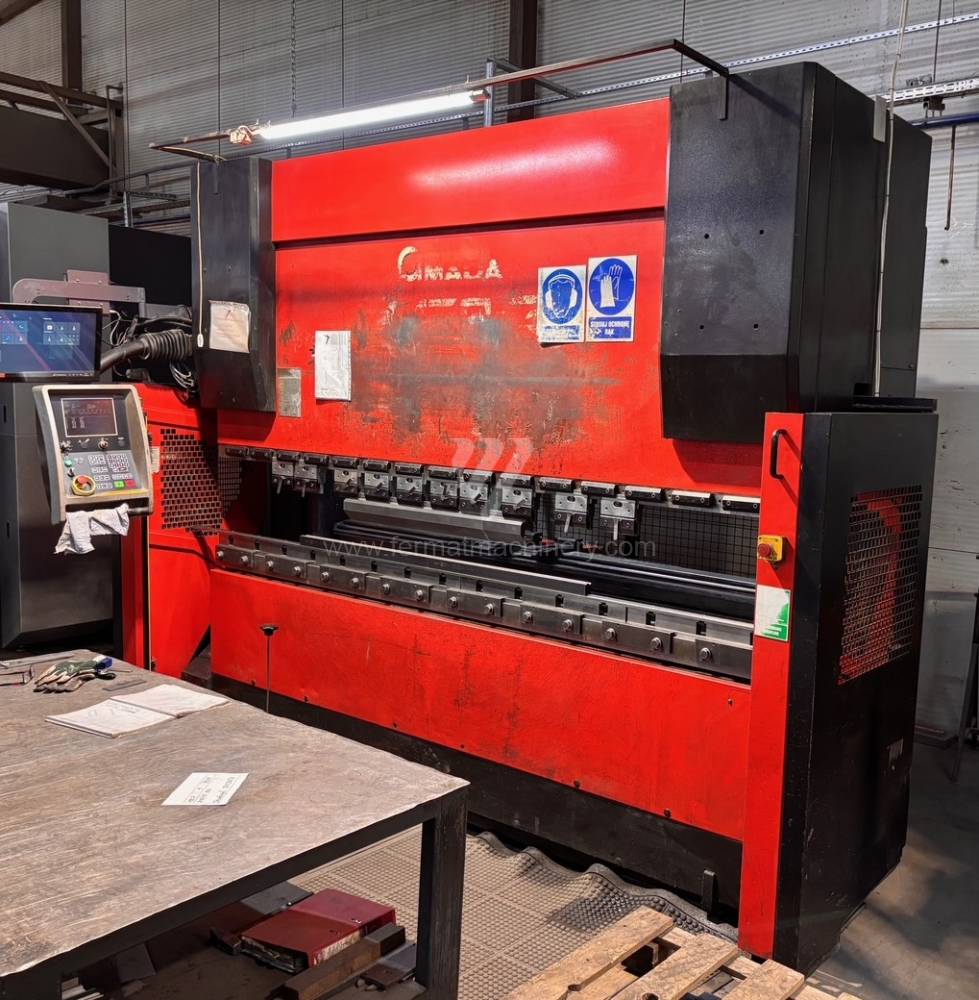
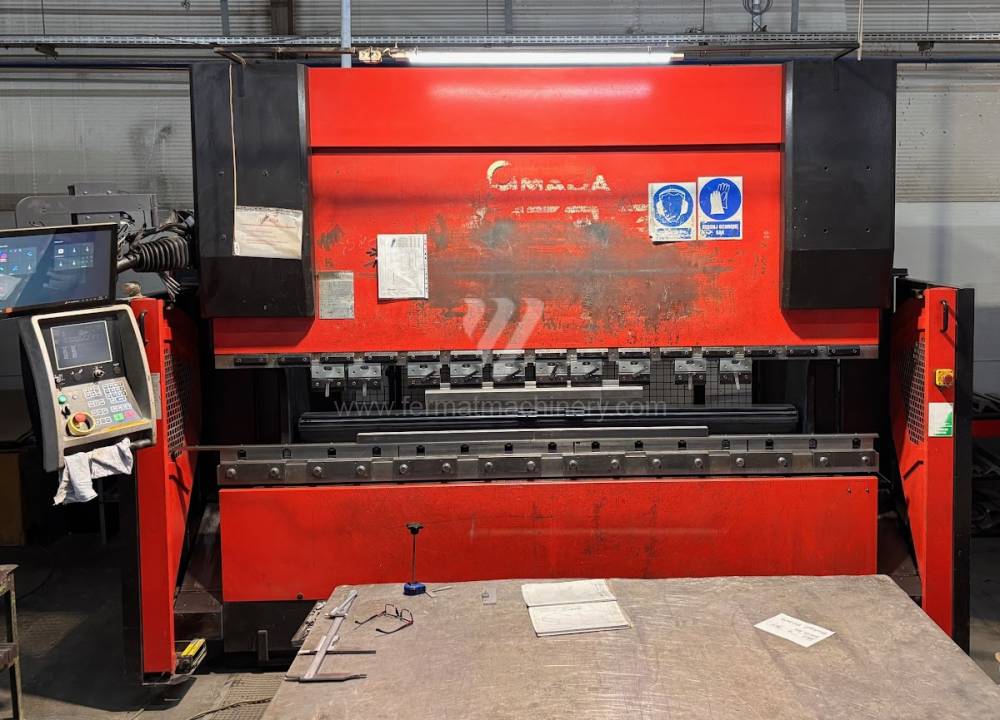
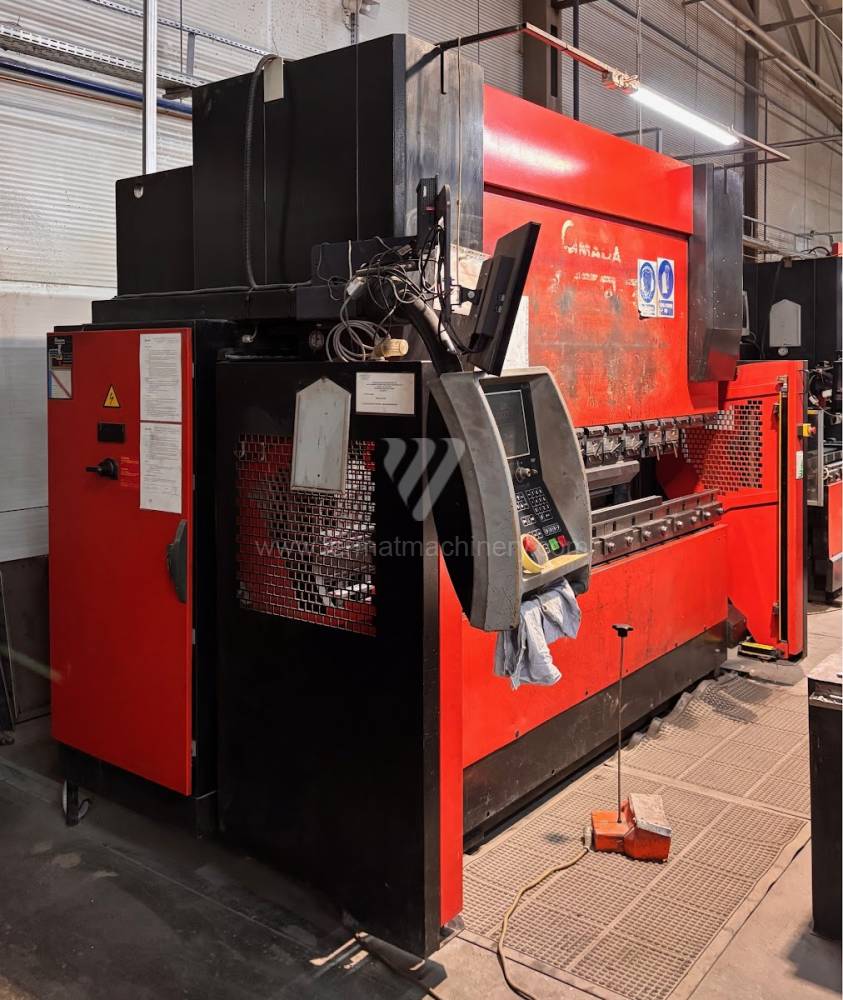



Gyártás éve:2000
Hajlítási erő: 130 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3110 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 7
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: nem
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A gép súlya: 8170 kg
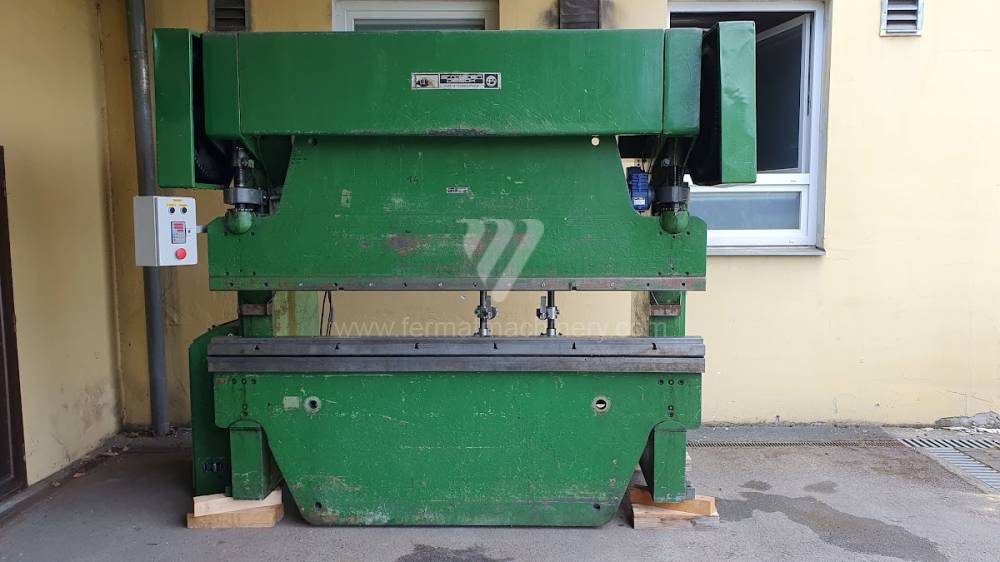
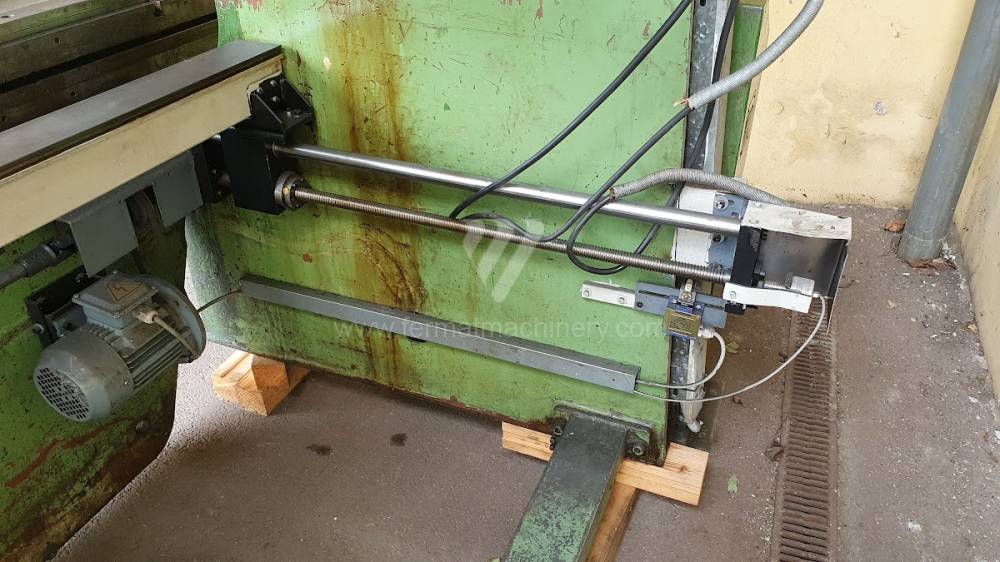
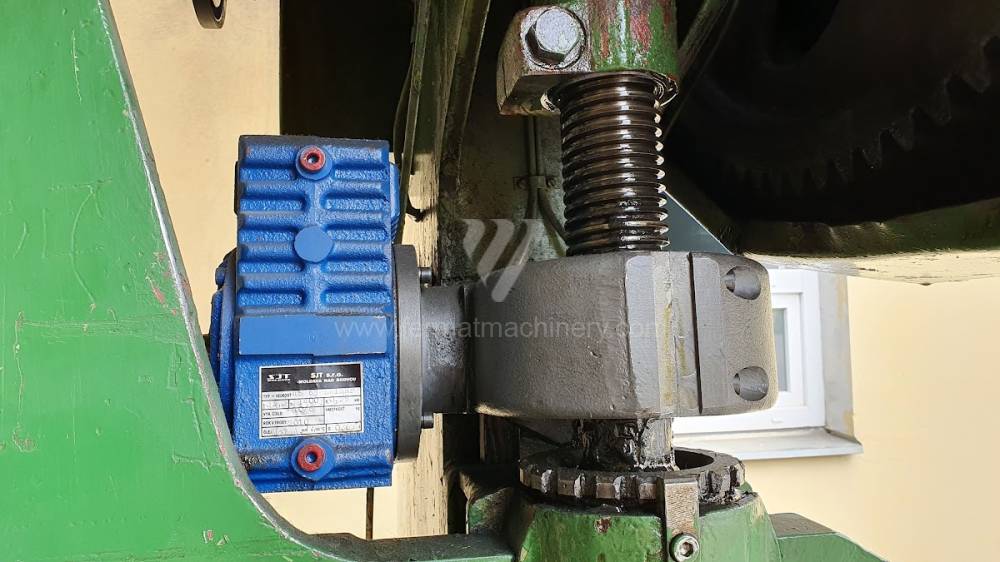
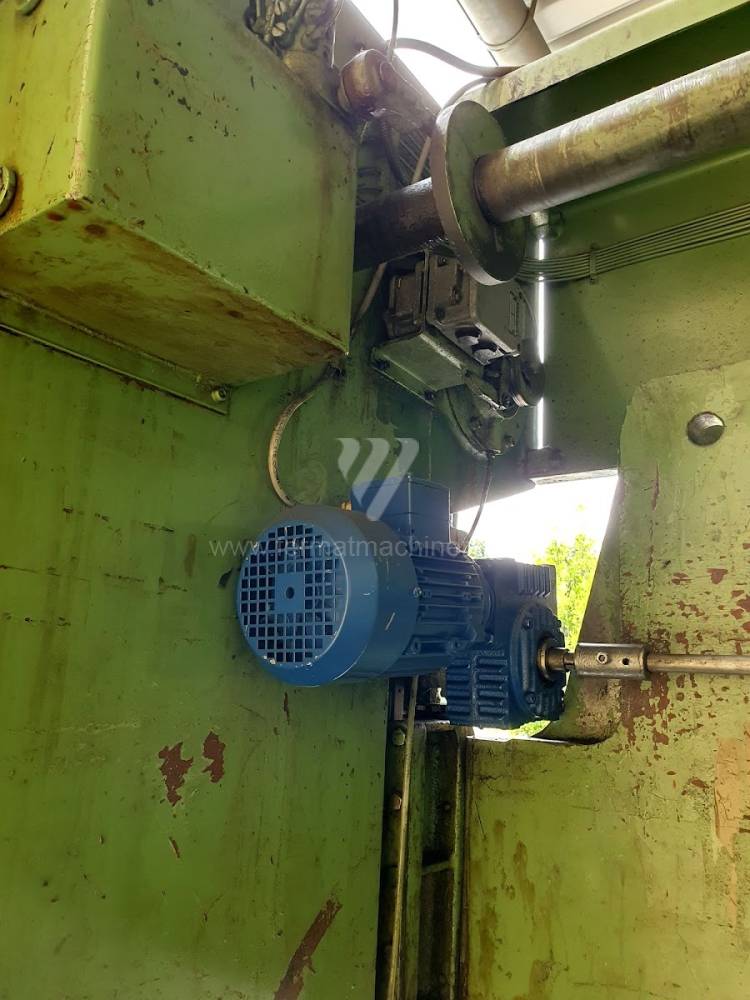
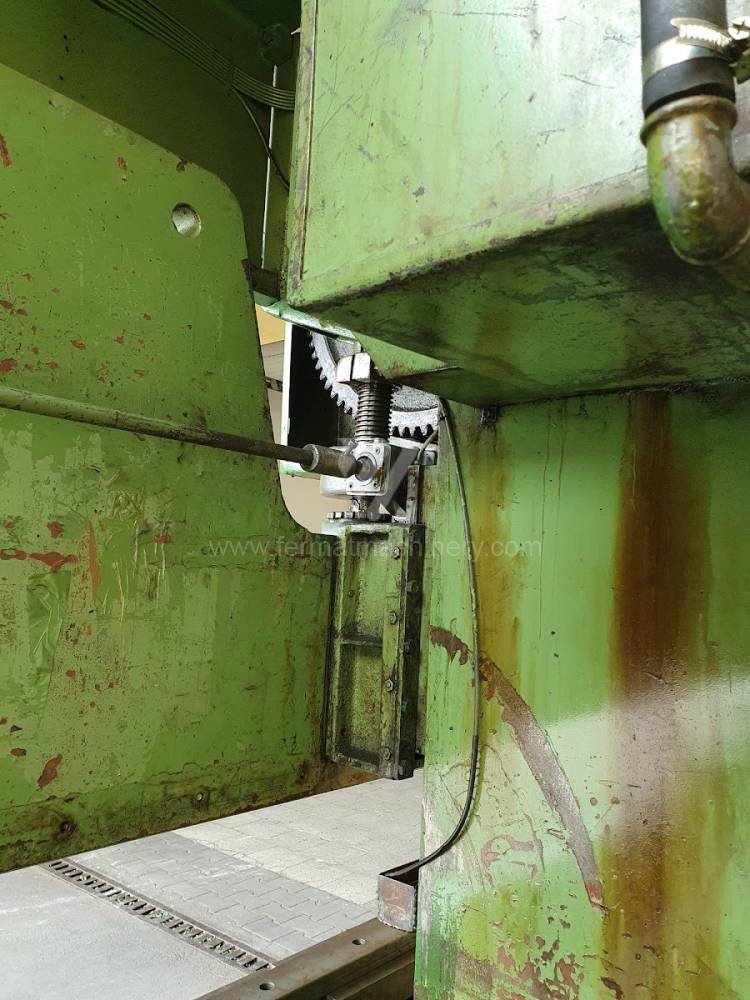
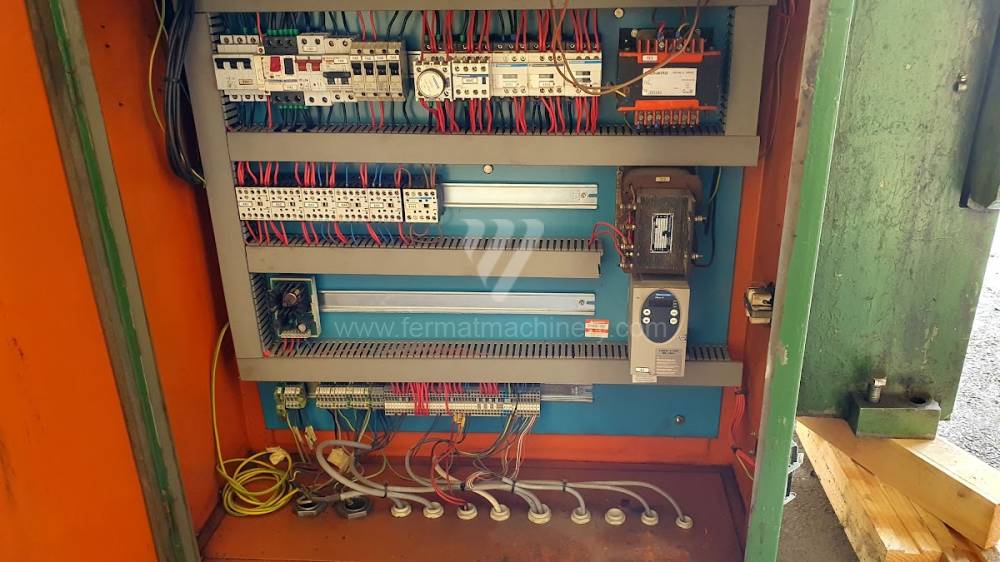
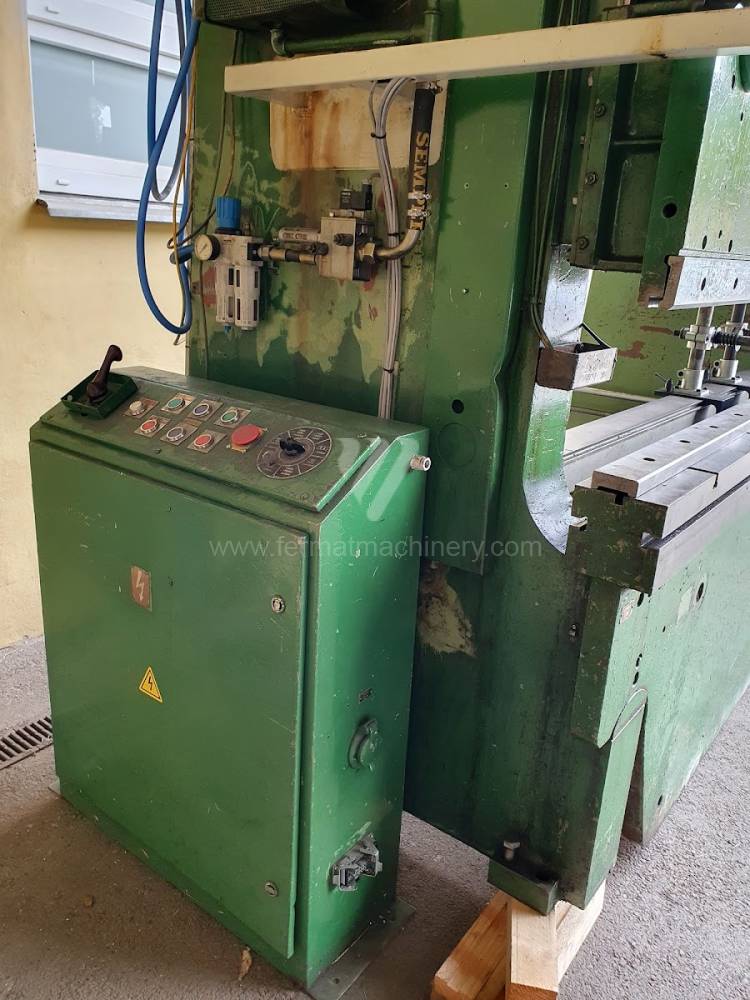











Gyártás éve:1969
Hajlítási erő: 50 t
Hajlítási hossz: 2500 mm
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: electro-mechanical
A főmotor teljesítménye: 5,5 kW
A medve lökete: 65 mm
A medve állíthatósága: 125 mm
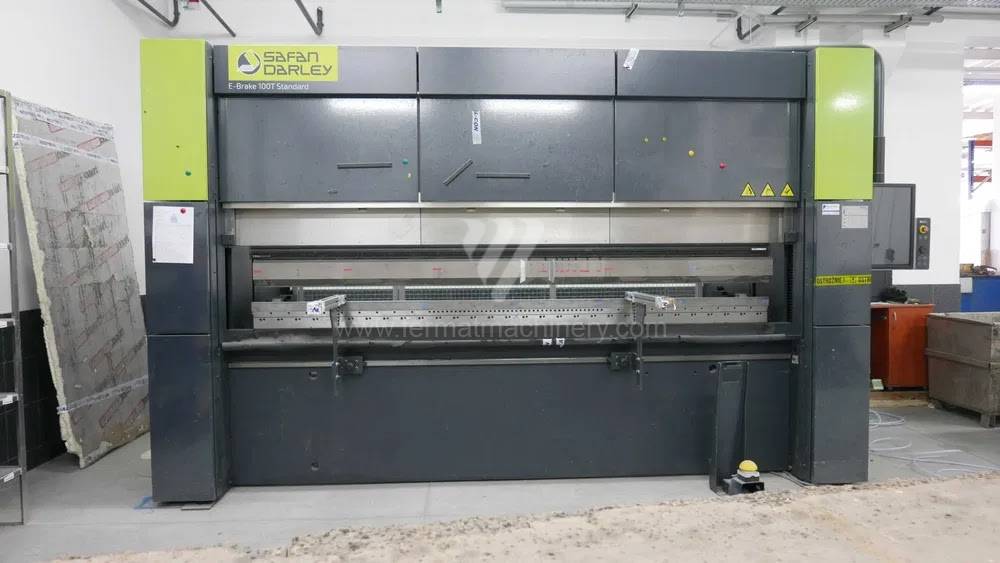
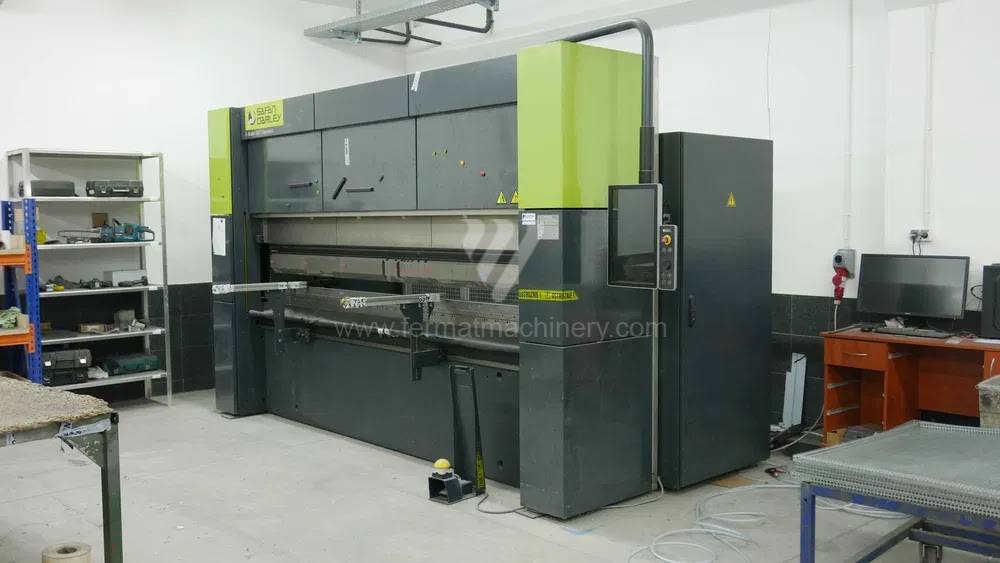
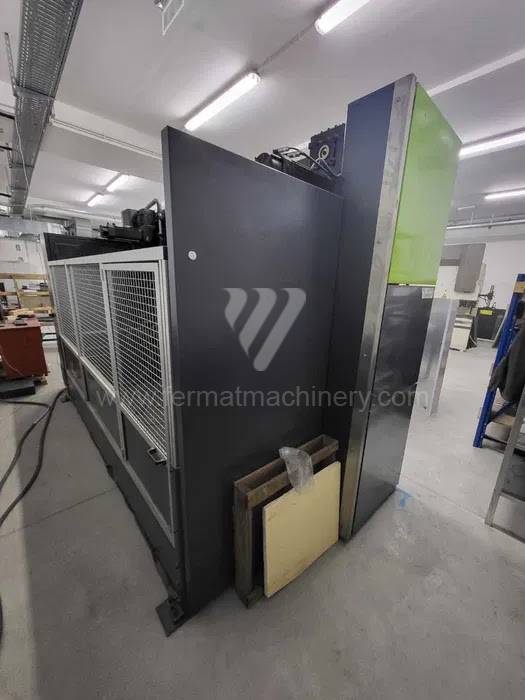
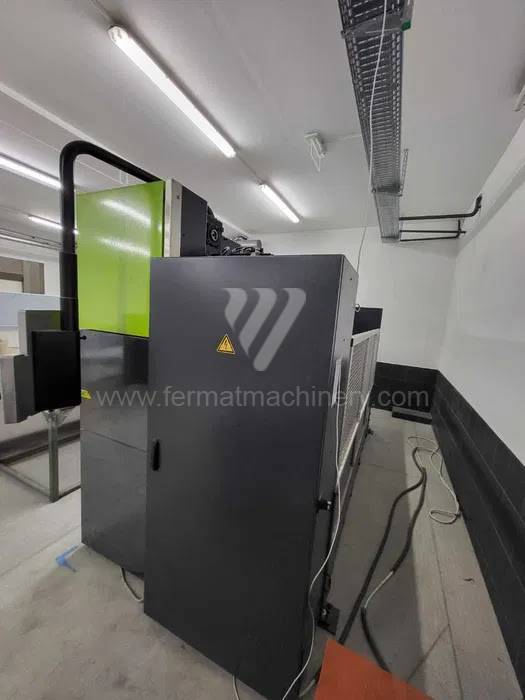







Gyártás éve:2021
Hajlítási erő: 100 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma:
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung:
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa:
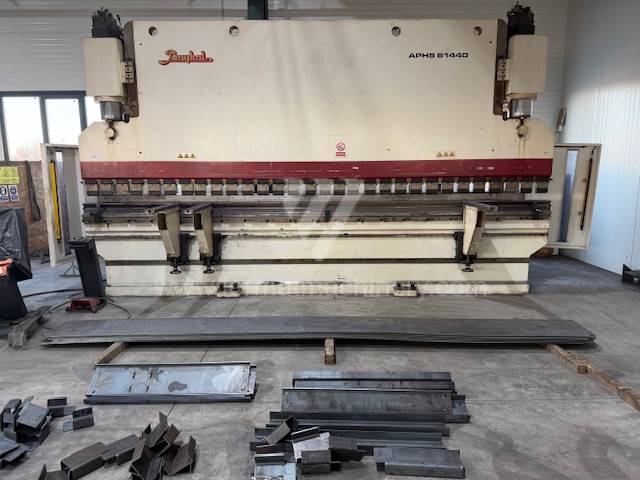


Gyártás éve:2015
Delem vezérlőrendszer:
Hajlítási erő: 440 t
Hajlítási hossz: 6100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa:
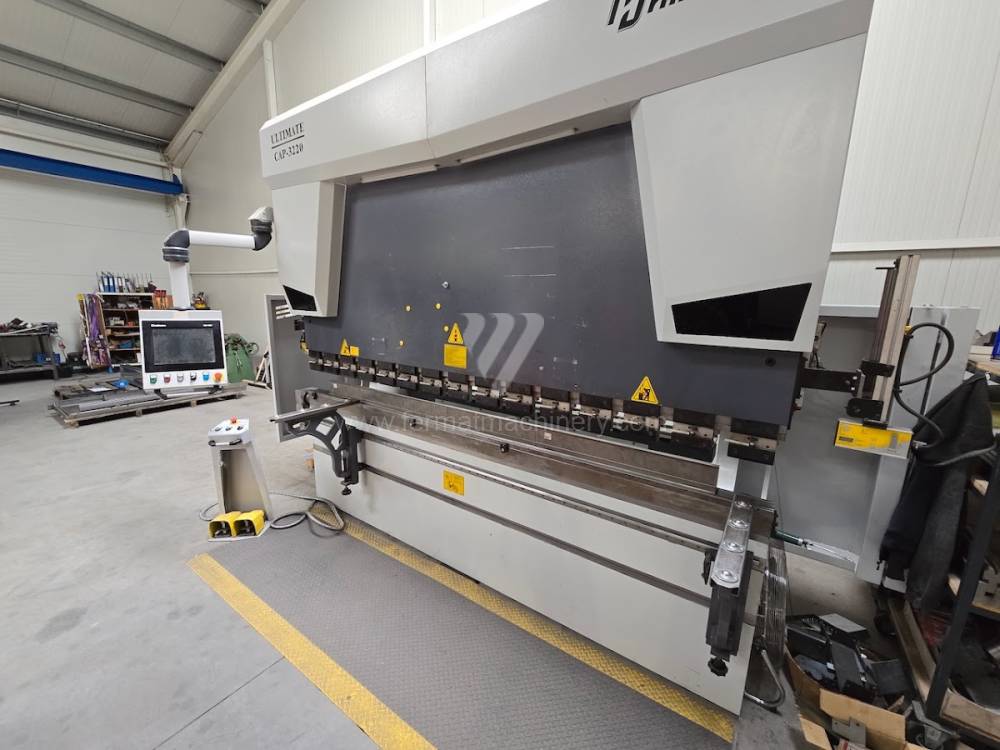
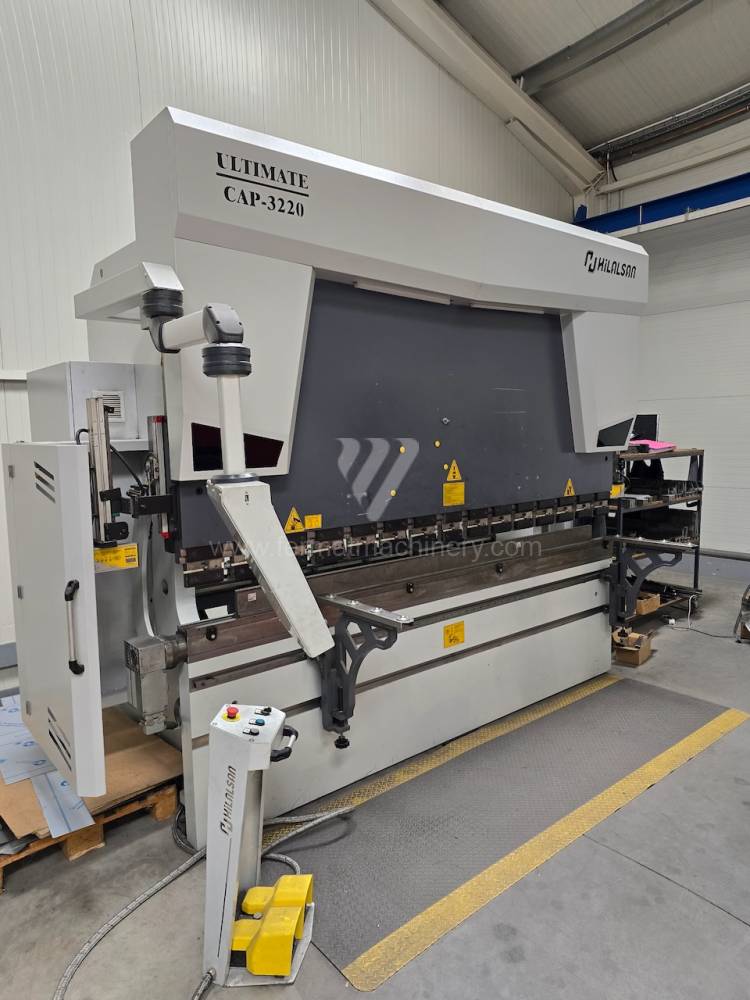


Gyártás éve:2021
Delem vezérlőrendszer: DA - 58T
Hajlítási erő: 220 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
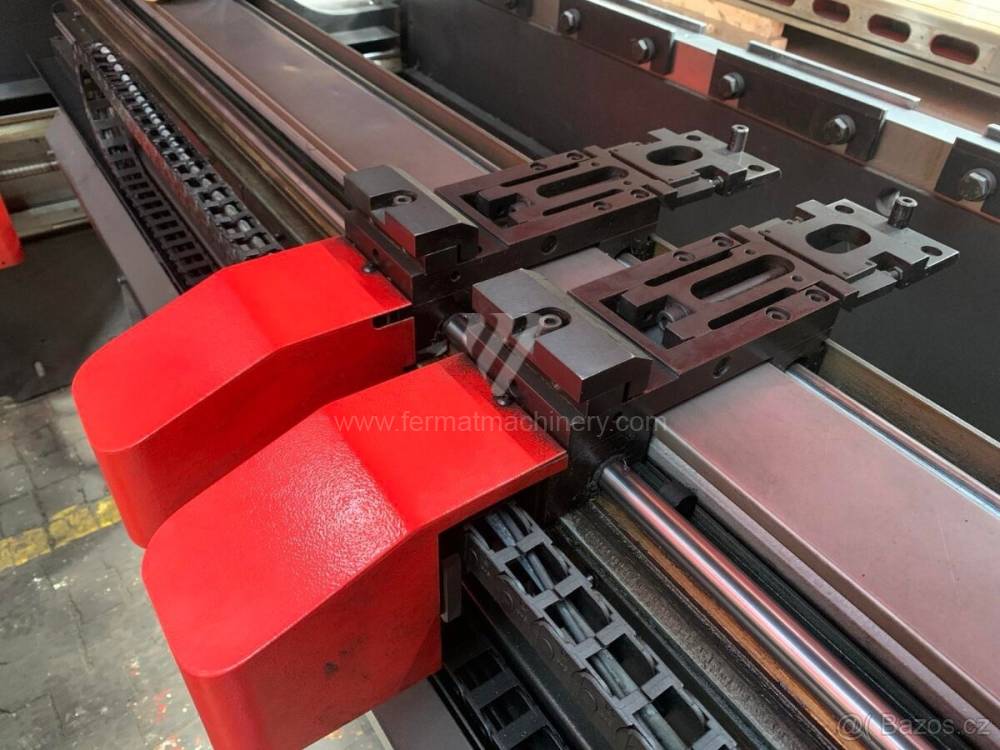





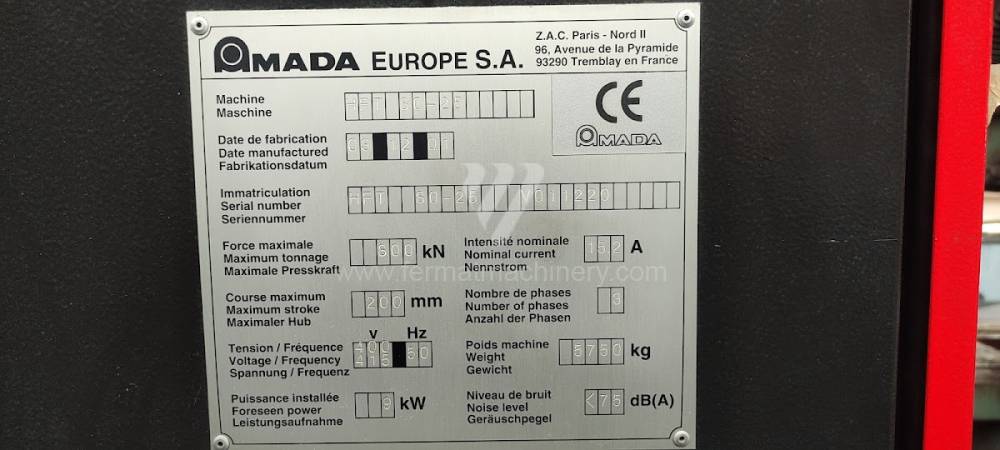
Gyártás éve:2006
Amada vezérlőrendszer: Operateur 2000
Hajlítási erő: 100 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3000 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 8
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: nem
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
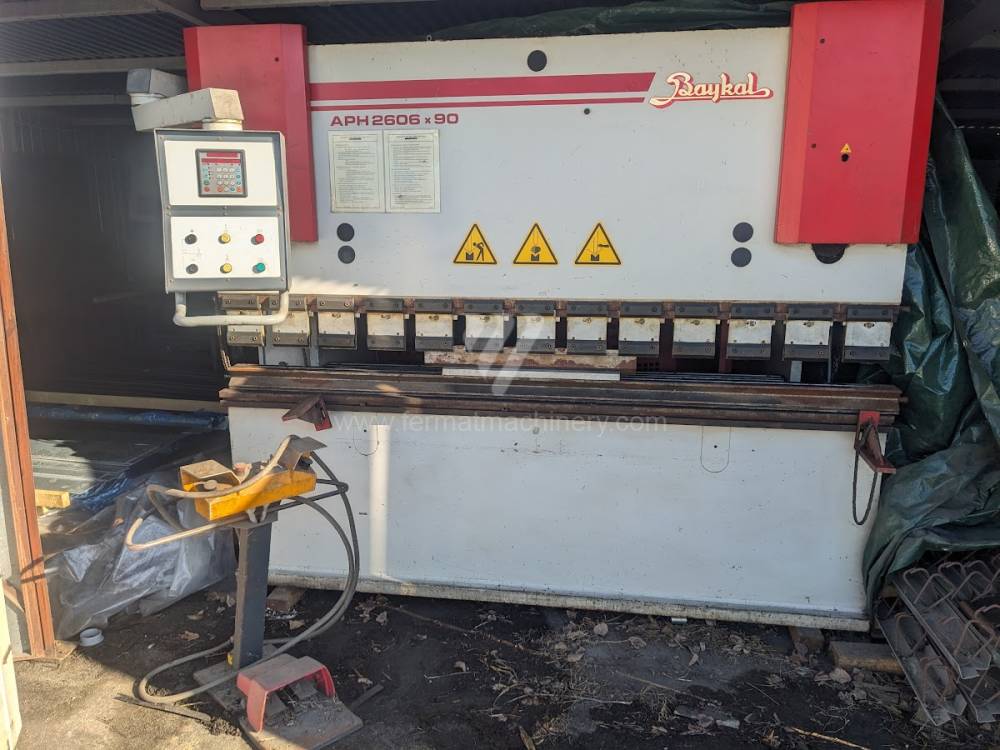






Gyártás éve:2004
Hajlítási erő: 90 t
Hajlítási hossz: 2600 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 2
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: nem
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A főmotor teljesítménye: 11 kW
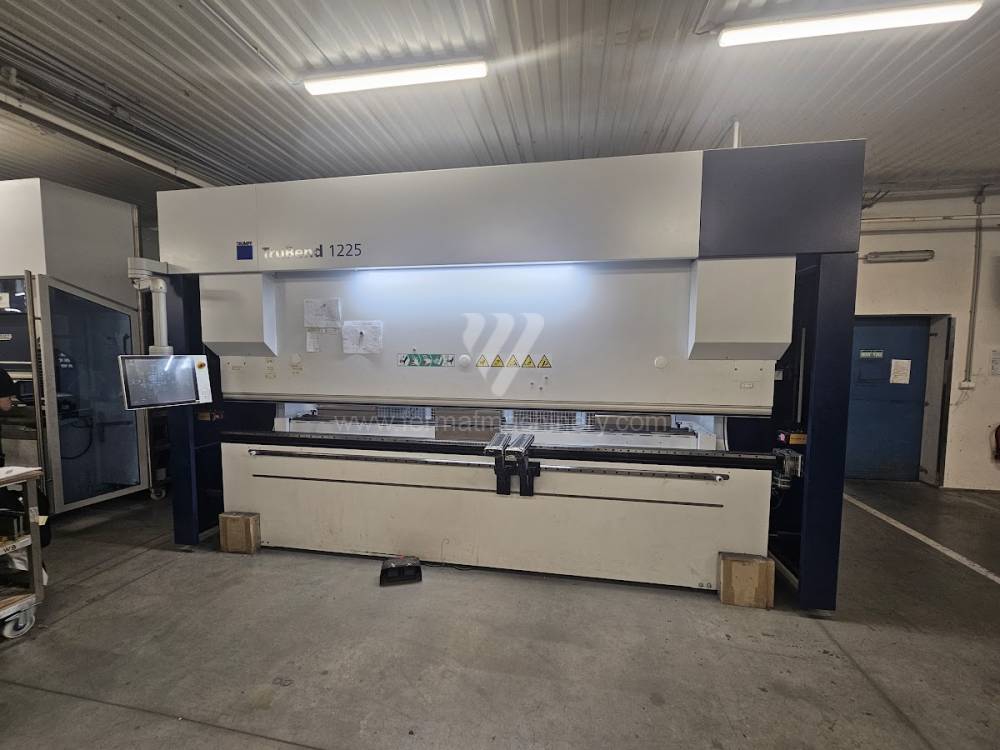


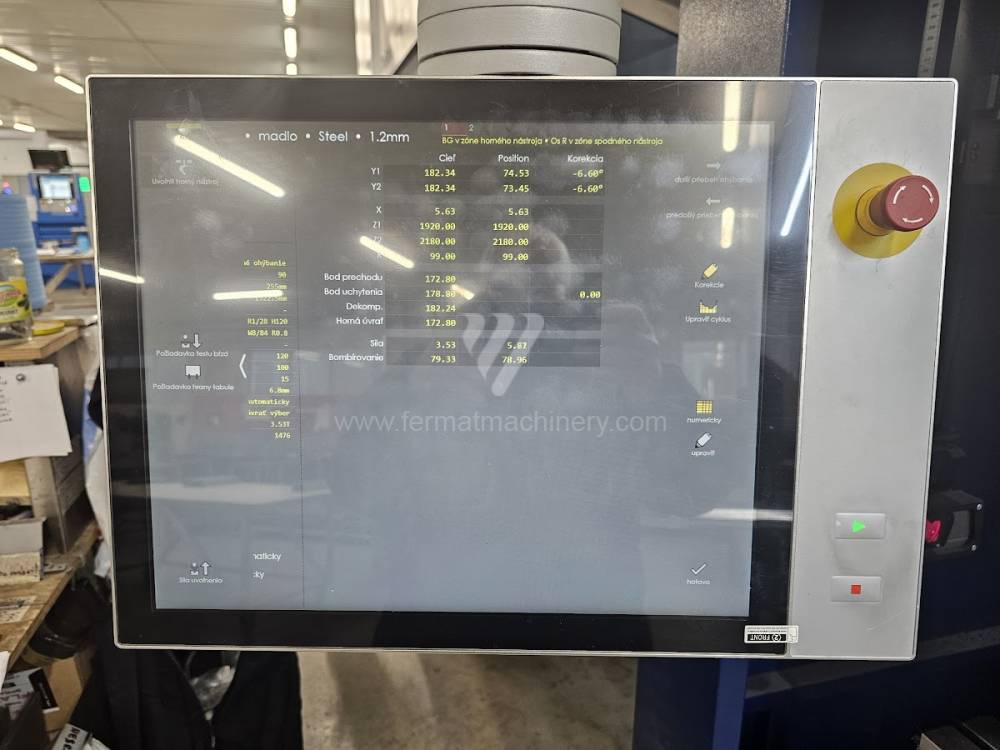




Gyártás éve:2023
Hajlítási erő: 225 t
Hajlítási hossz: 4000 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 6
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A medve lökete: 205 mm
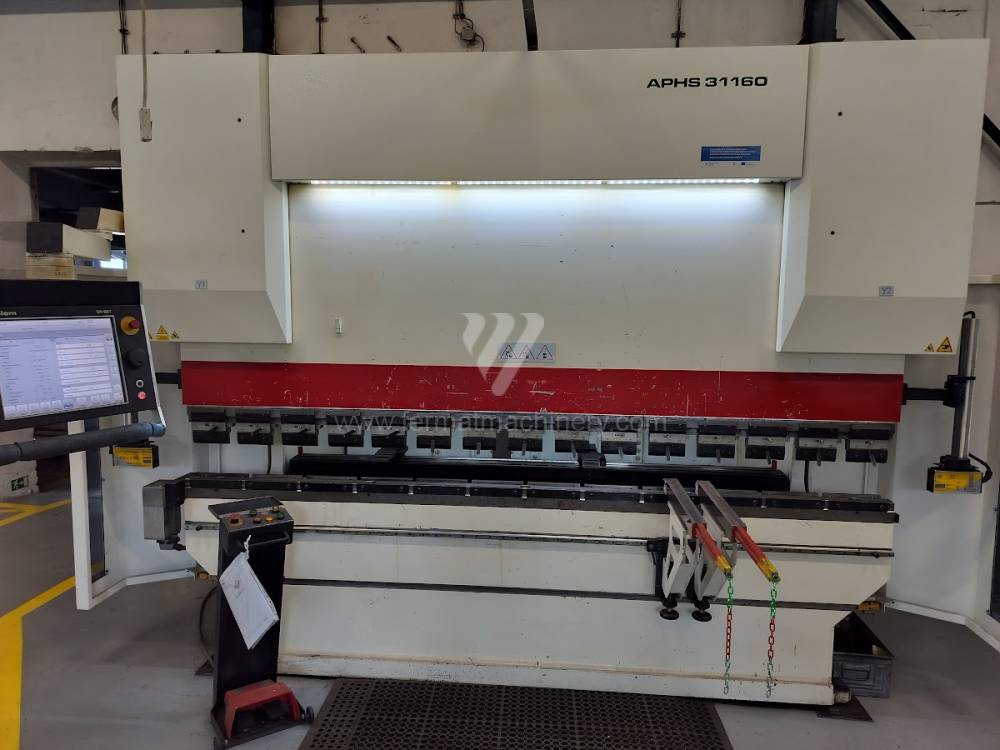
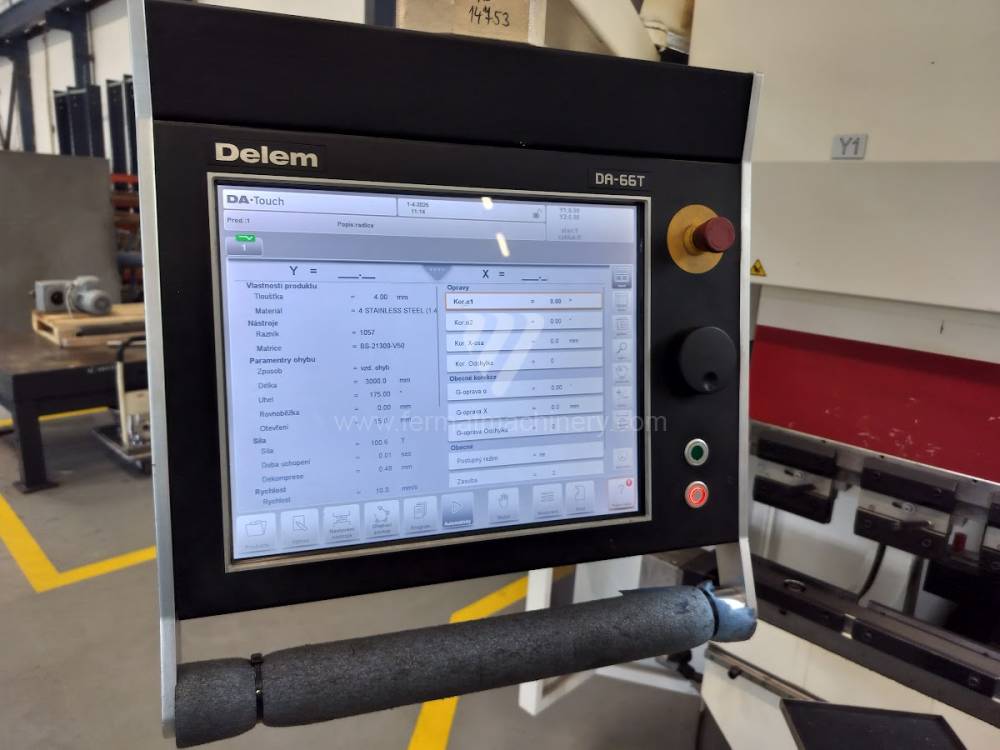
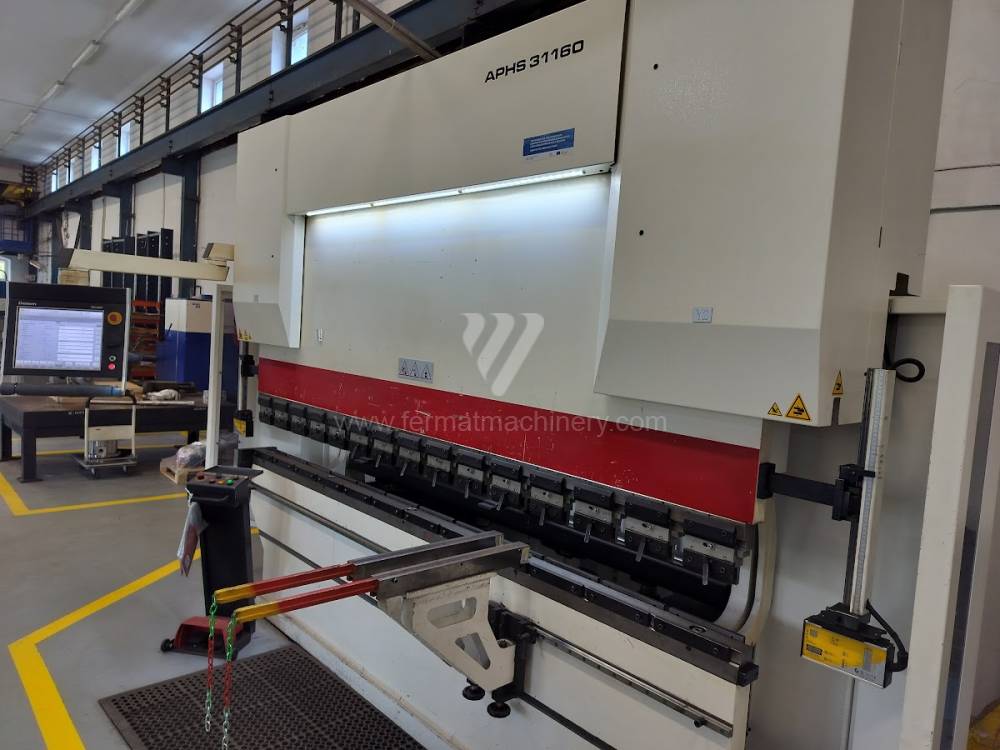
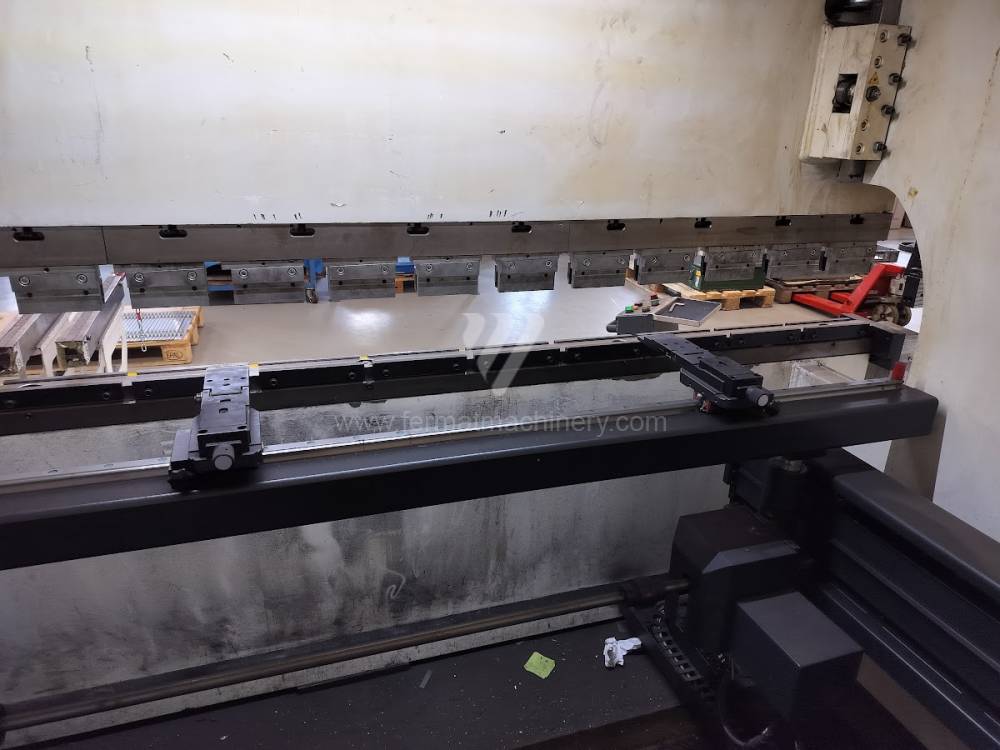
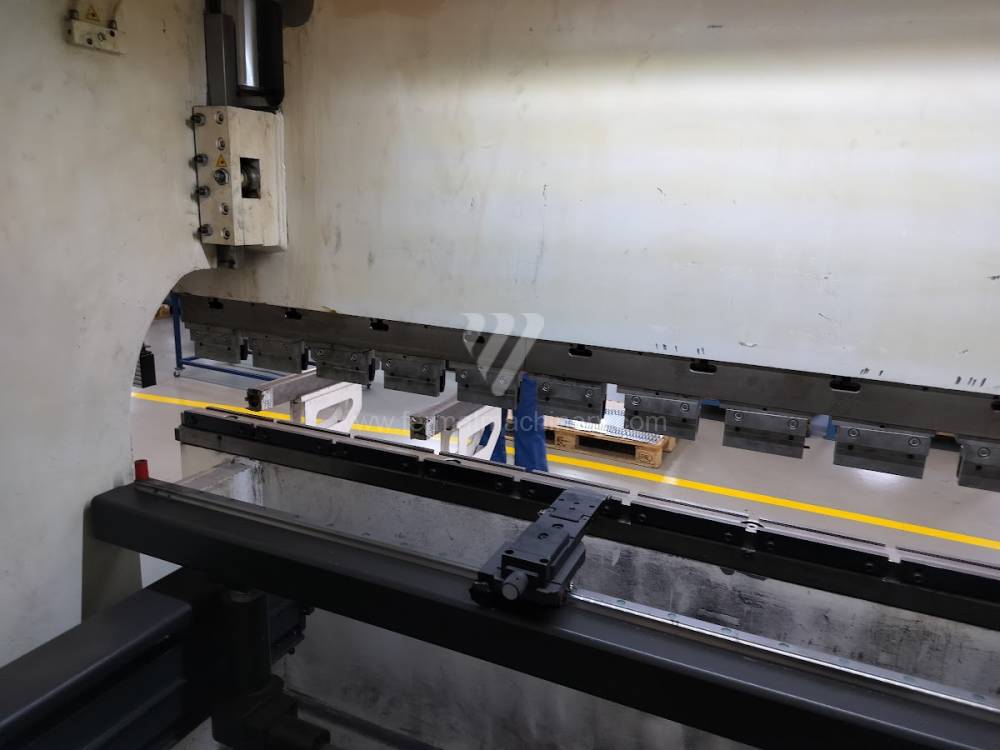






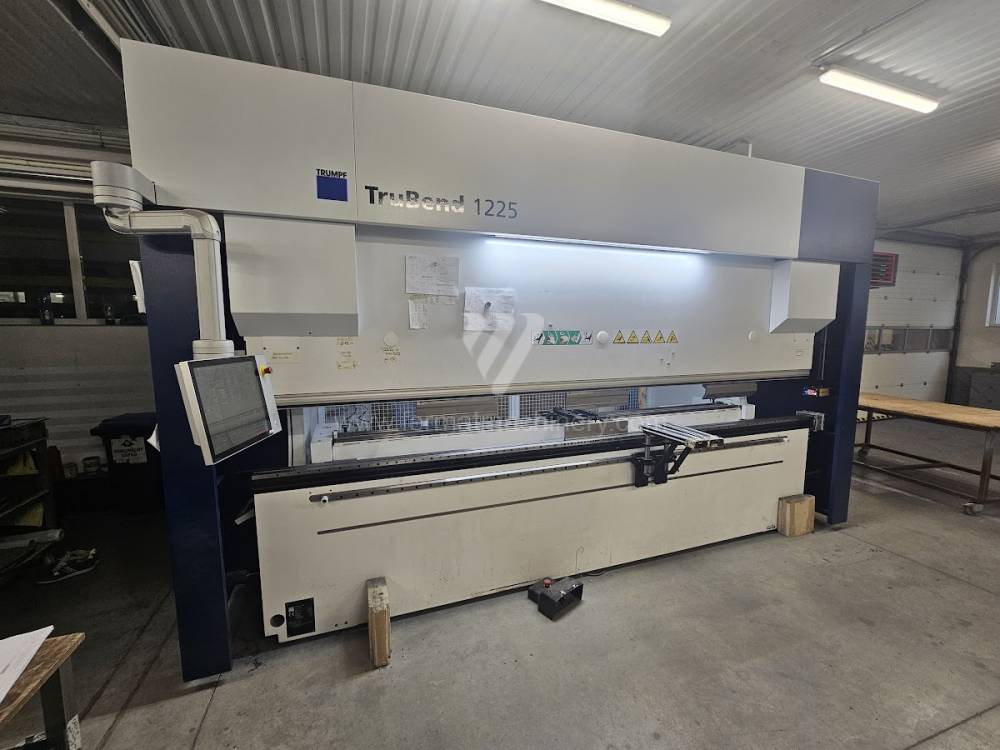
Gyártás éve:2014
Delem vezérlőrendszer: DA - 66 T
Hajlítási erő: 160 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3100 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: nem
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
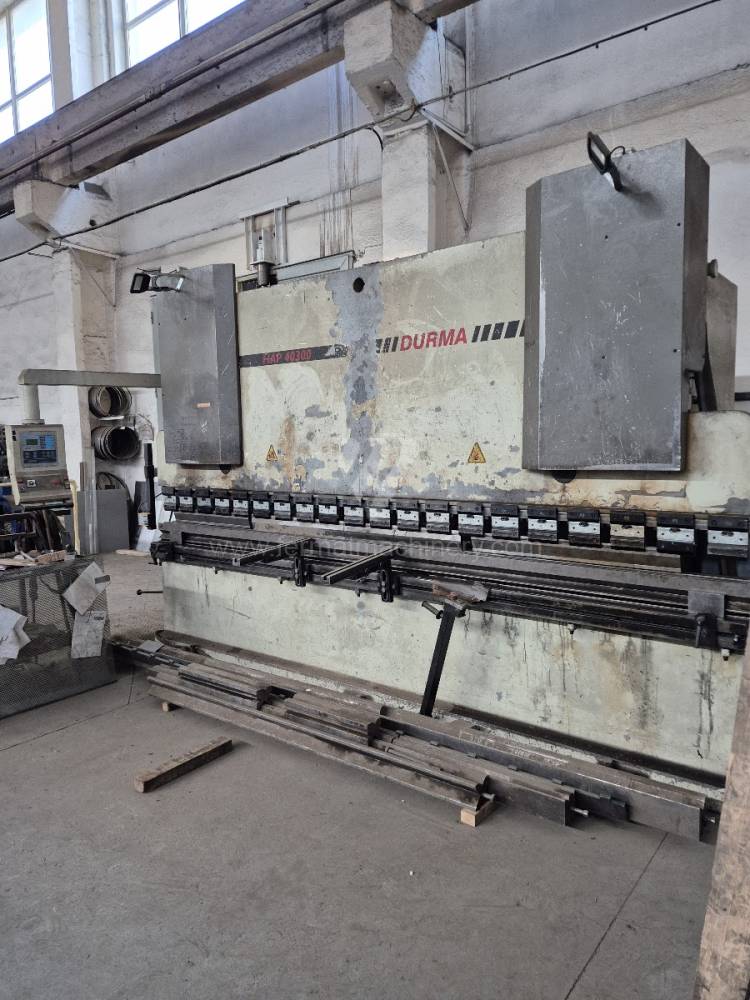

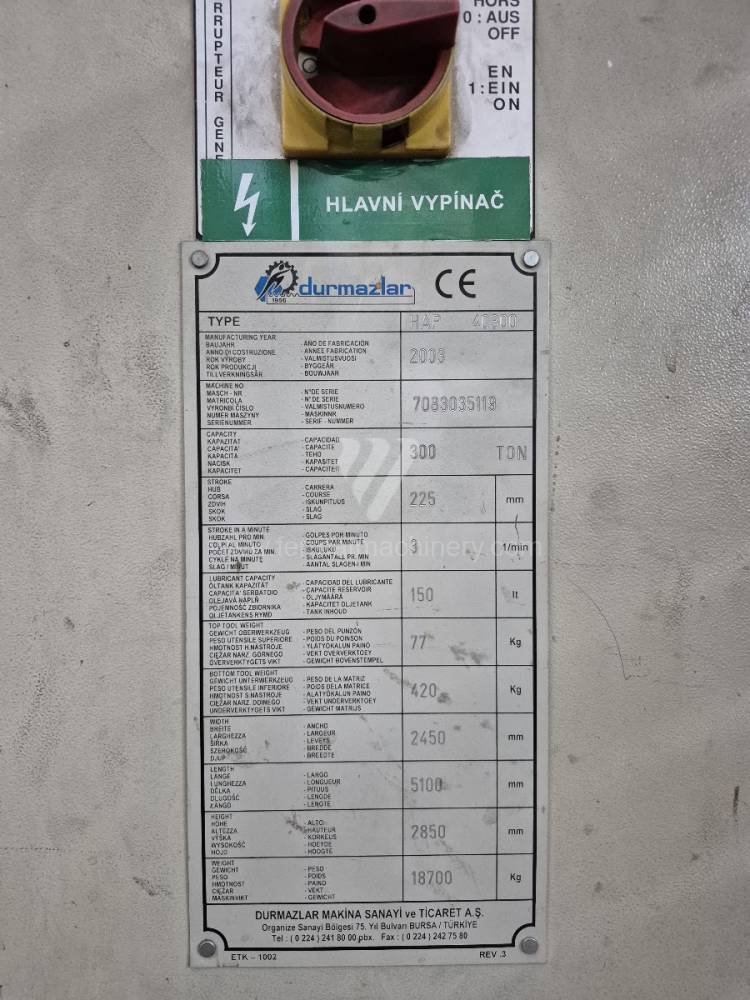

Gyártás éve:2003
Cybelec vezérlőrendszer: DNC 80
Hajlítási erő: 300 t
Hajlítási hossz: 4050 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 4
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
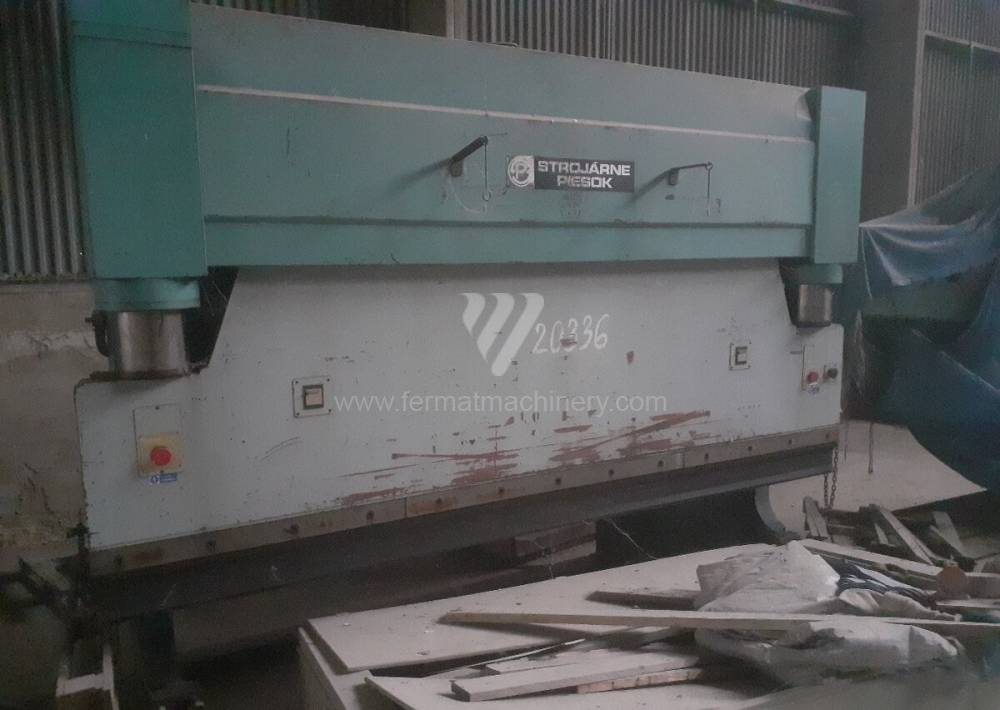

Gyártás éve:1991
Hajlítási erő: 160 t
Hajlítási hossz: 3150 mm
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A gép súlya: 11500 kg
Méretek hossz.×szél.×mag.: 3350x1600x2630 mm
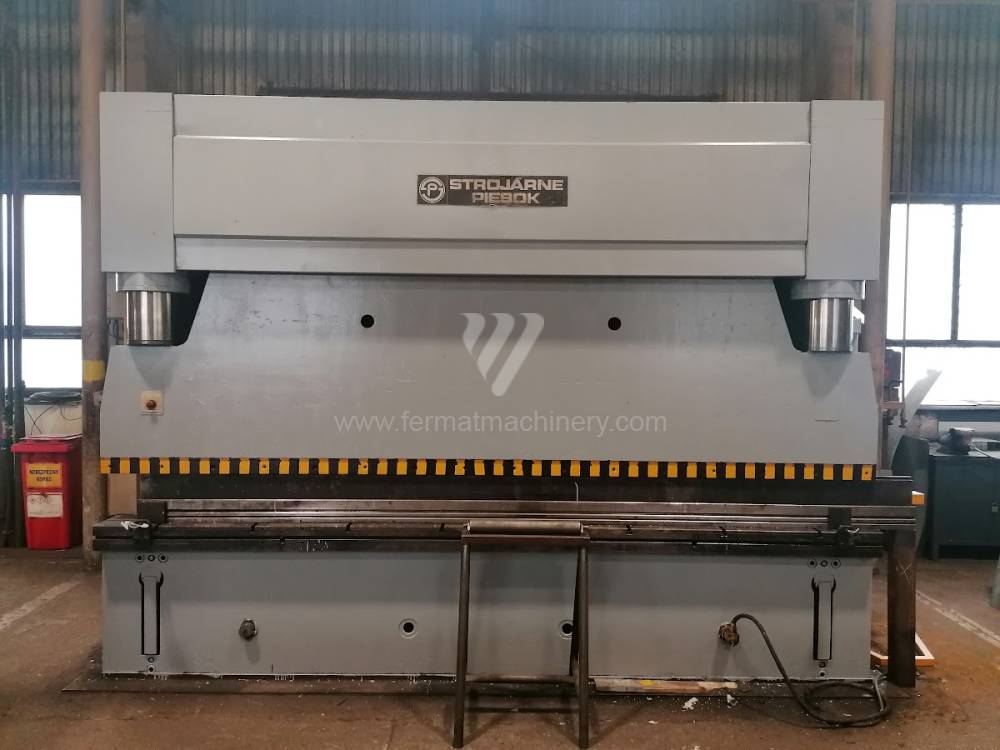





Gyártás éve:1990
Hajlítási erő: 250 t
Hajlítási hossz: 4000 mm
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A medve lökete: 300 mm
Oszlopok közötti távolság: 3430 mm
A gép súlya: 18650 kg





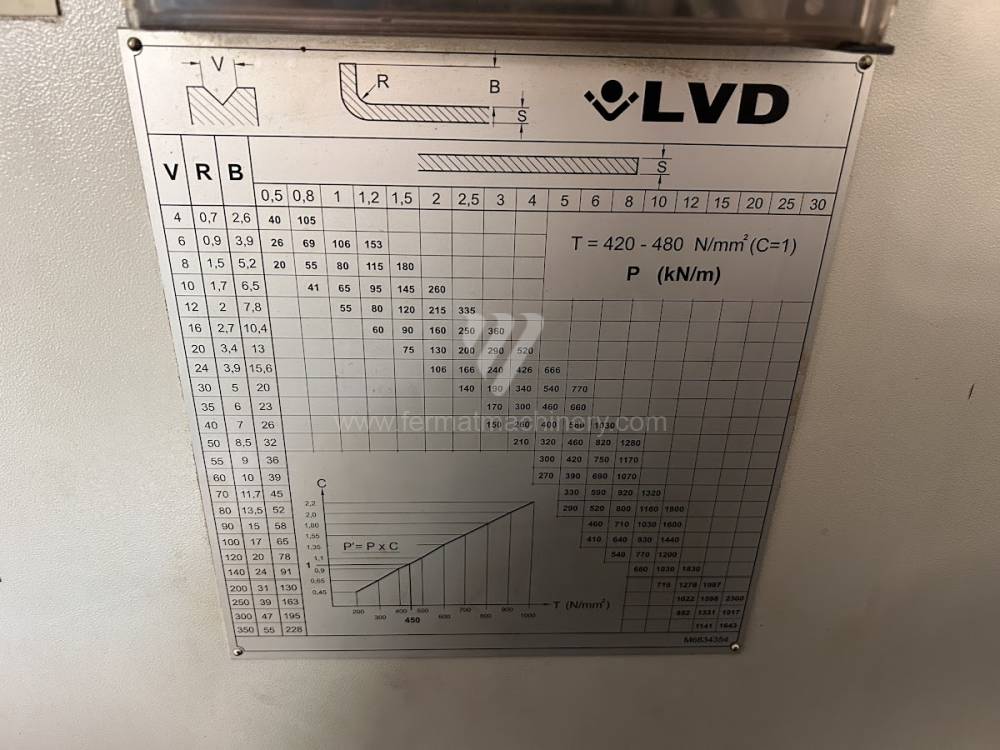

Gyártás éve:2008
Hajlítási erő: 80 t
Hajlítási hossz: 2000 mm
Vezérelt tengelyek száma: 6
Asztal-előfeszítés - bombírung: igen
Az élhajlító meghajtásának típusa: Hydraulický
A főmotor teljesítménye: 12,5 kW
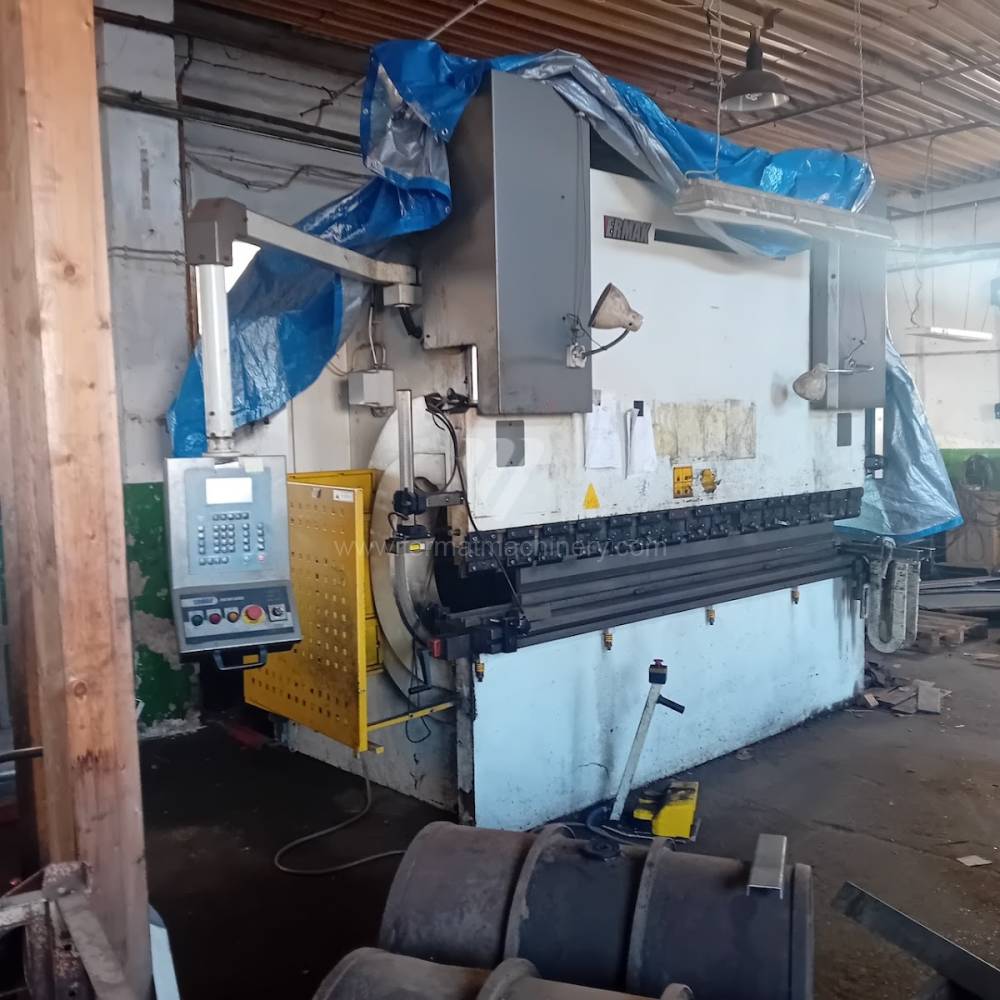
Forming machines used for processing (bending) of sheet metal. These machines are currently replaced by bending machines, because they are hydraulically driven and can work with greater pressures and lengths of bent parts.
During this kind of material processing , there is no waste and semi-finished products are used. It is also possible to bend very small workpieces of very small radius.
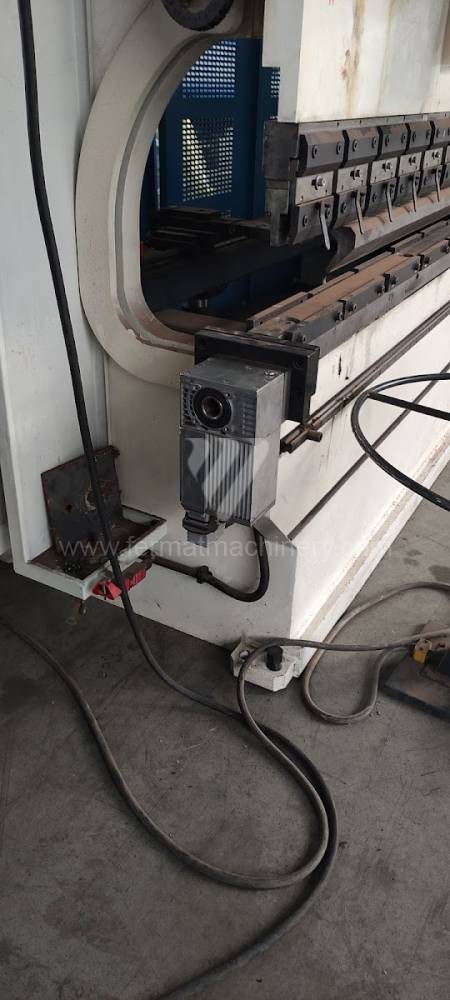
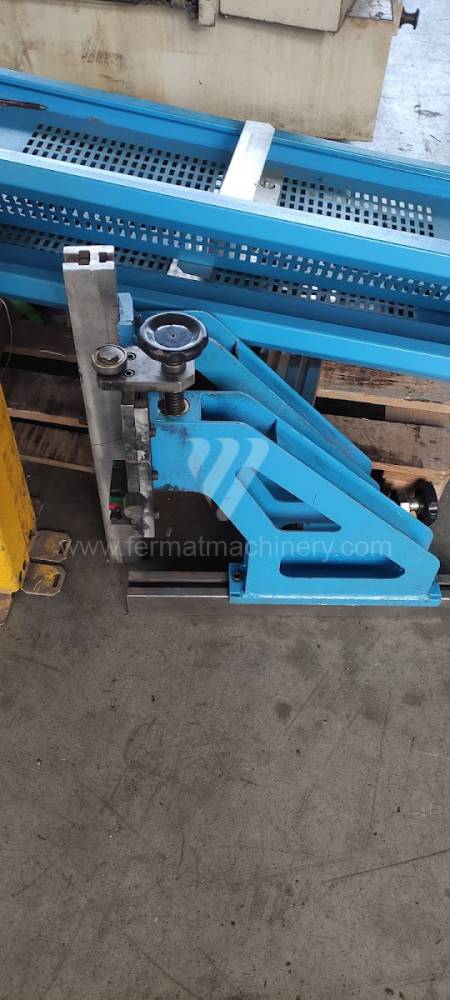
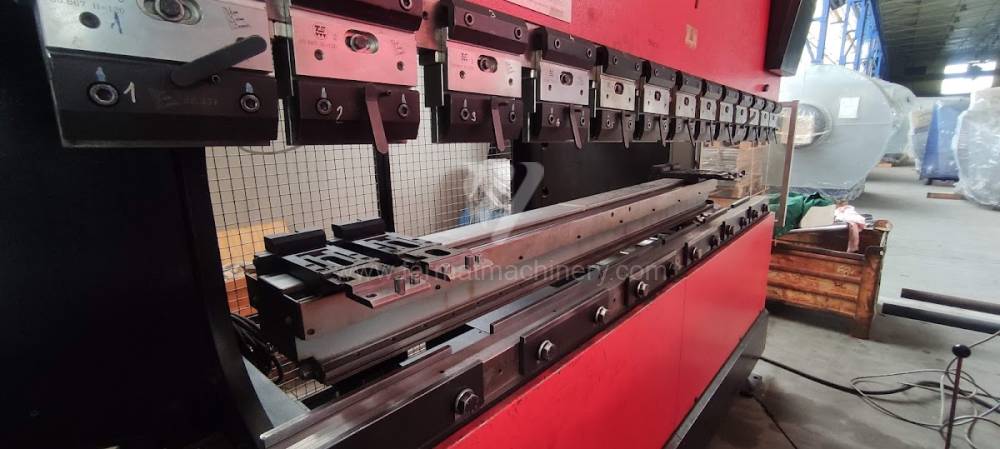
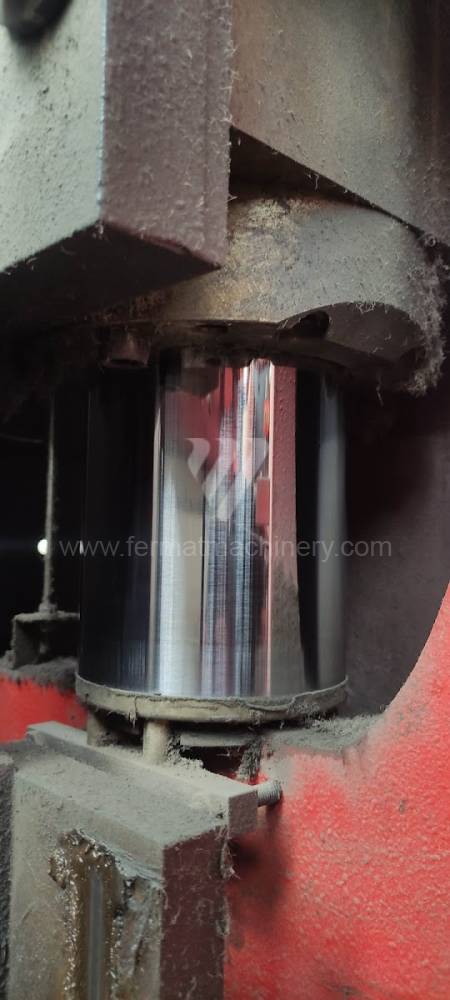
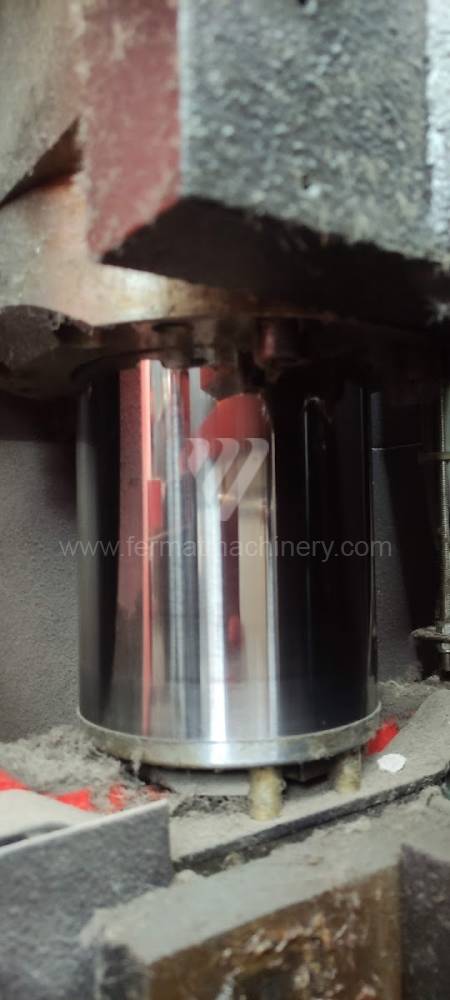
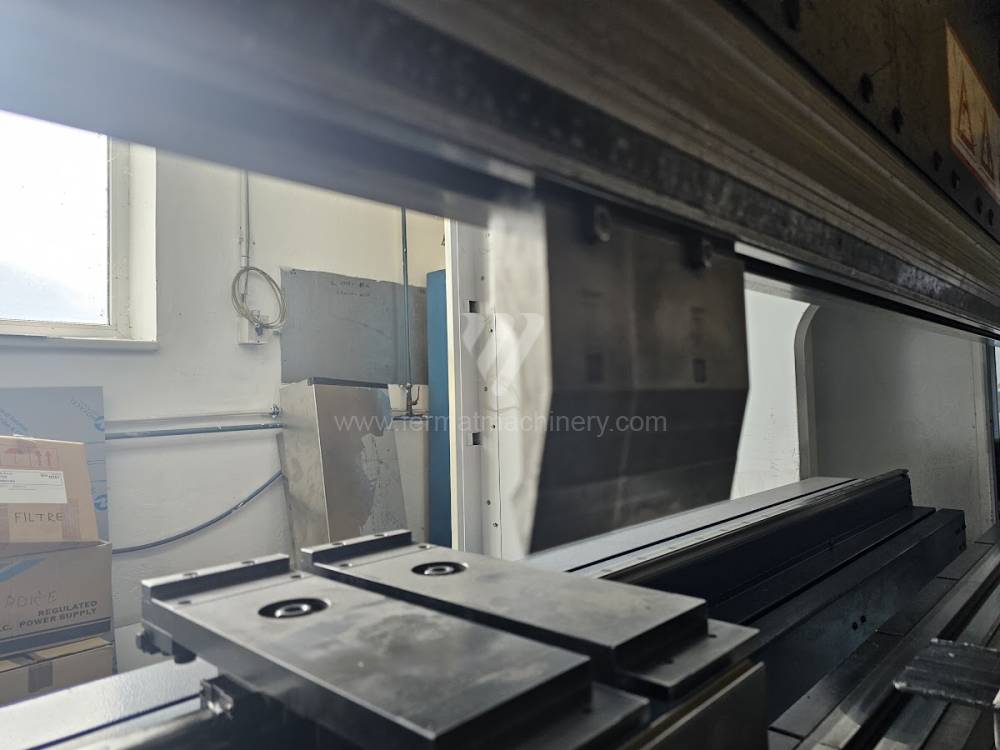
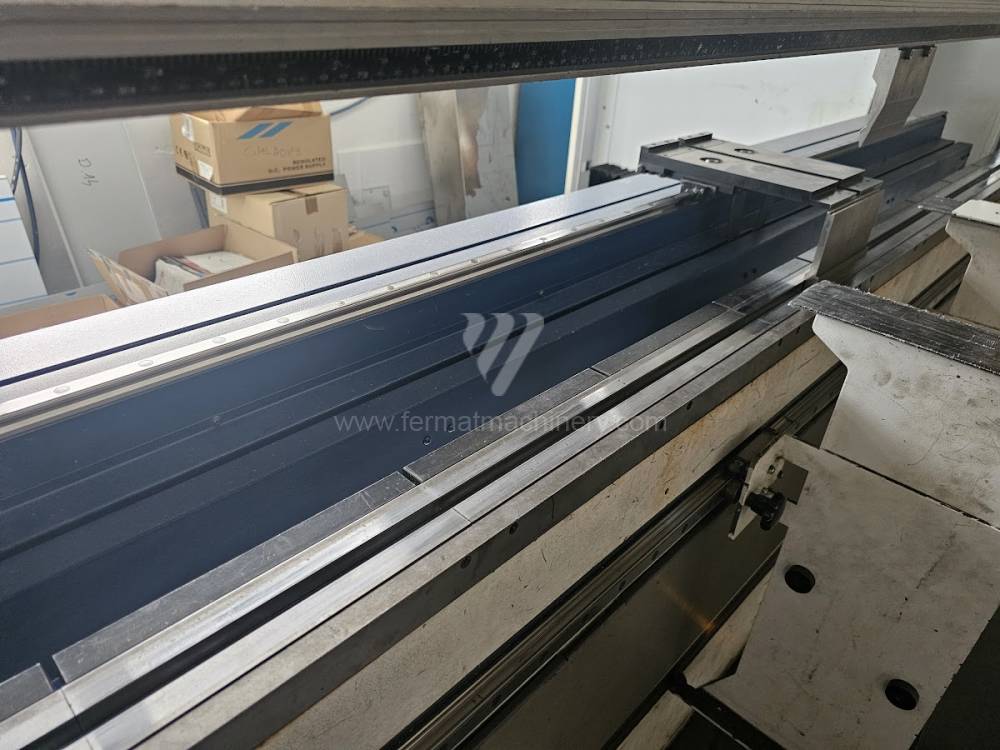
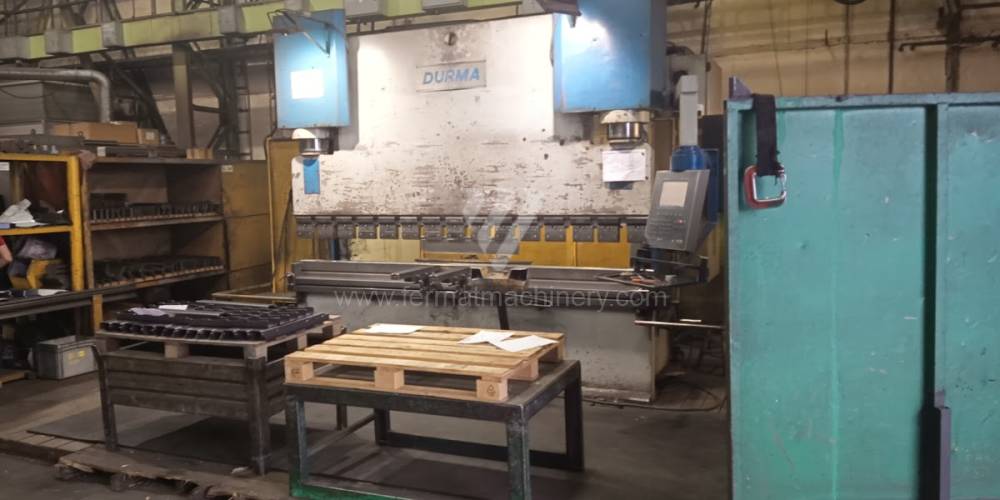
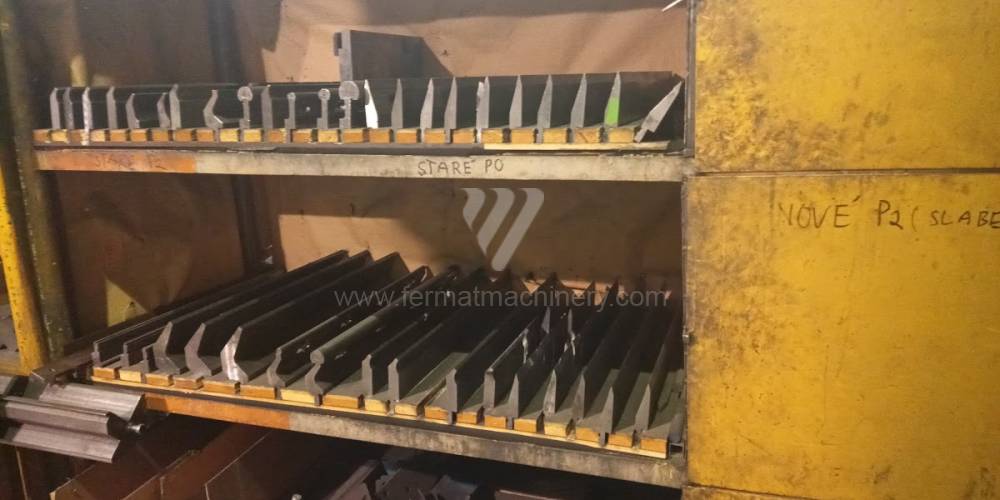
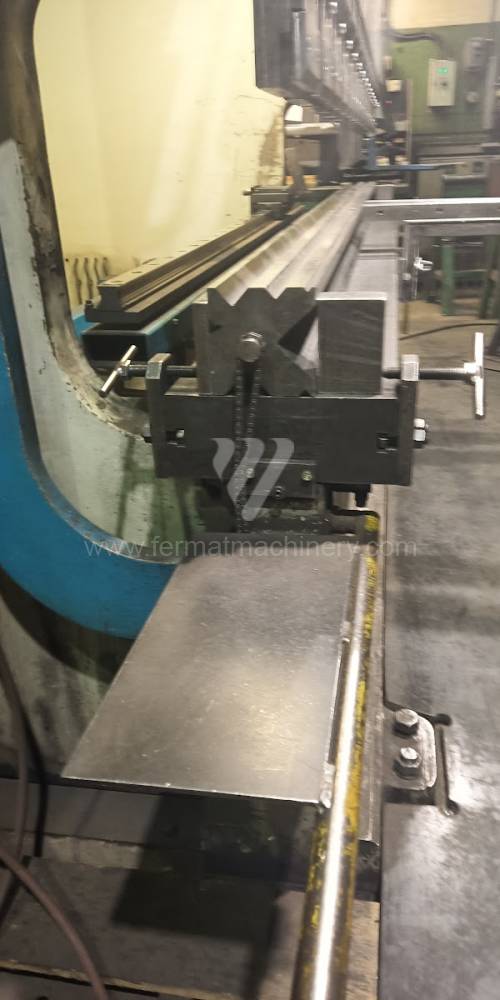
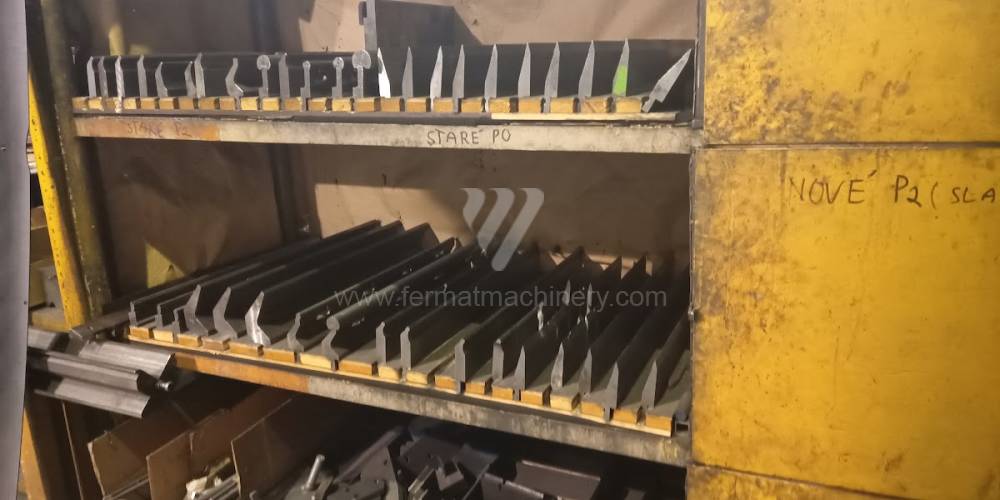
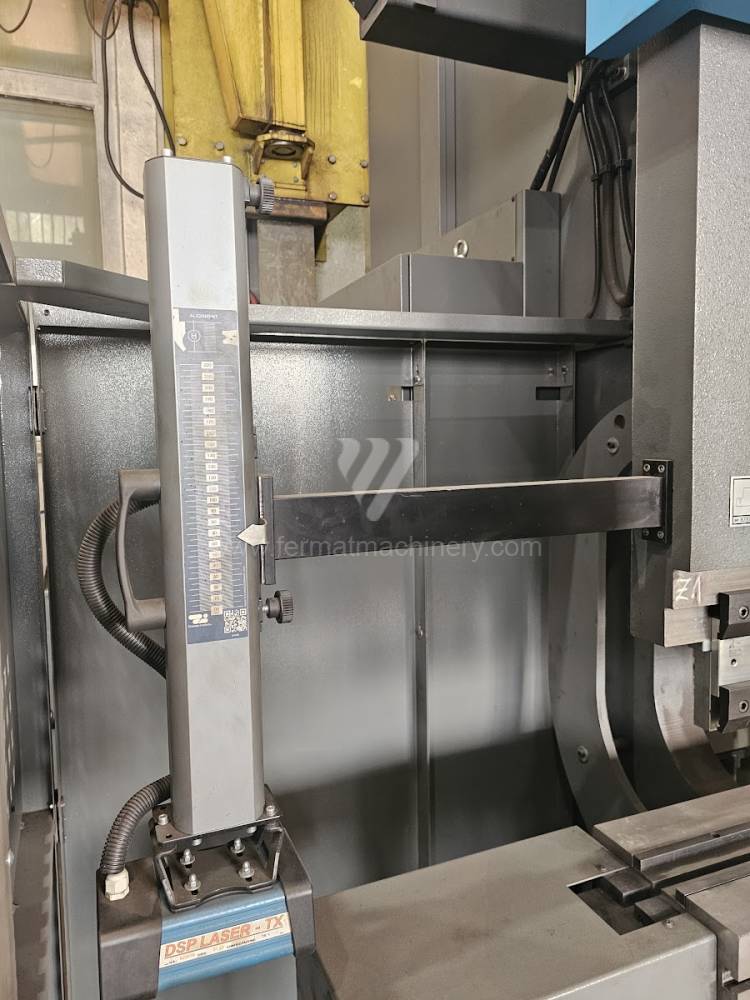
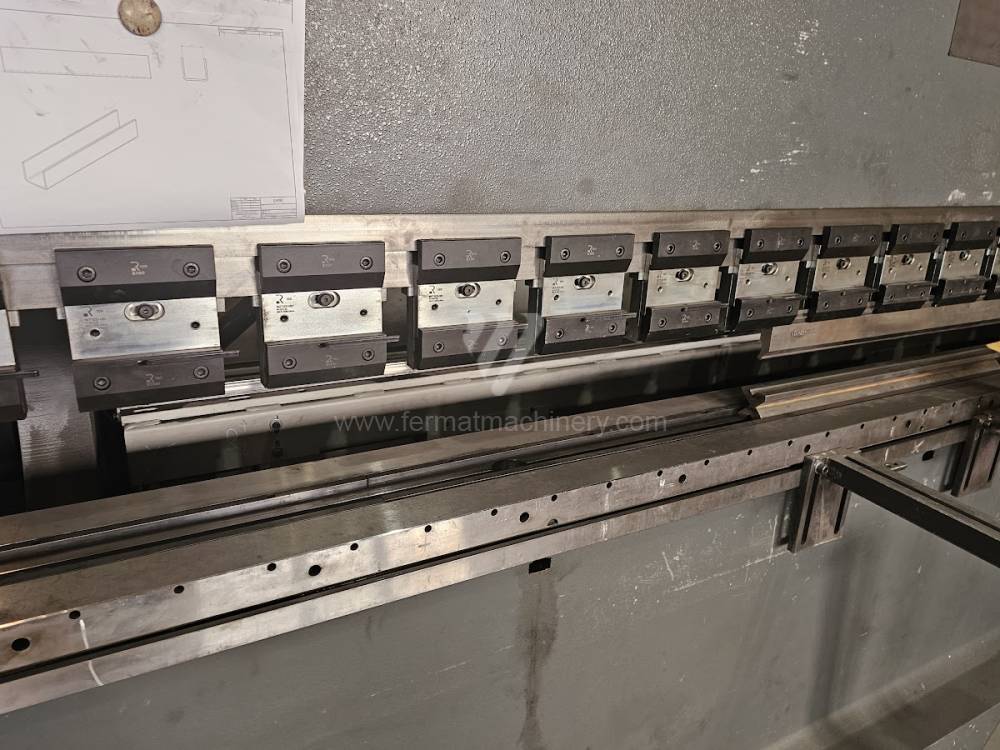
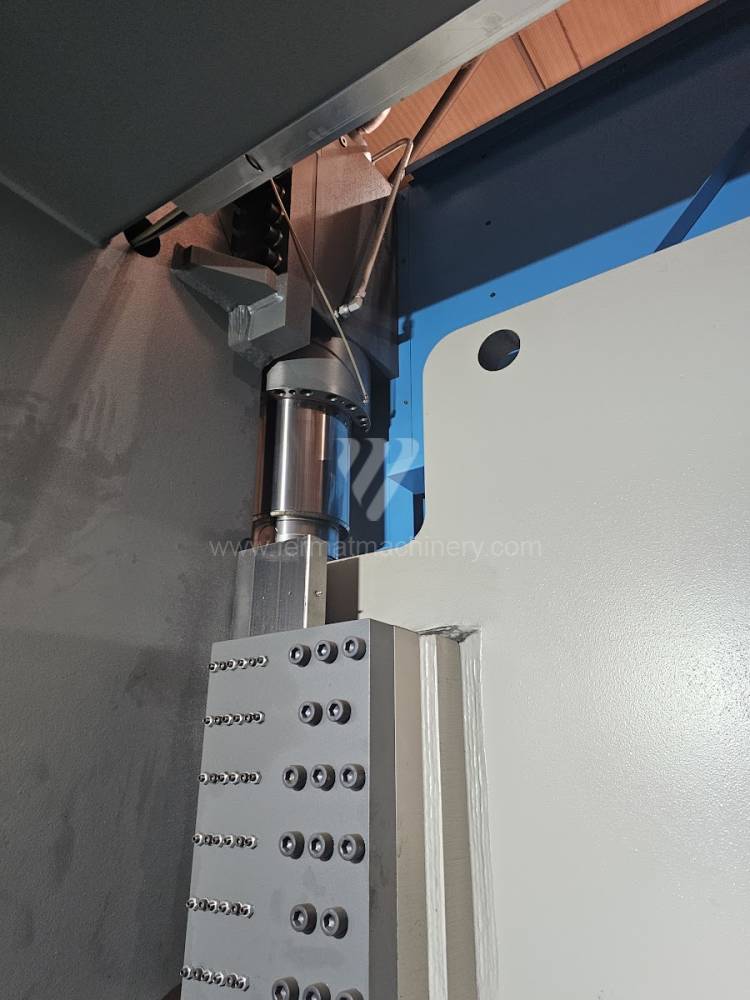
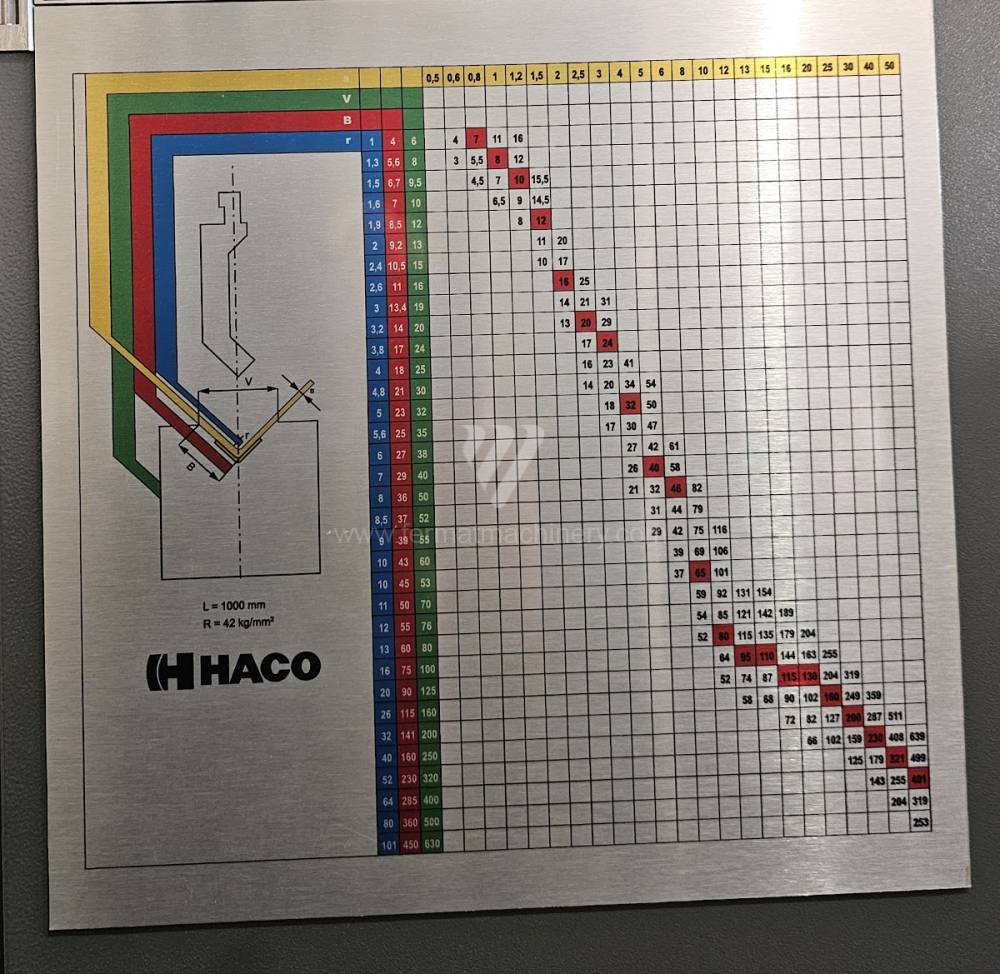
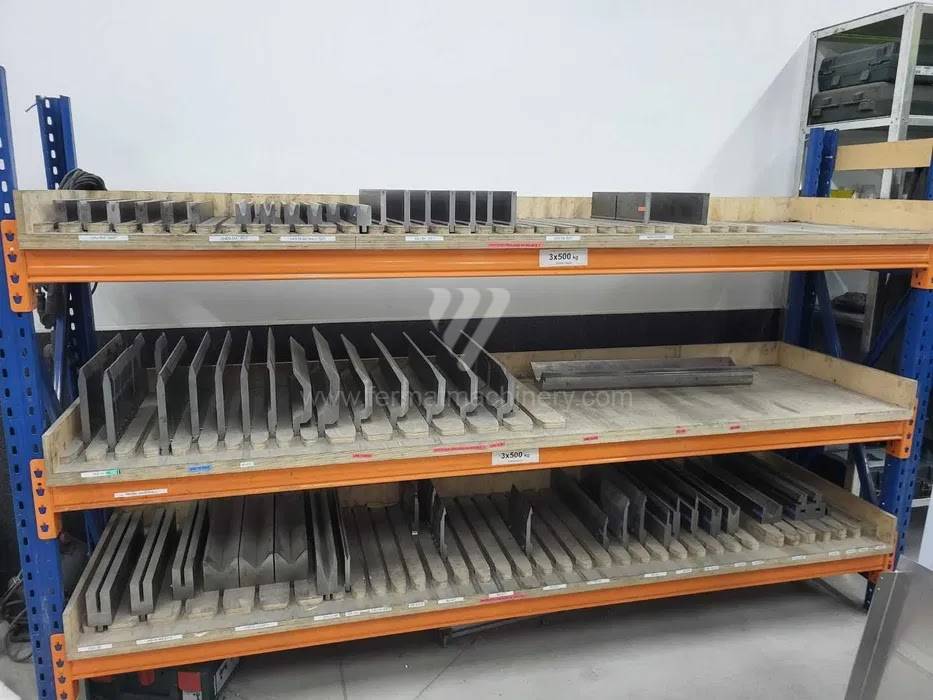
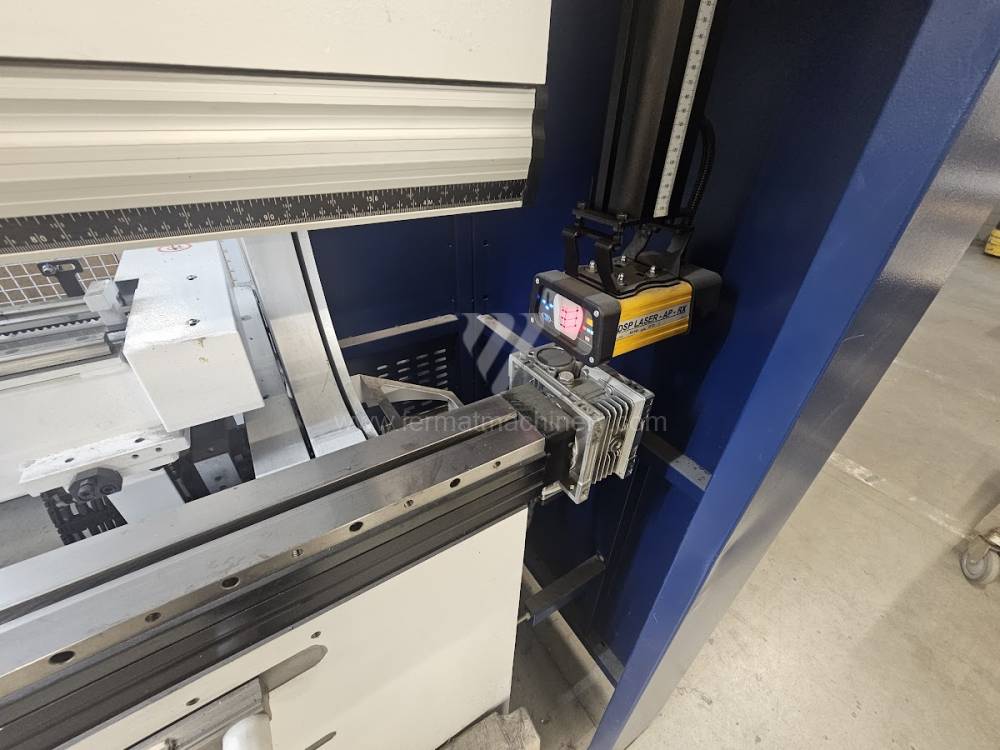
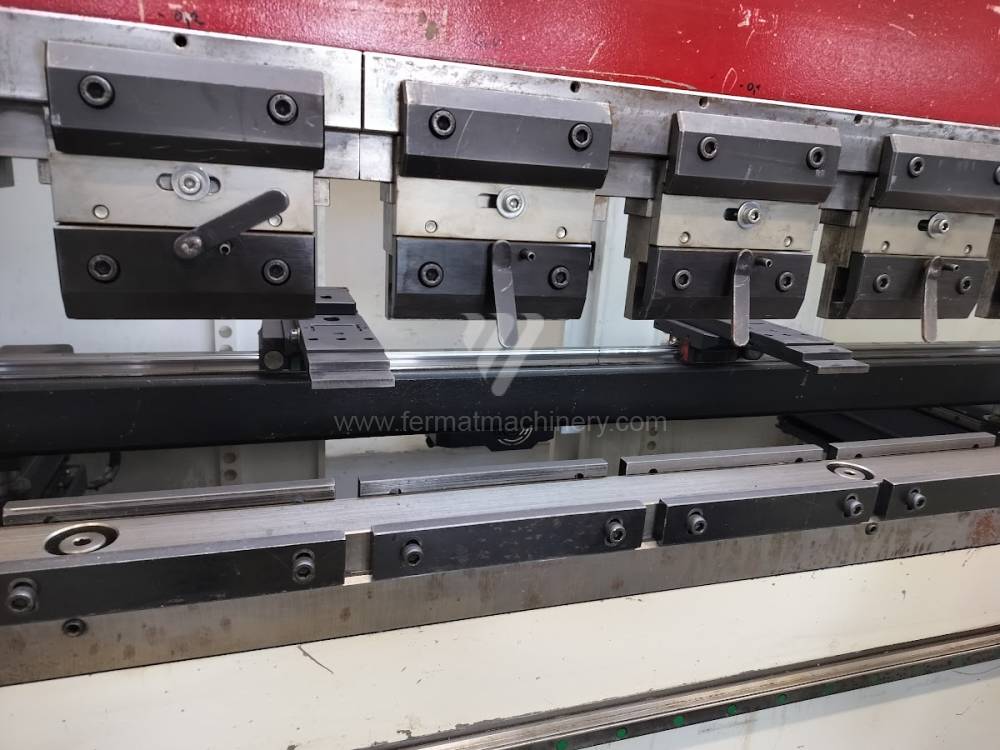
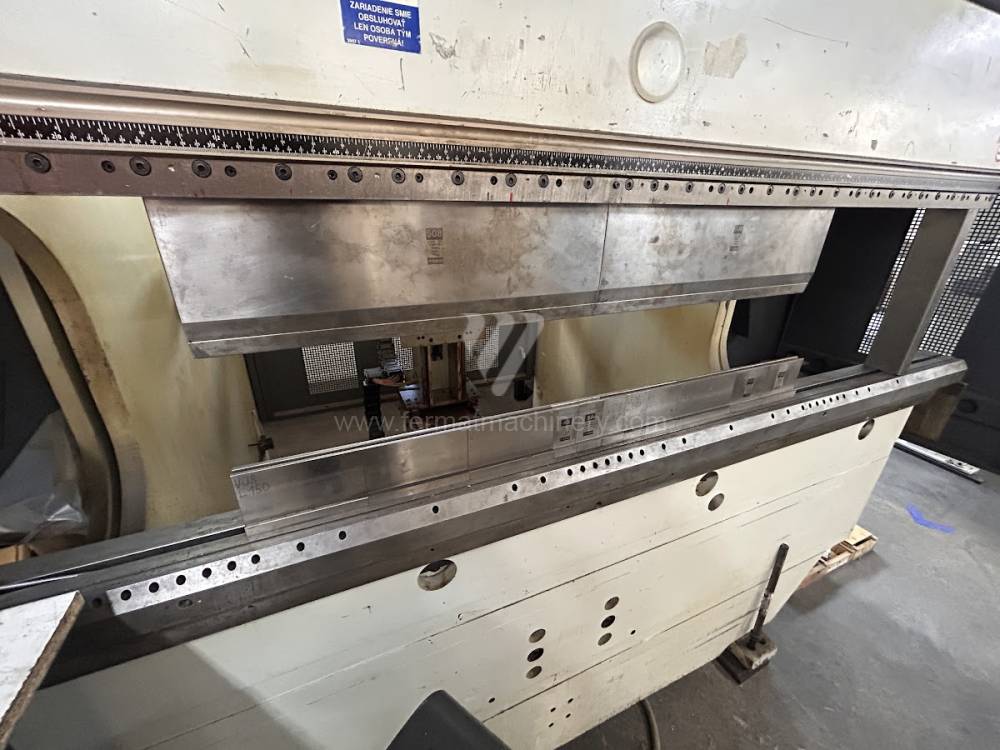
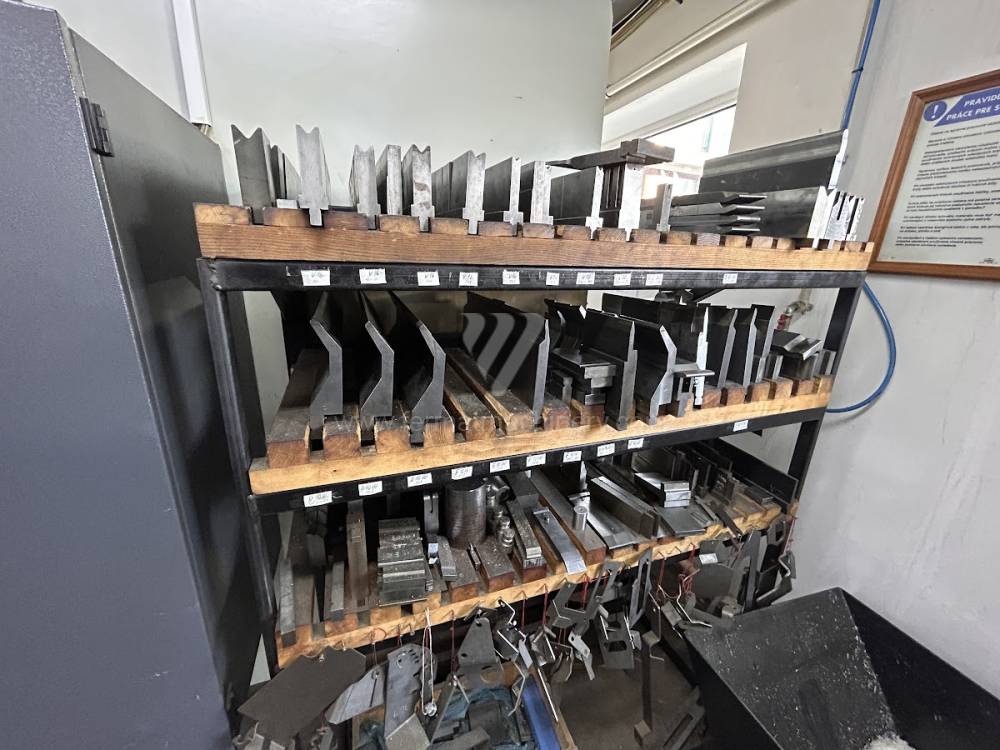
Different types of punches and dies are used here as tools. These tools can be of different shapes and lengths. To clamp these tools mechanical or hydraulic clamping is used. Laser inspection can be used for maximum tool accuracy. Mechanical systems are used to drive the press, with an electric motor driving a system of pulleys and belts. Or a hydraulic one, which drives the hydraulic unit via an electric motor and the latter moves the ram through the pressure of the cylinders.
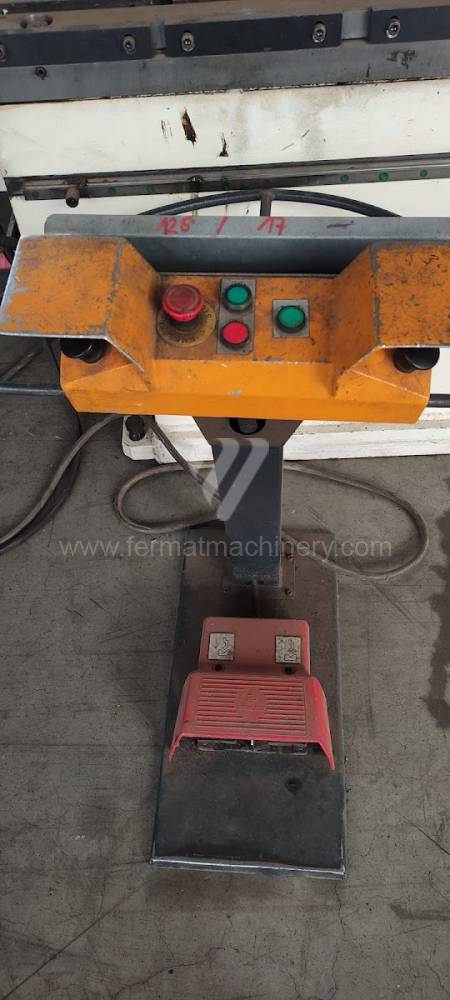
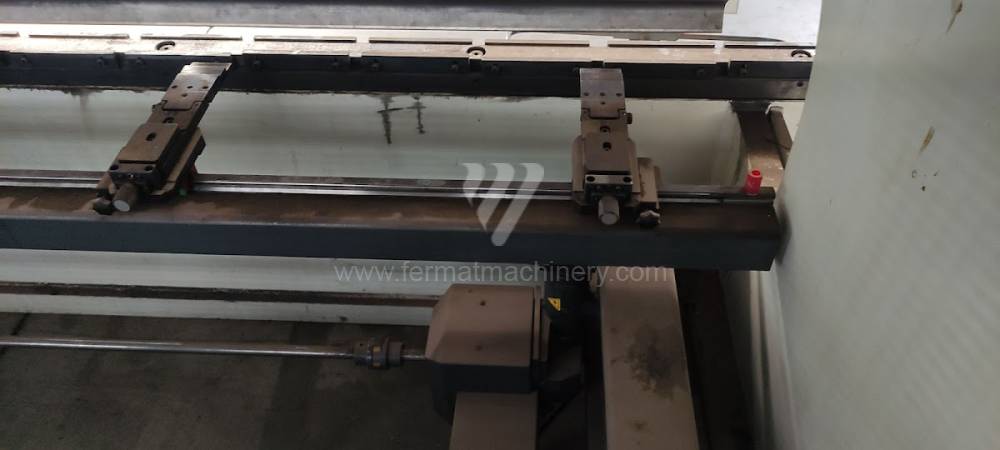
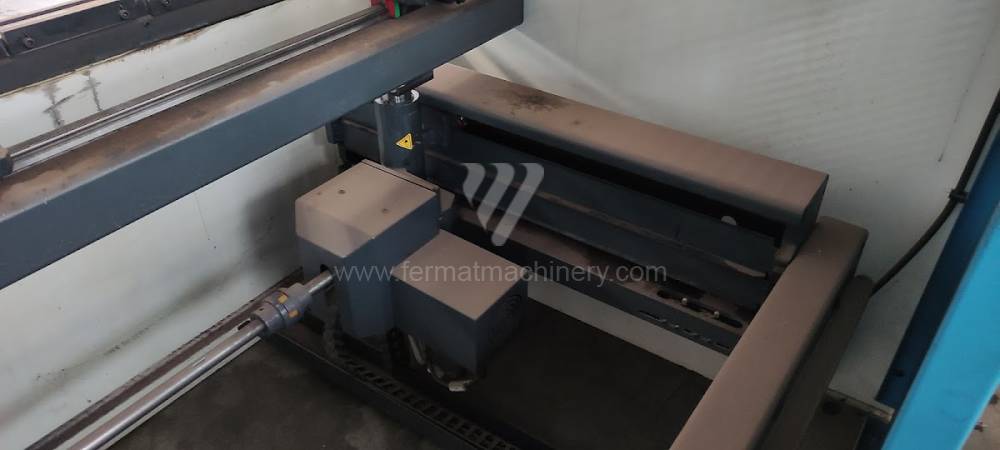
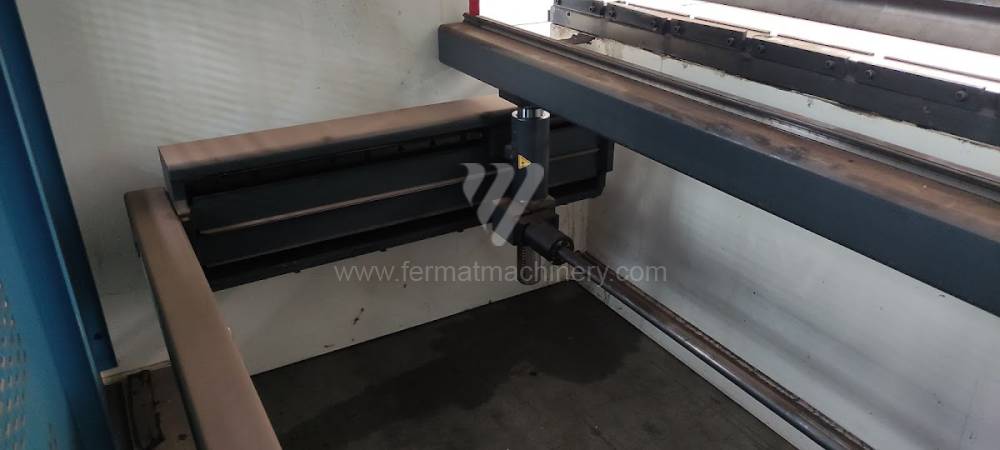
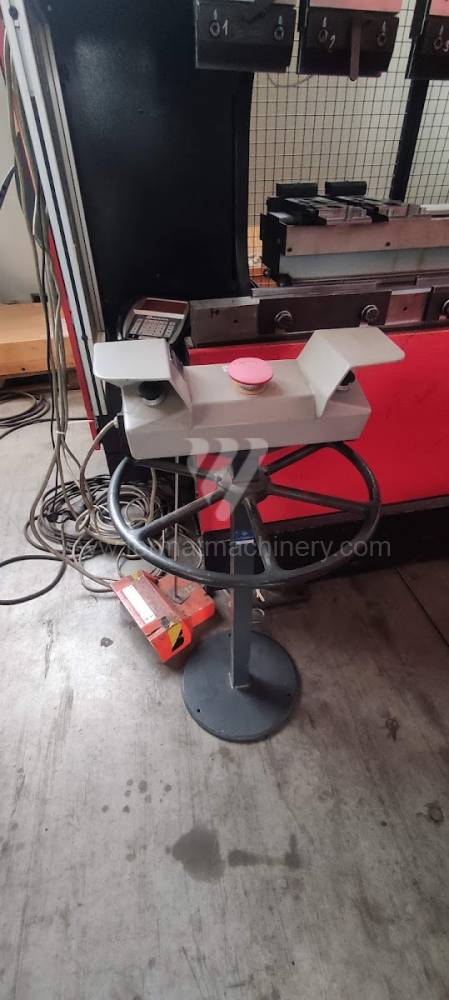
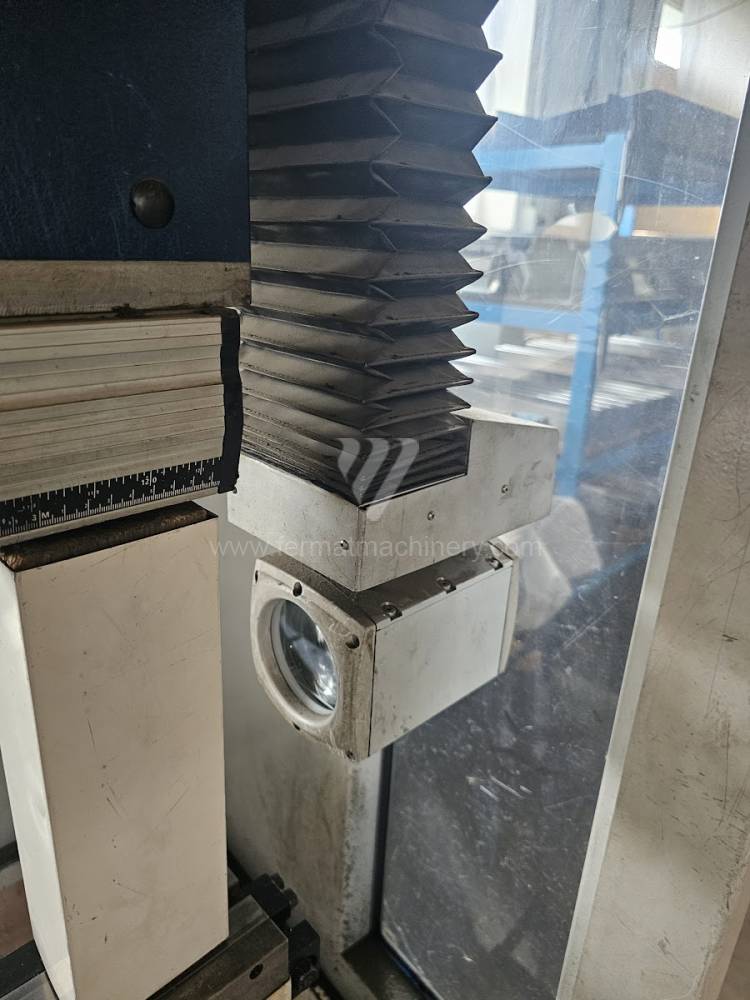
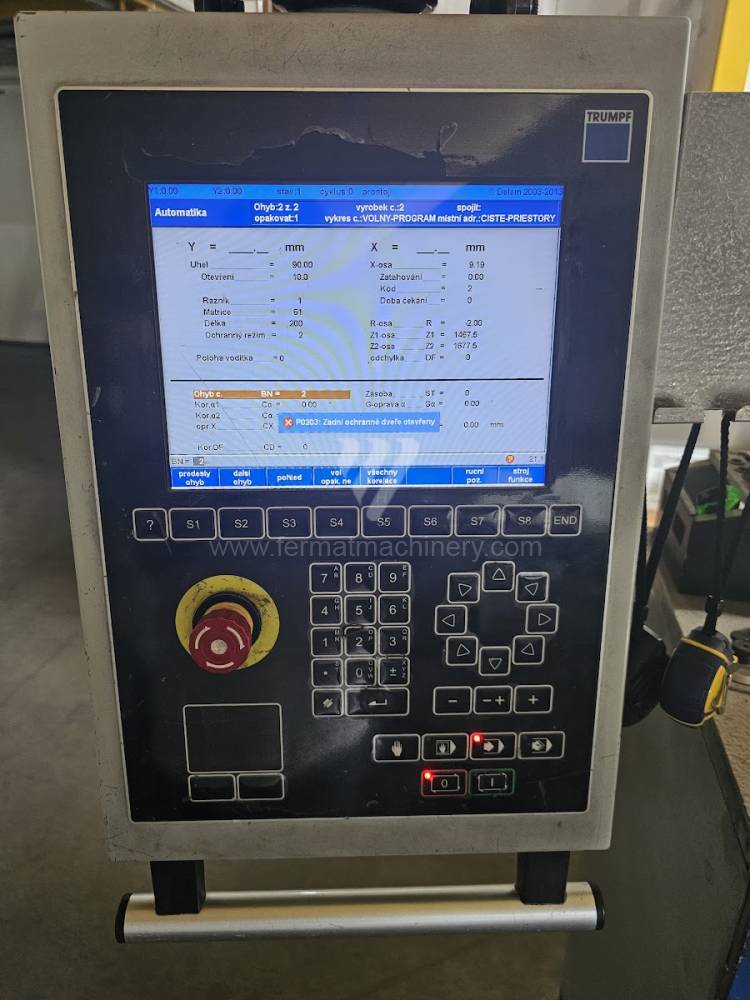
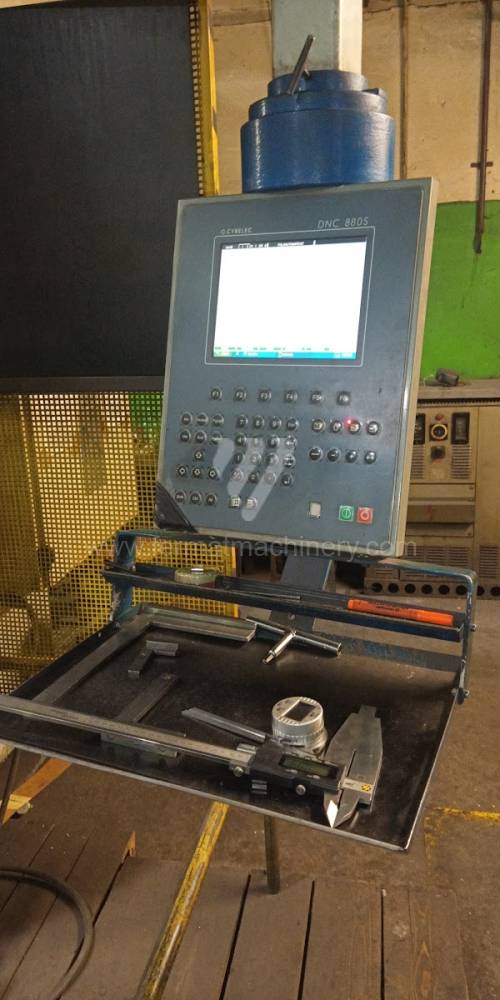
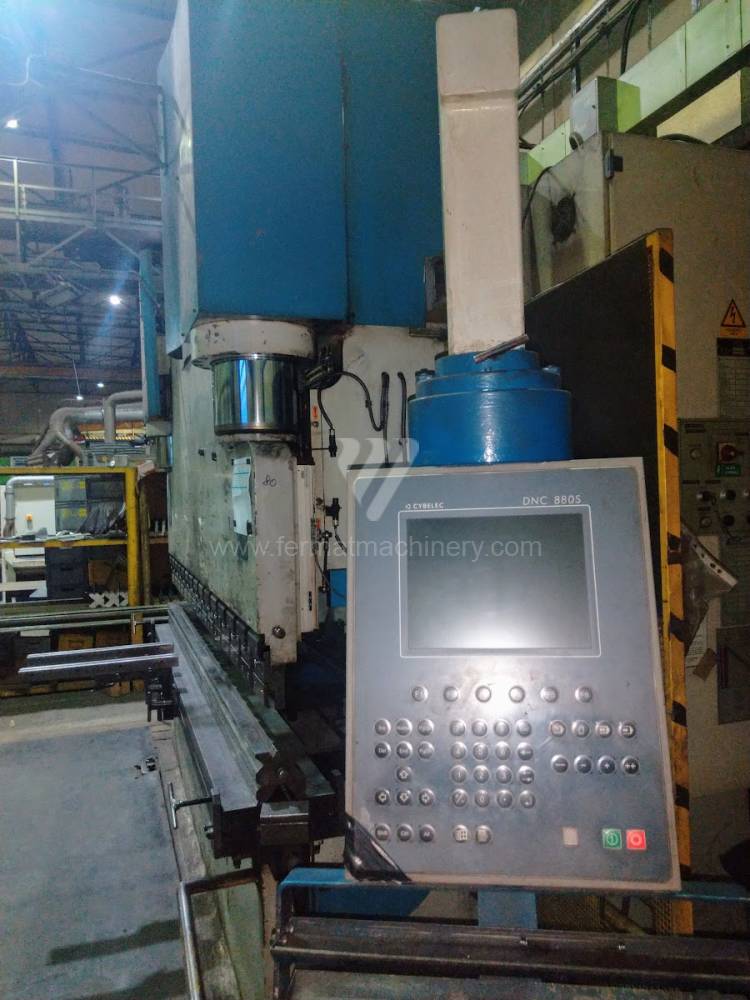
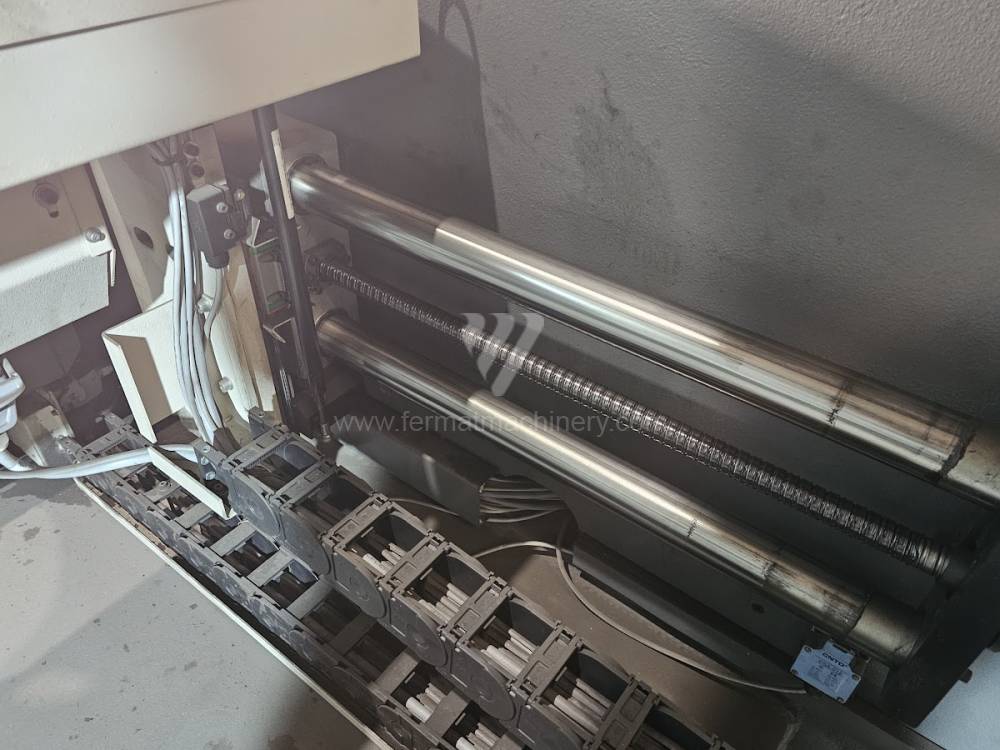
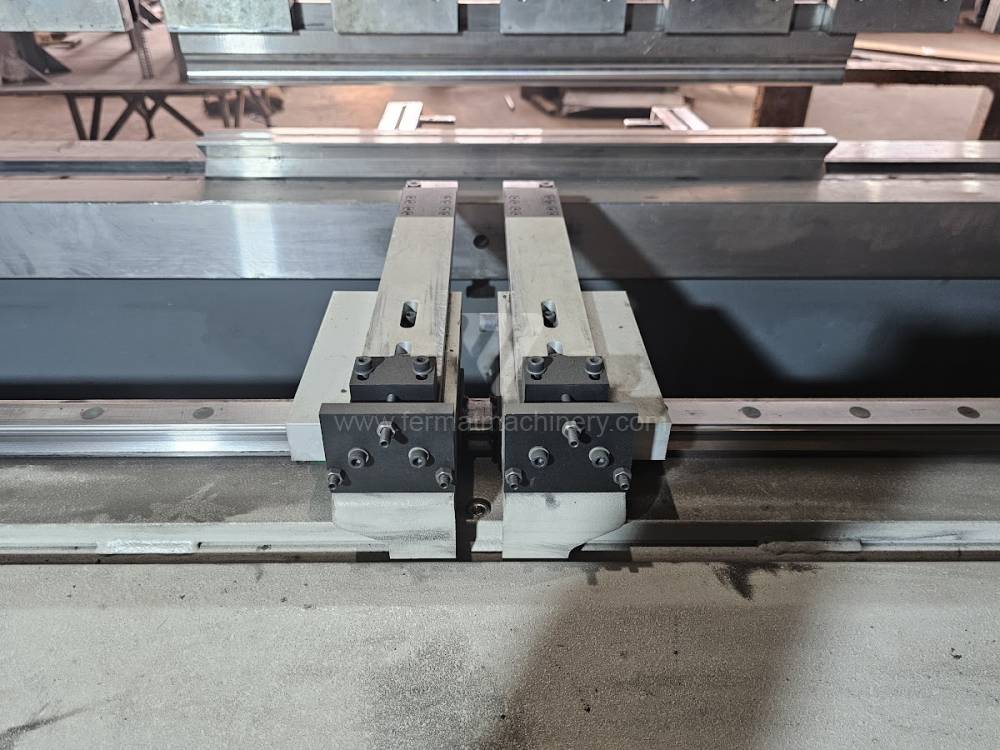
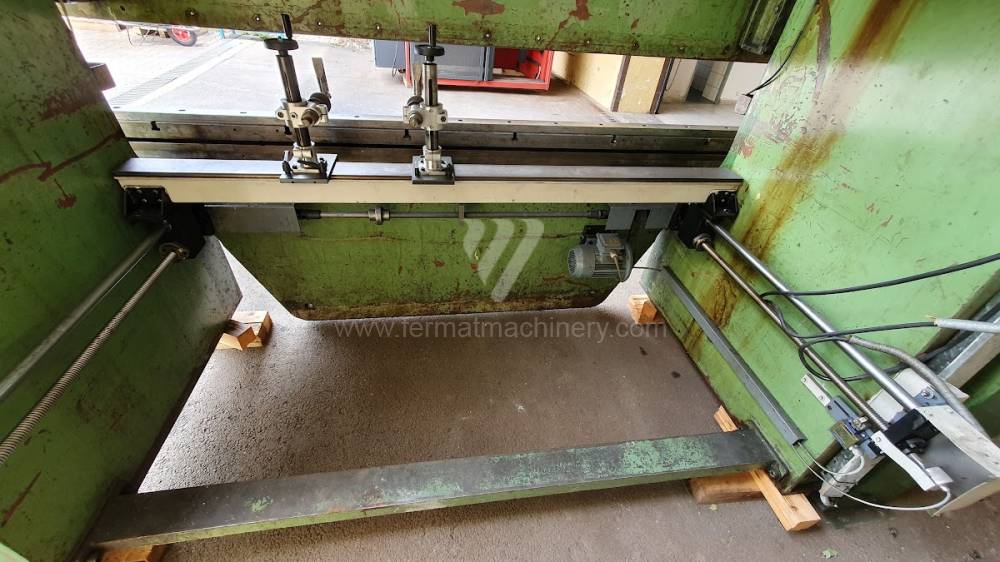
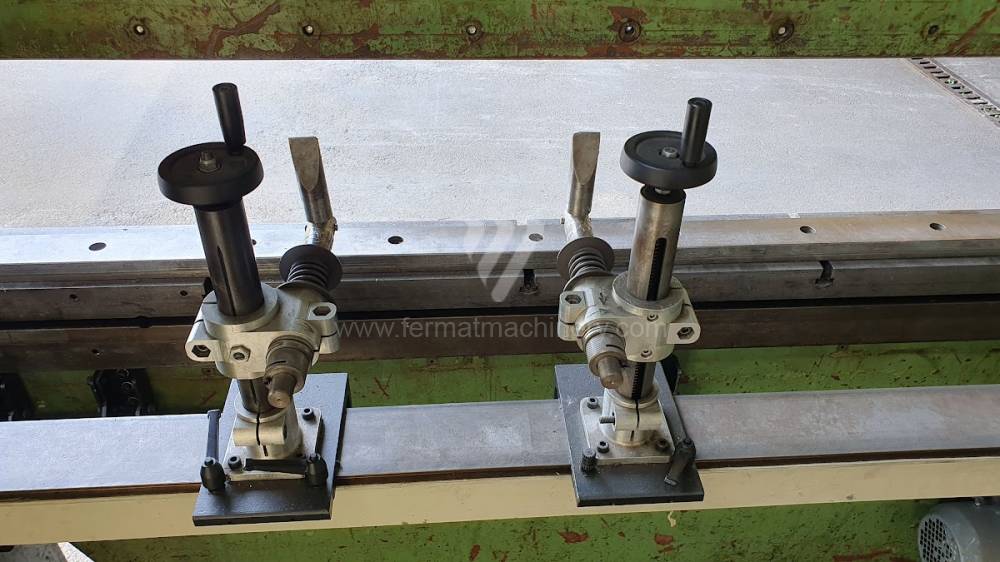
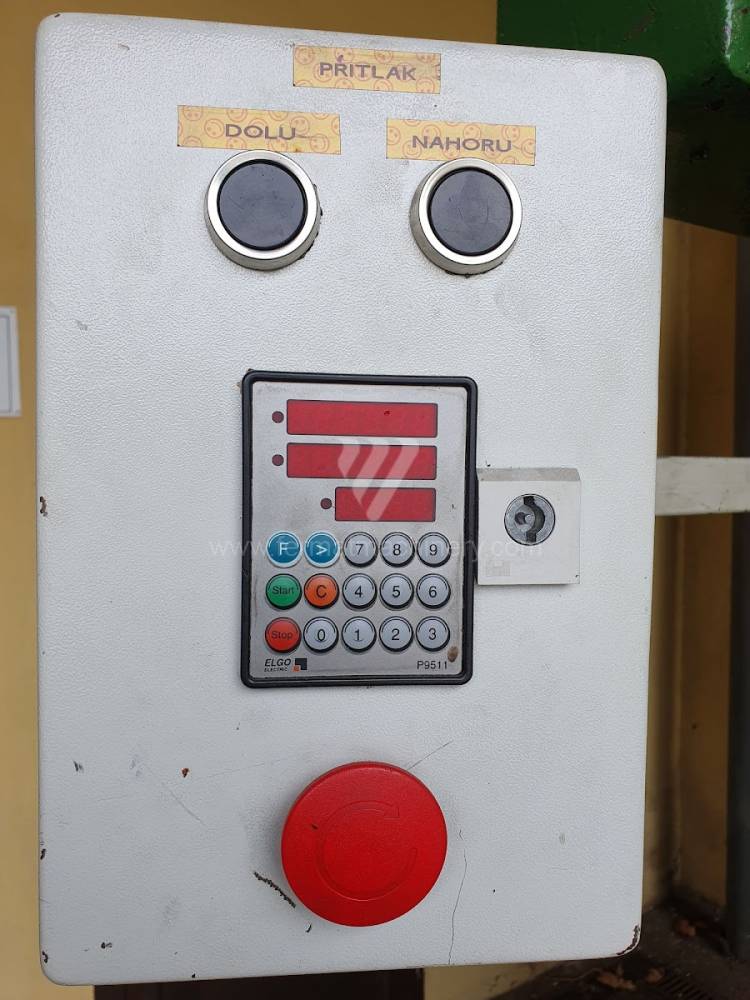
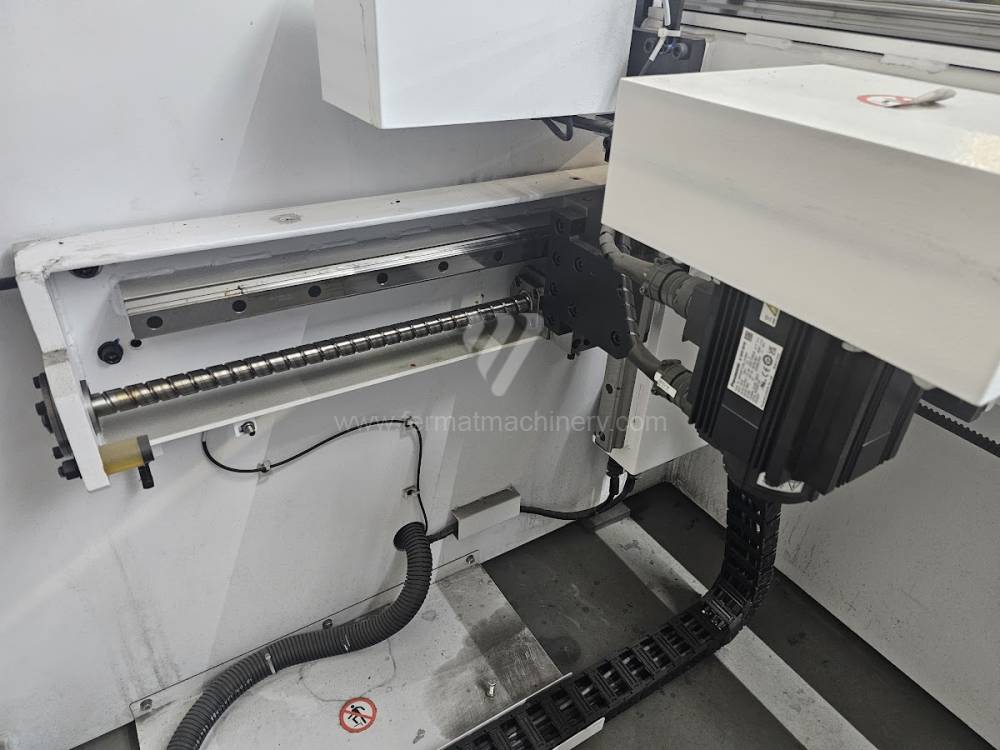
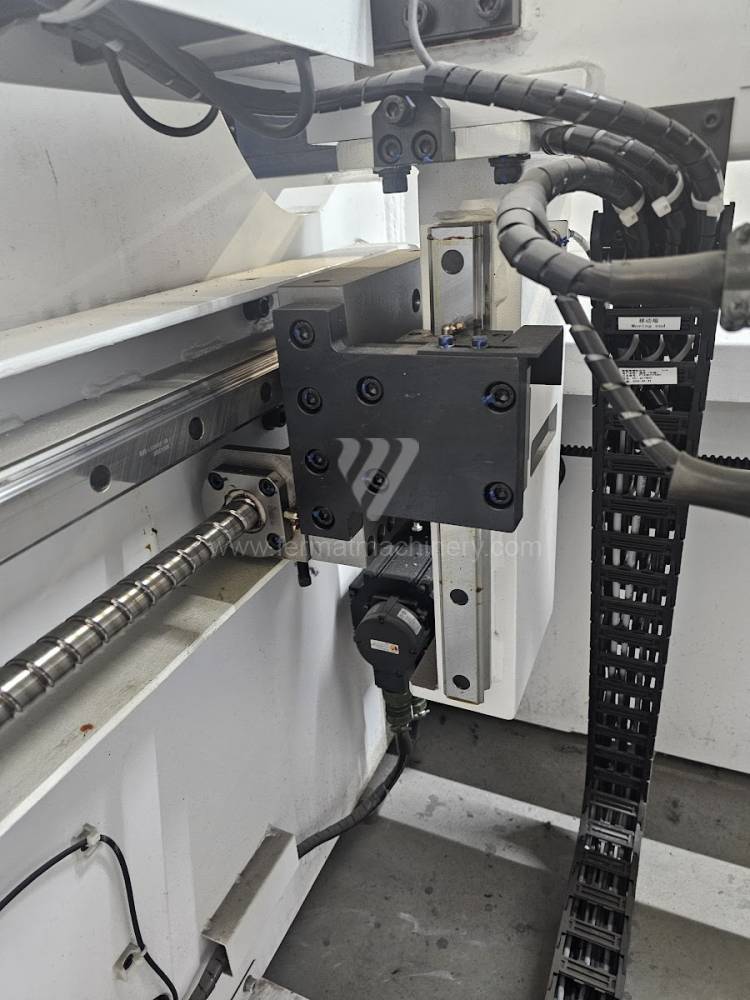
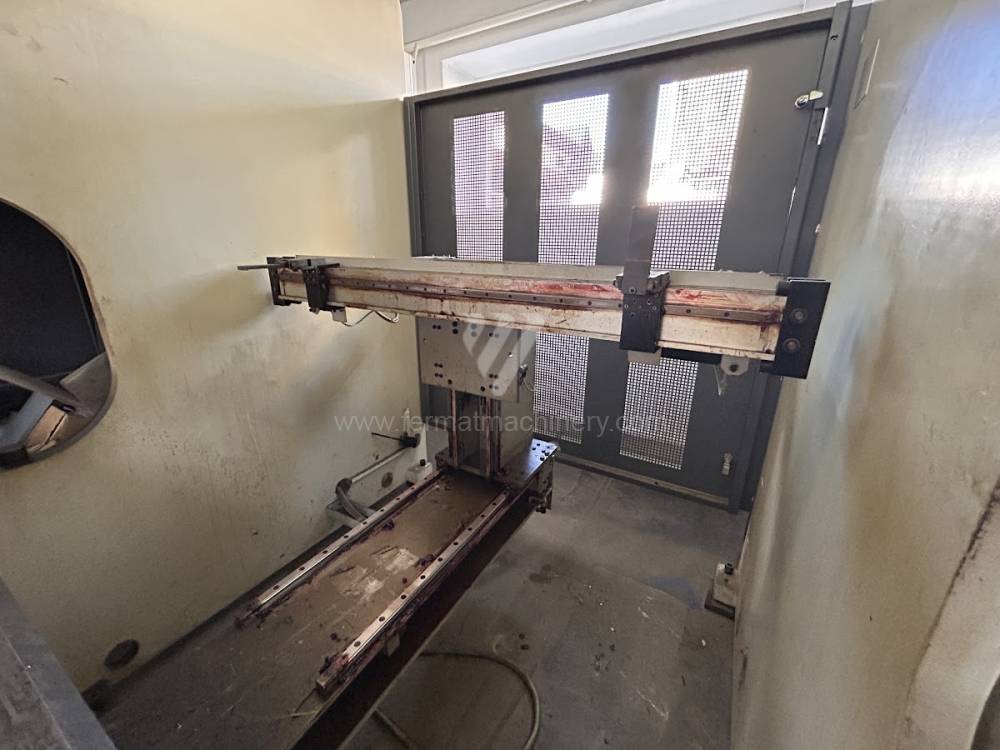
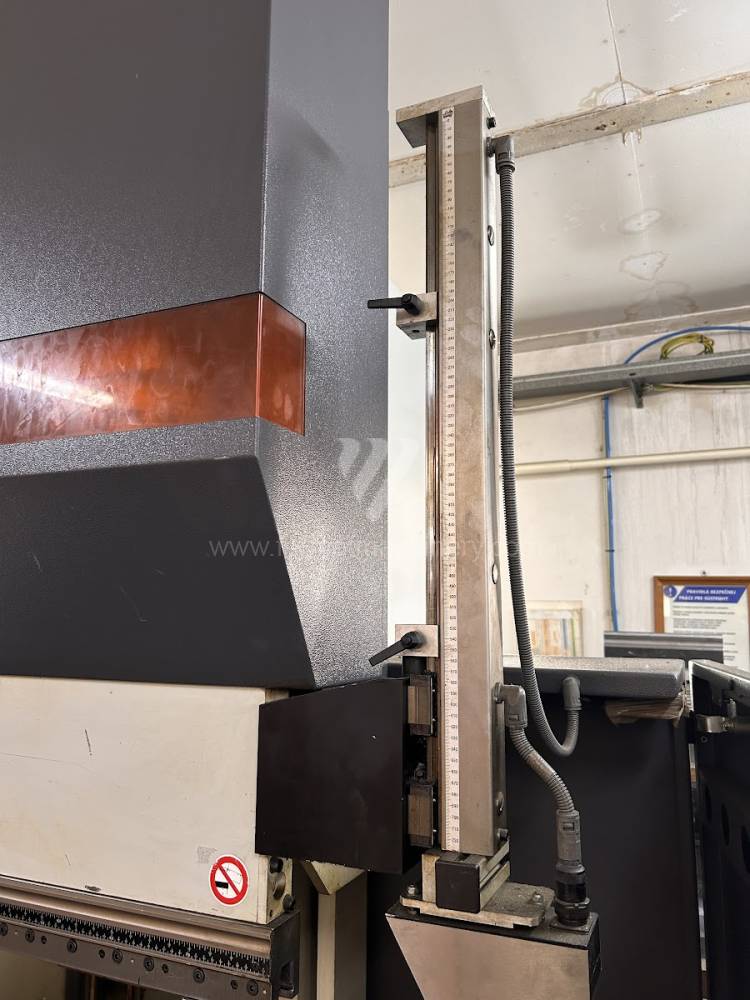
The rear stop is very important for a press brake. It ensures the correct positioning of the workpiece in the machine. Semi finished product is pressed against the thumb, which is on the stop and ensures the correct position with respect to the tool. The rear stop is controlled by a CNC system and it moves to precise positions according to the program. Machine can operate in up to 6 axes.
X - along which the stop moves forward and backward
Z - along which the stop moves to the left or to right
R - along which the stop moves up and down
Another important function of press brakes is cambering. It is a process when the the long parts are bended the resistance of the material to the upper tool, elastic deformation of the part of the ram with the punch occurs. This can be prevented by underlying the matrix in the central part, grooves on the edges of the working table or automatic system.
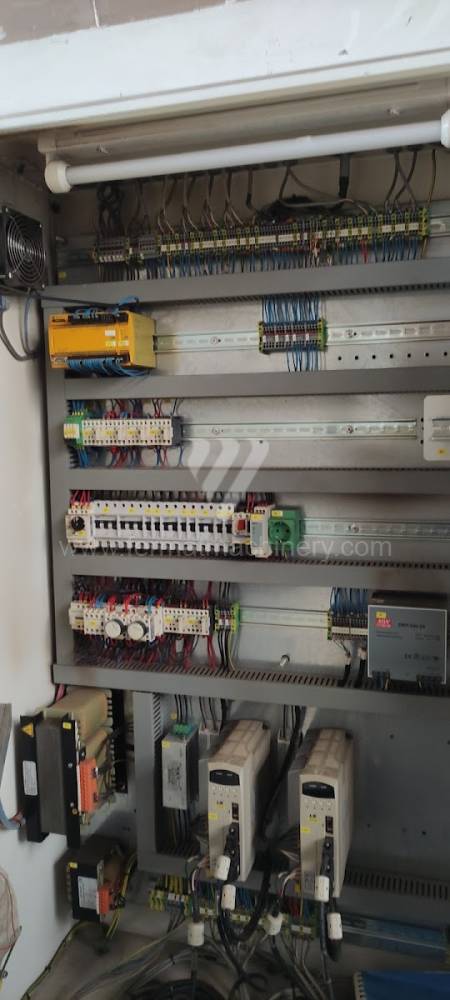
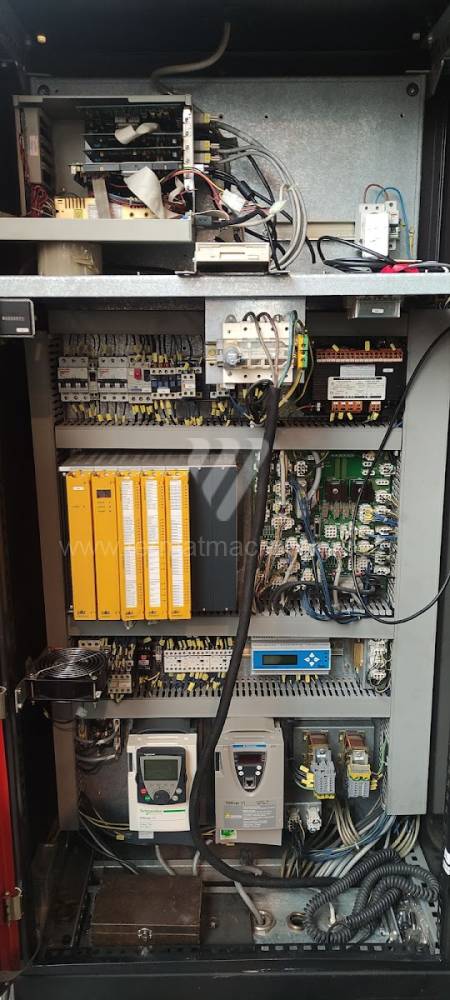
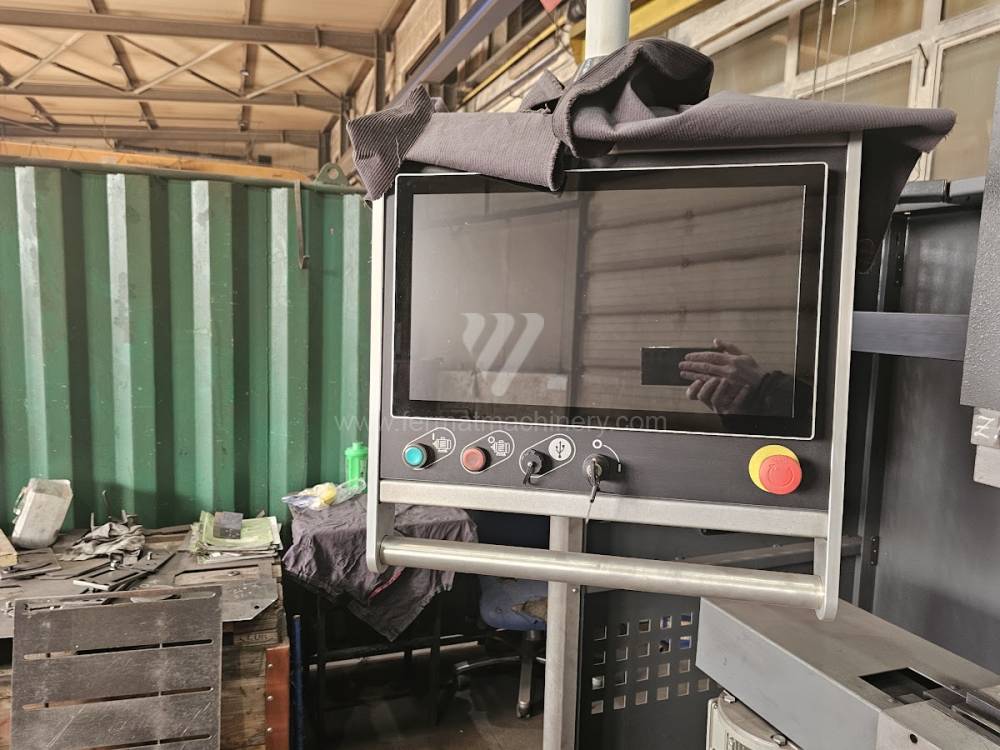
Today, press brakes are controlled by a computer systems. Based on the entered values (material, tools, length, etc…) calculates the production process, the movement of the stops or the bending force. Afterwards the machine can work in three following modes .
Press brakes are designed with different types of drivers such as machines with manual control, mechanical or hydraulic driver. Each has its advantages and disadvantages. Furthermore, it is possible to divide press brakes according to their construction into segmental, tandem and combined.
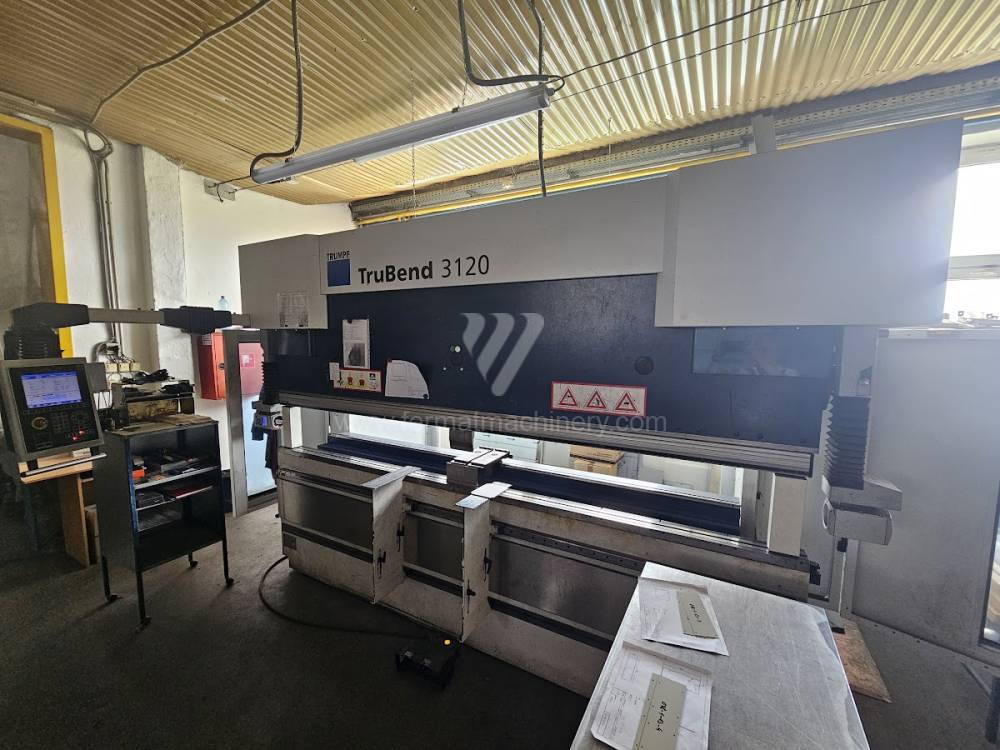
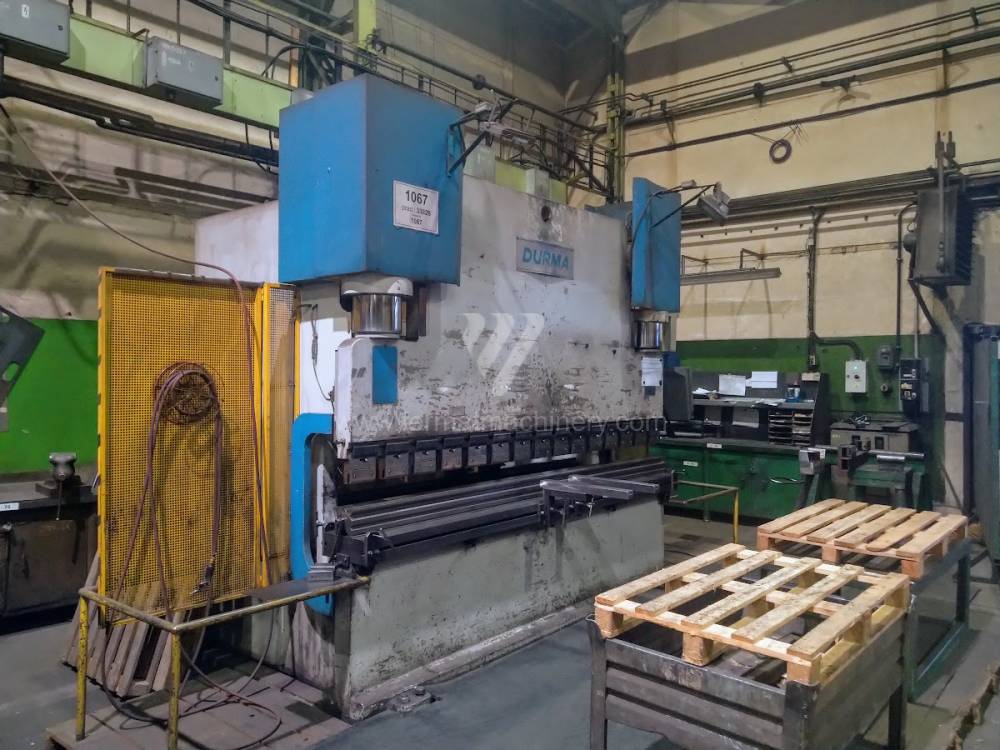
Most popular manufacturers are TRUMPF, DURMA, SAFAN DARLEY, BYSTRONIC, GASPARINI, Haco, Beyeler, Promecam, Hämmerle.
Currently, the most widely used and manufactured are hydraulic press brakes, which are CNC controlled.Top machines are from following manufacturers: Trumpf, Amada, Bystronic. These manufacturers use either their own CNC system for control or universal ones such as Delem, Cybelec, ESA.. These machines achieve a high level of automation of the operating cycles and therefore the maximum use of their capabilities. Of course press brakes from these top manufacturers are very expensive to purchase.