Vicino
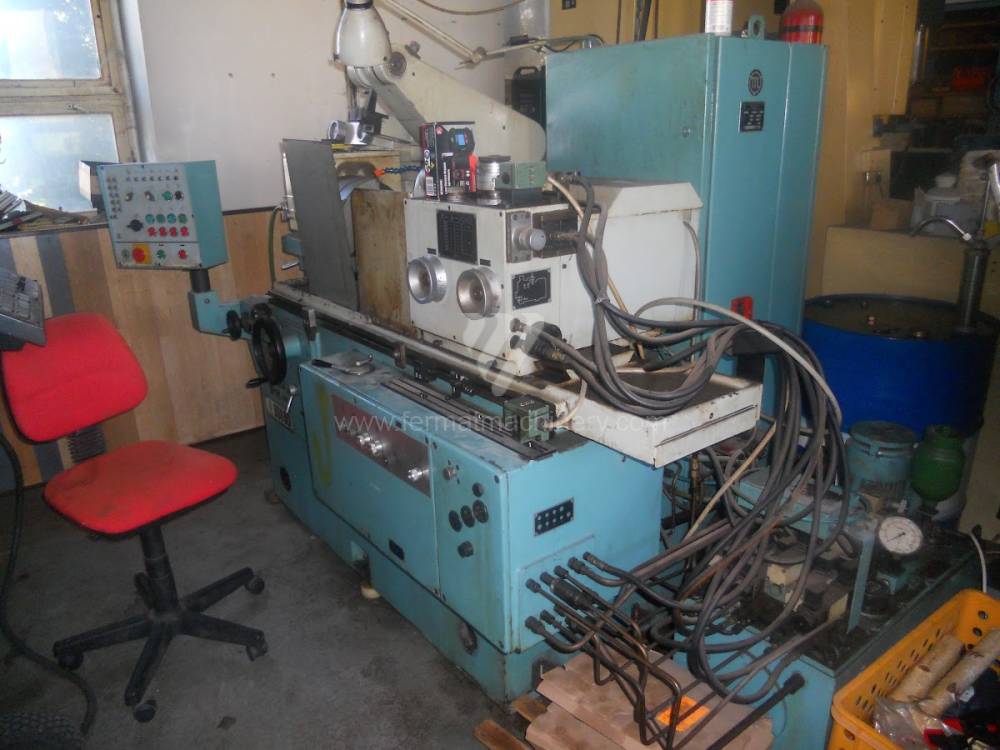
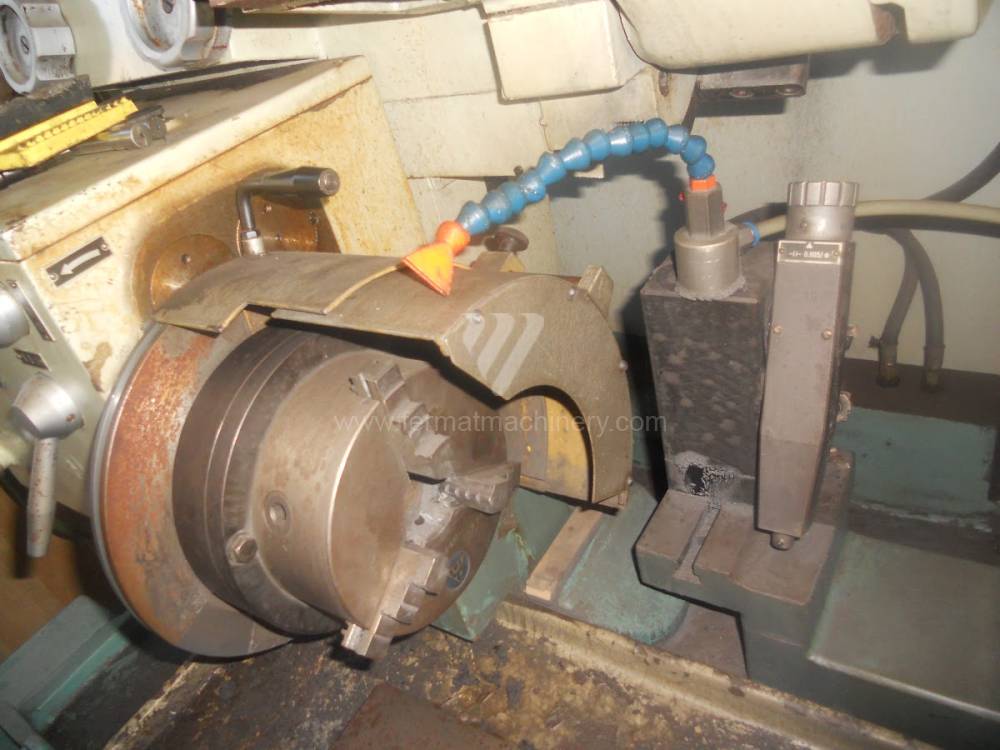


Anno di fabbricazione:1990
Diametro max. del pezzo lavorato: 220 mm
Diametro max. del foro a rettificare: 120 mm
Max. profondità di rettifica: mm
Peso della macchina: 2600 kg
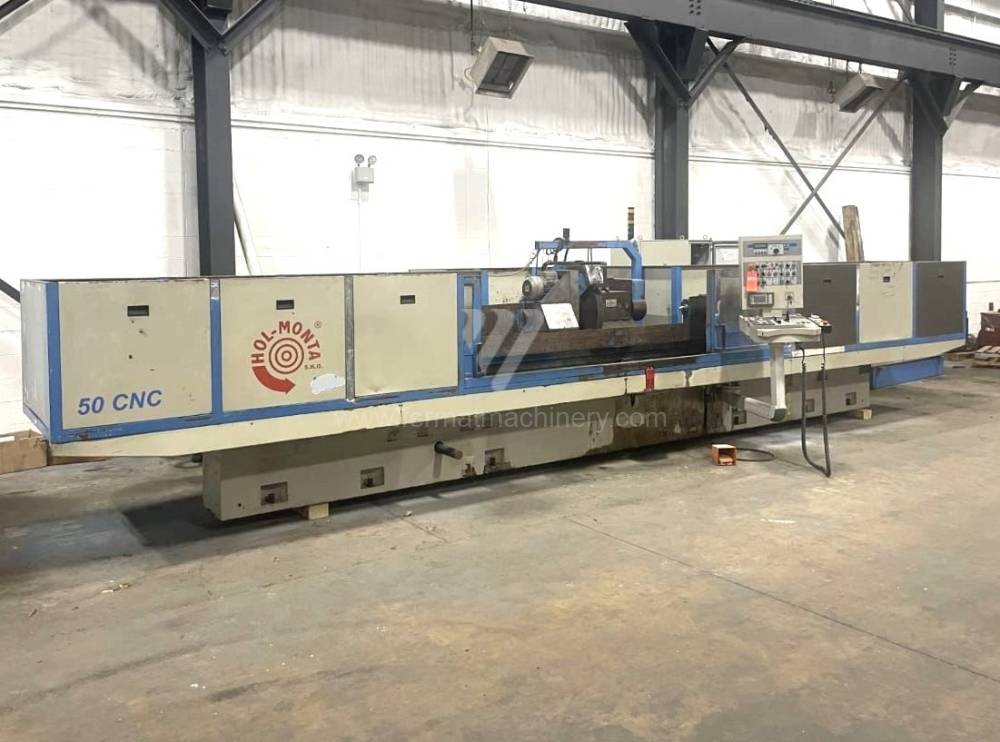
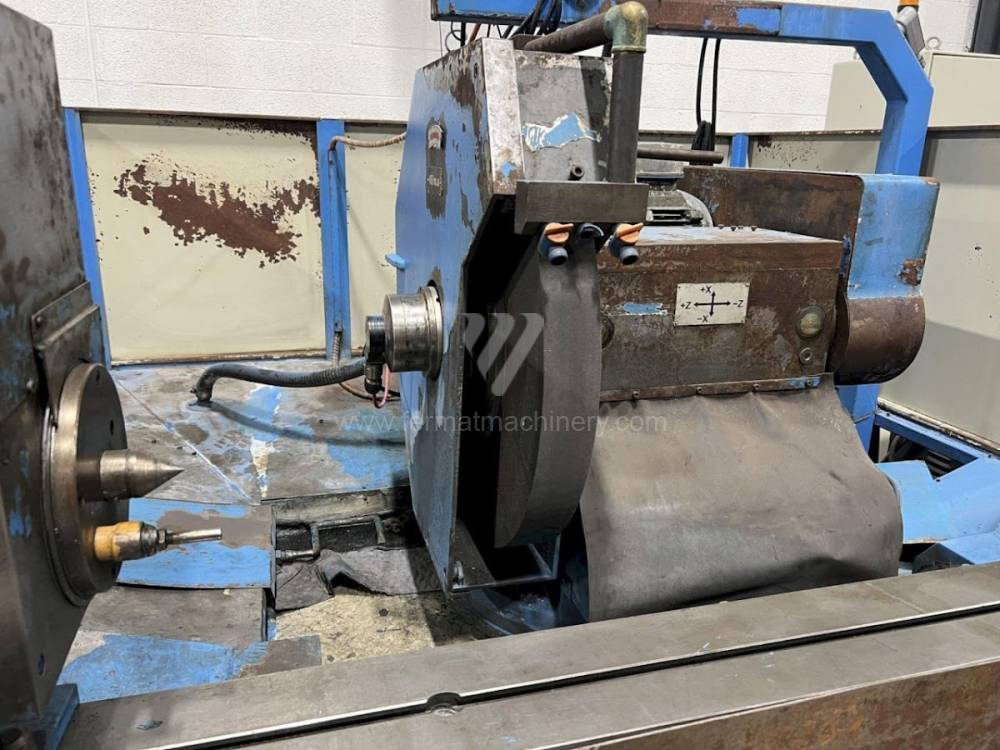
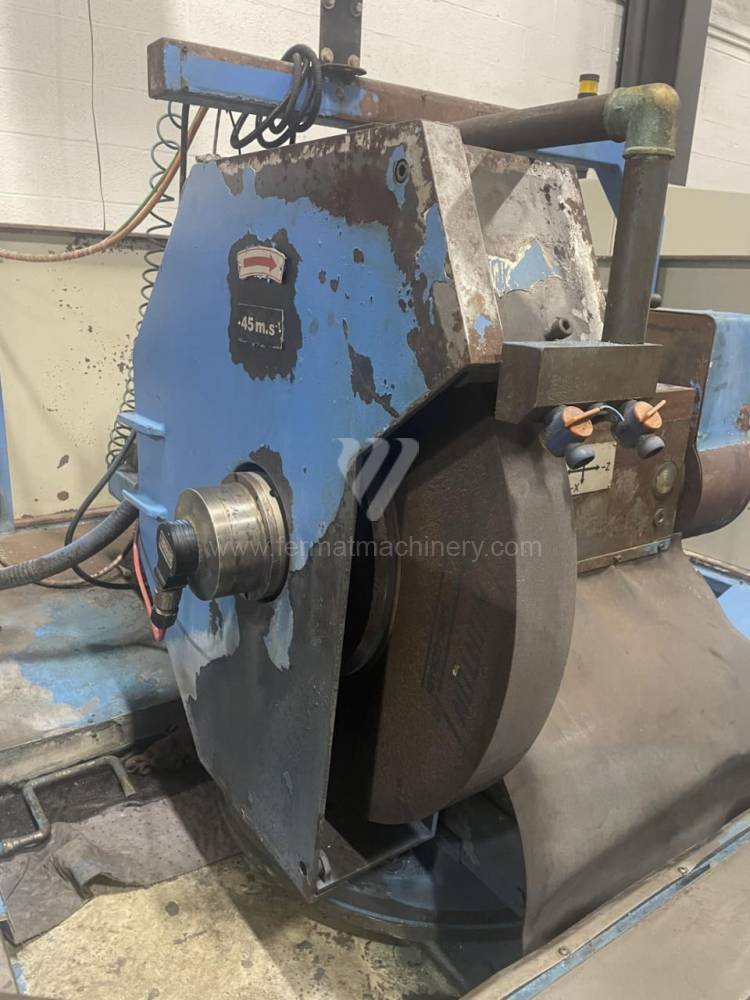
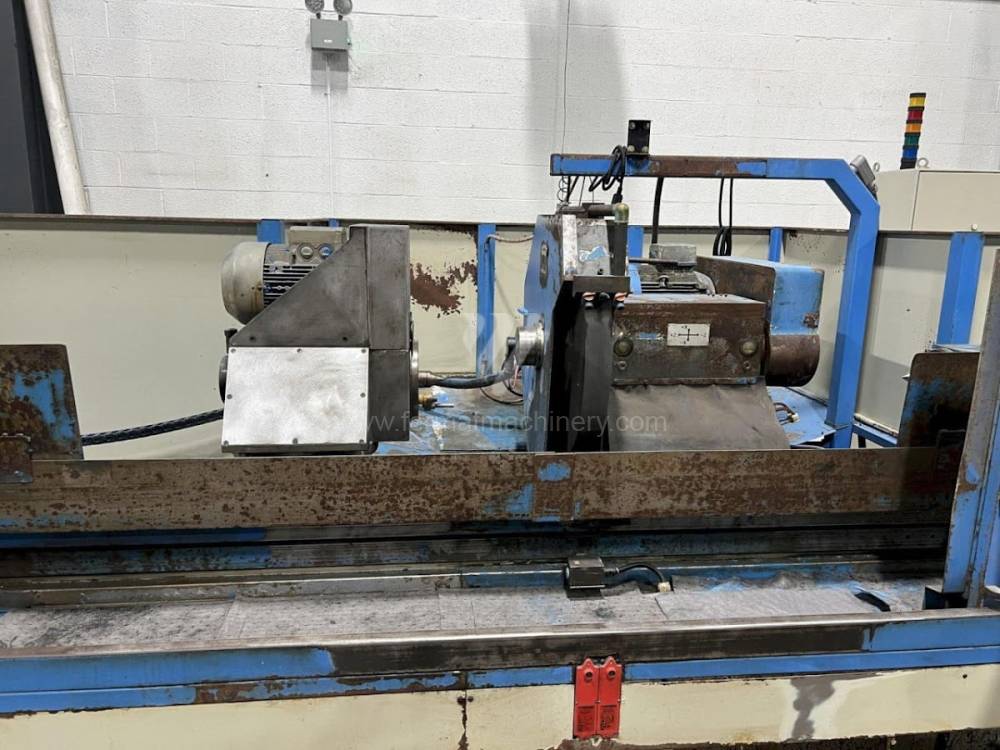
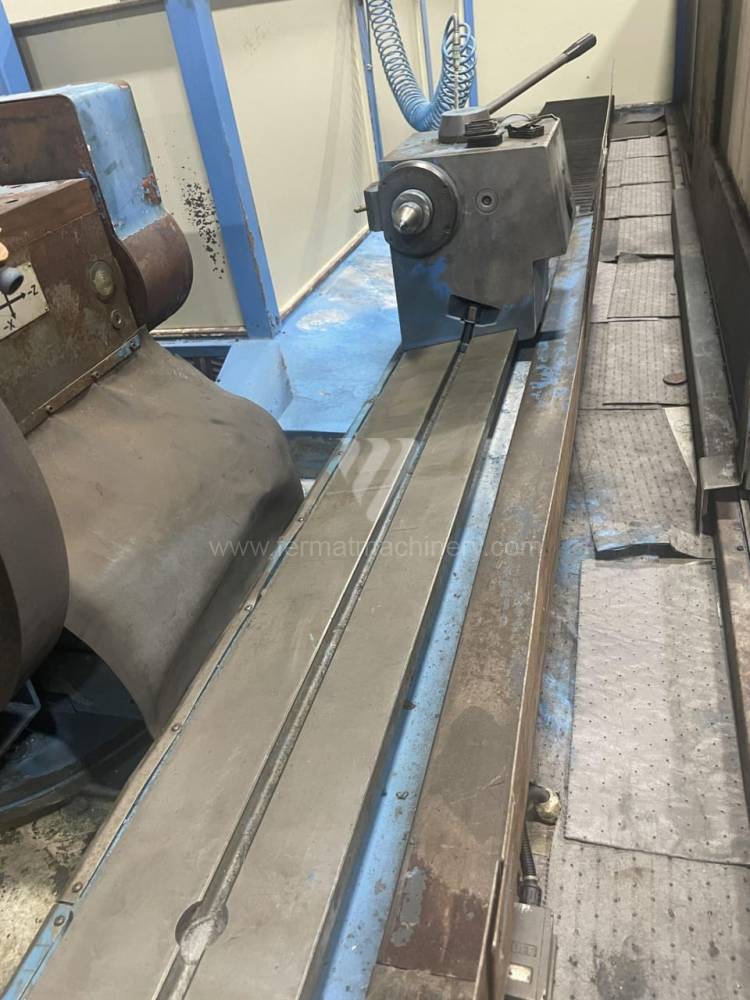
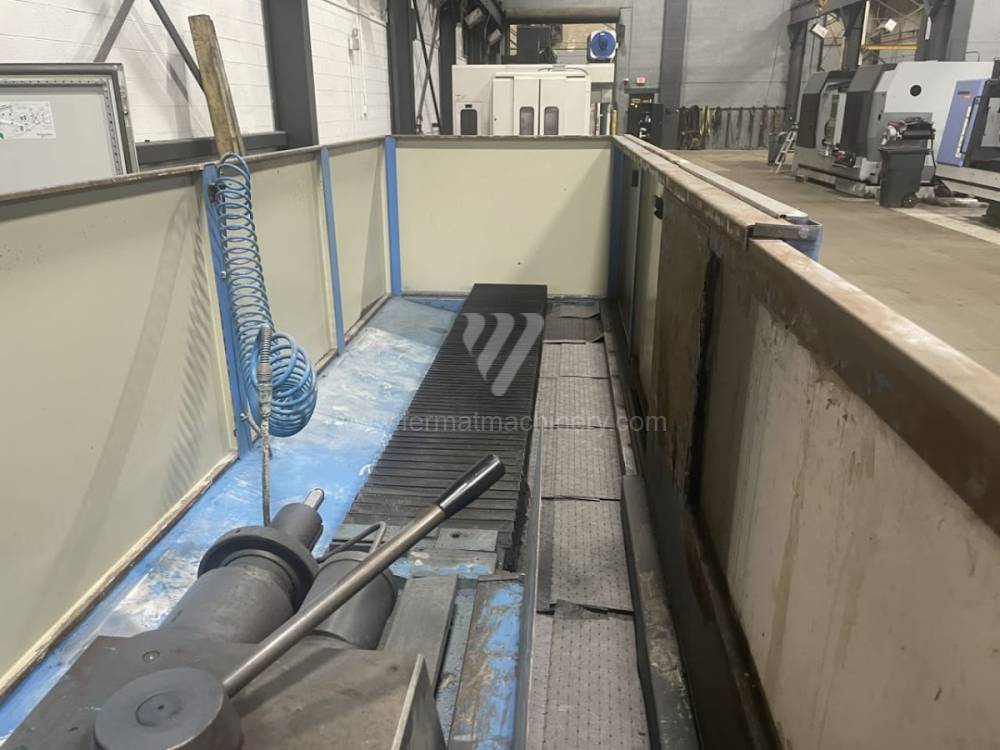
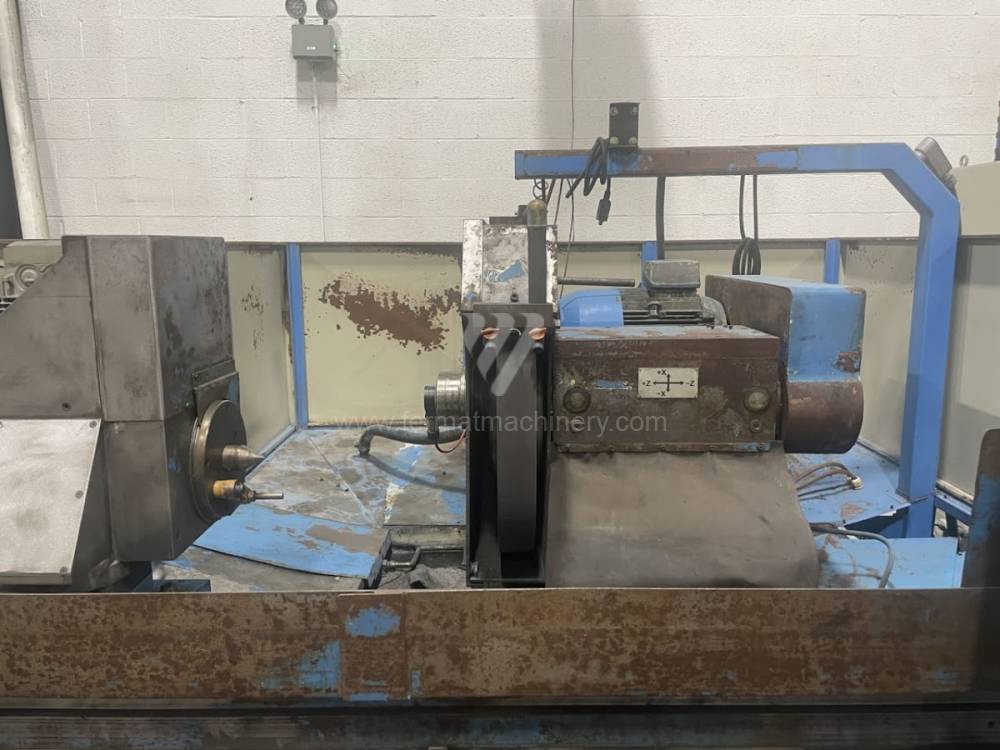
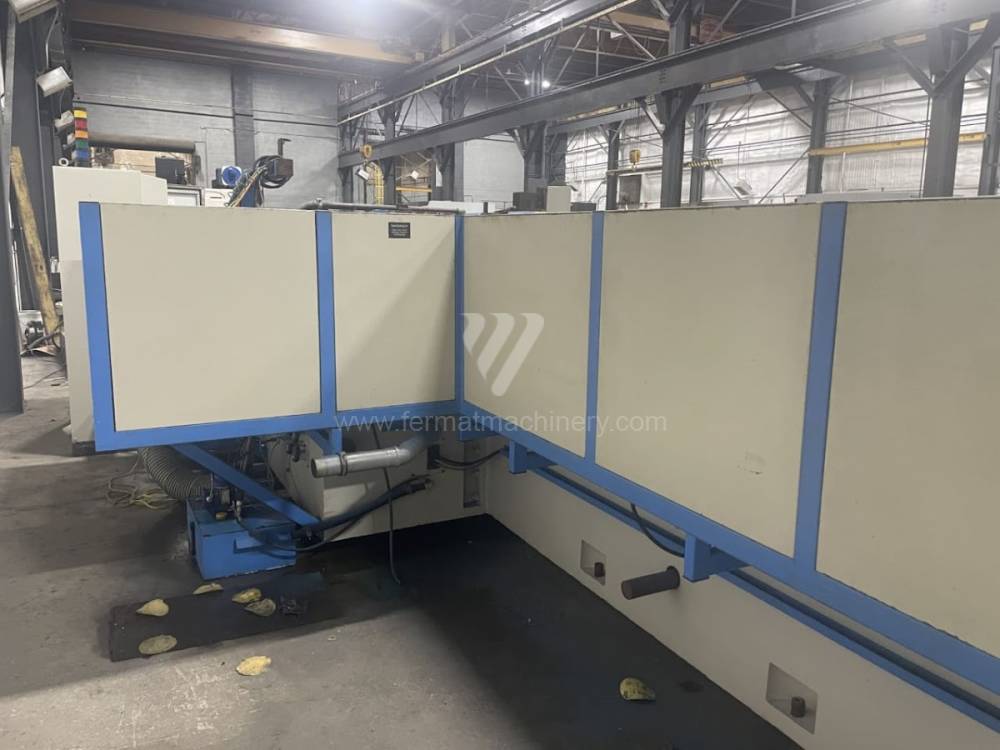
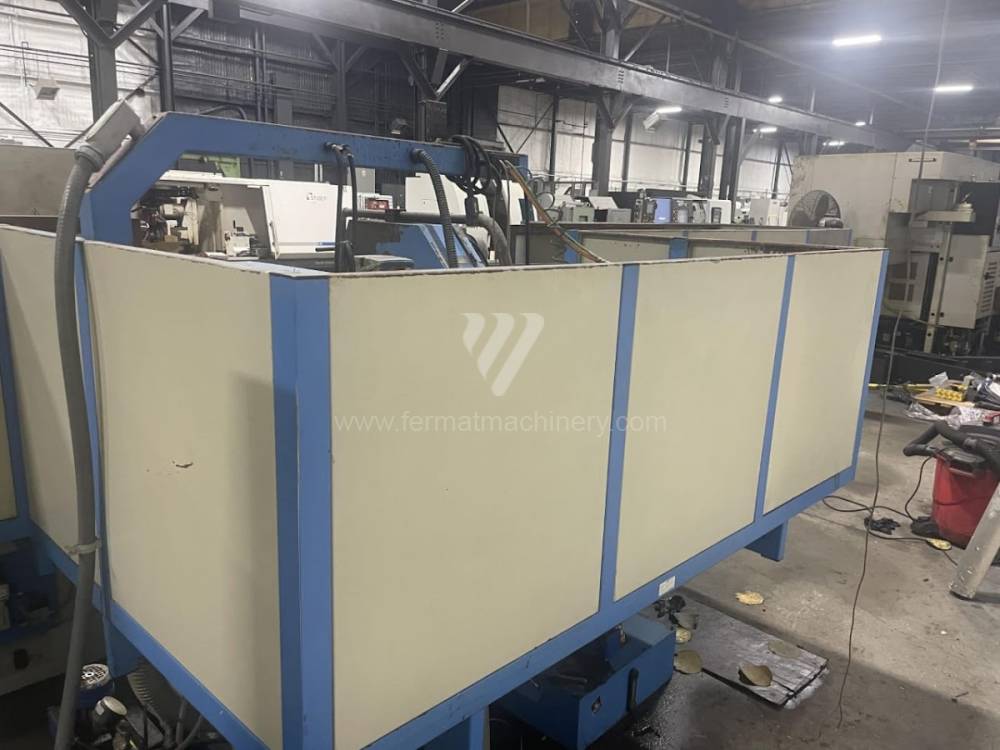
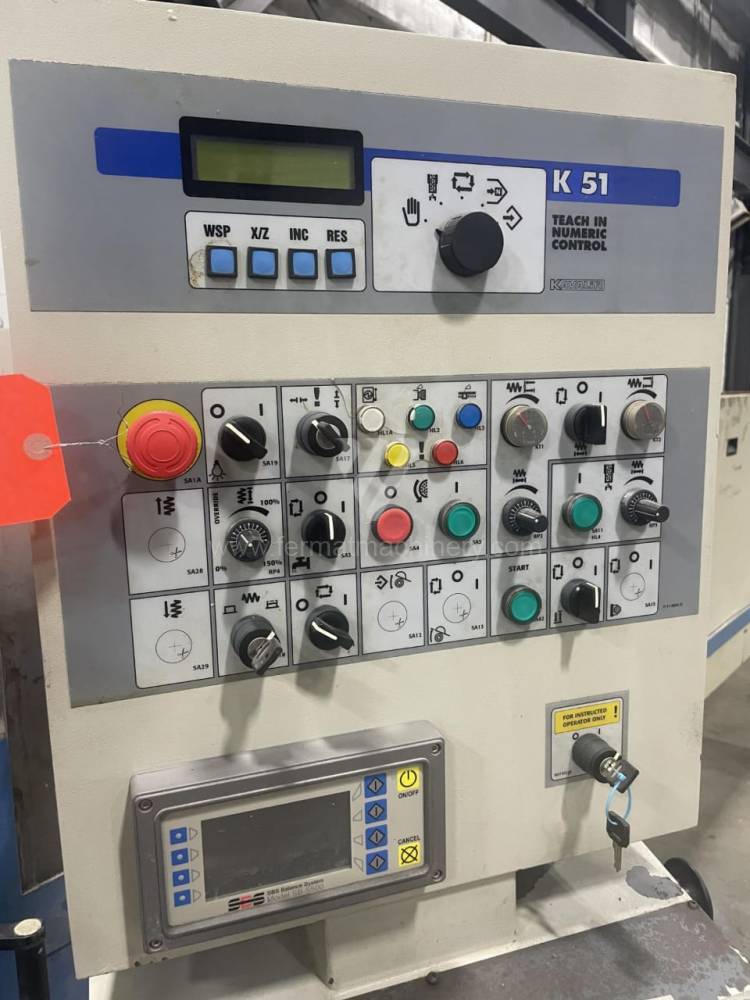
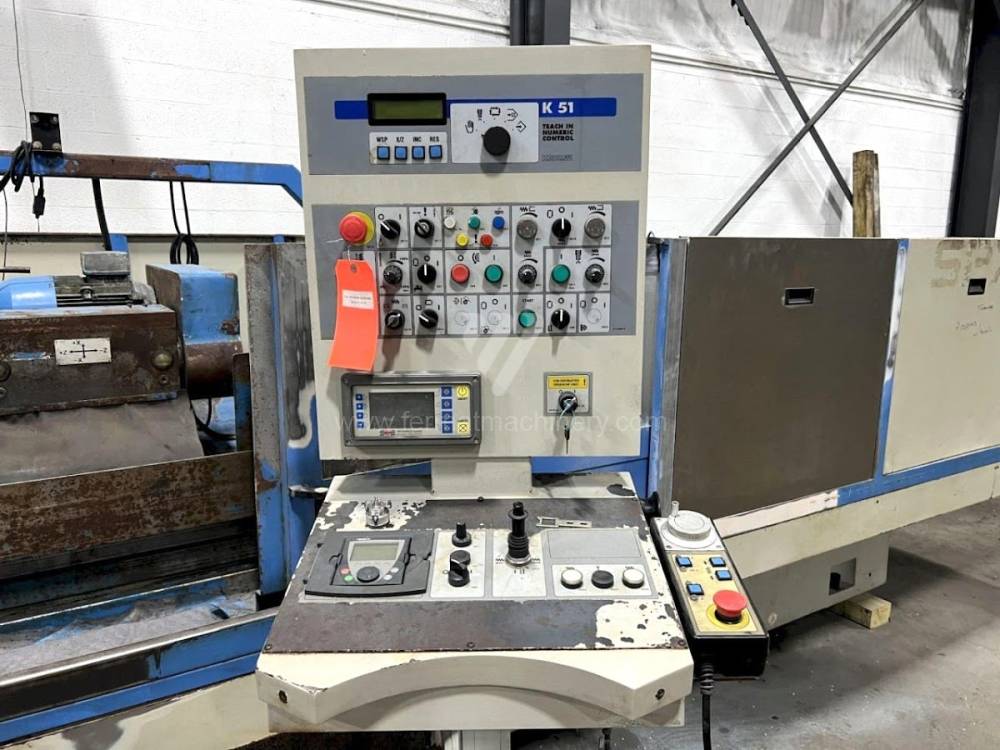
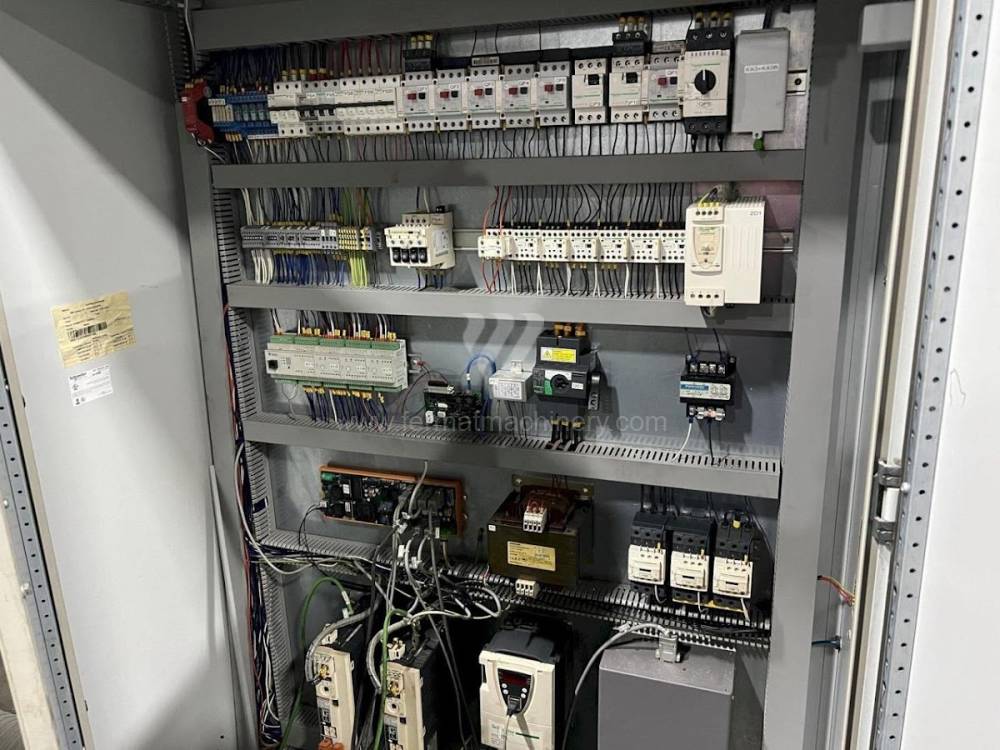

















Sistema di controllo Kavalír: K51-1
Diametro massimo di rettifica: 500 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 3000 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 600 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: No
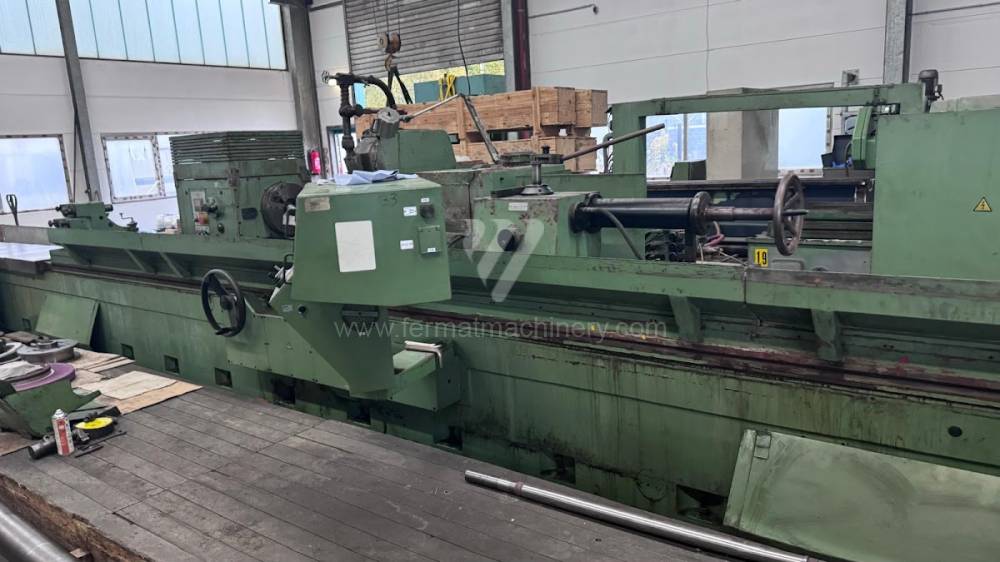
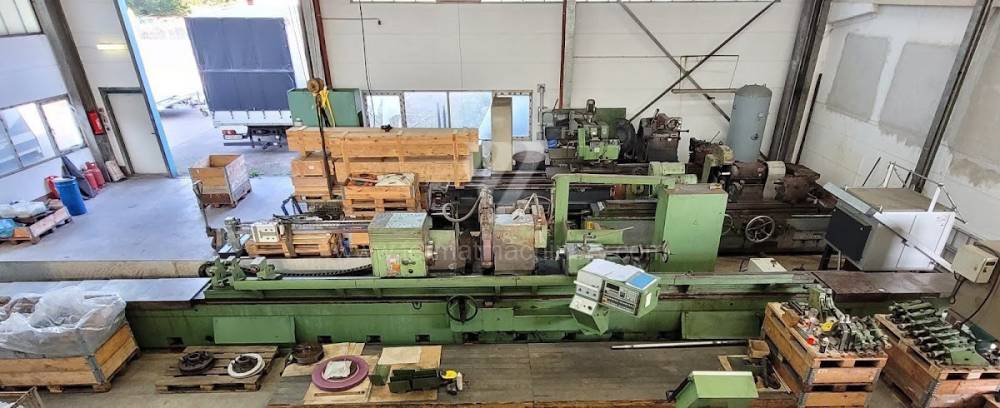
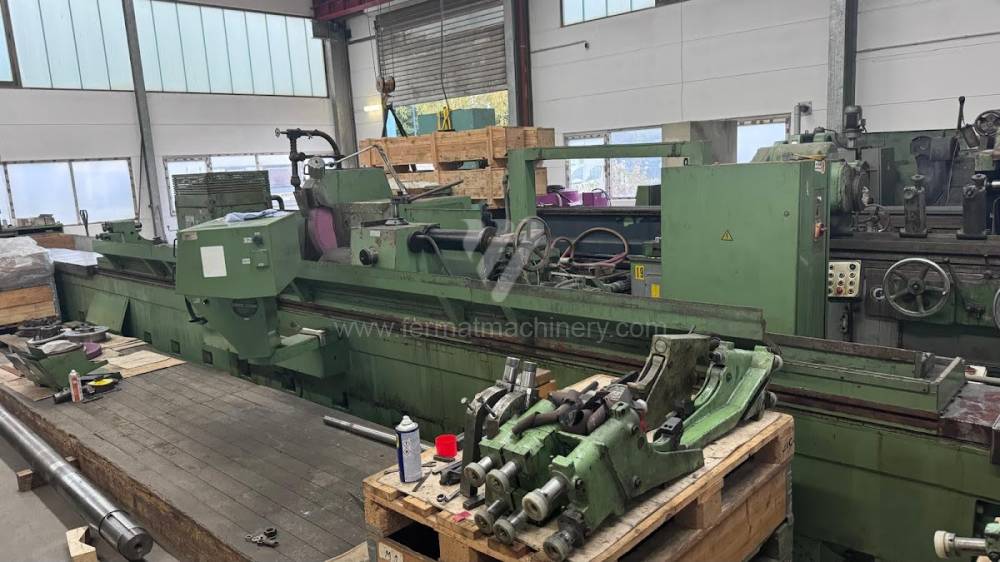
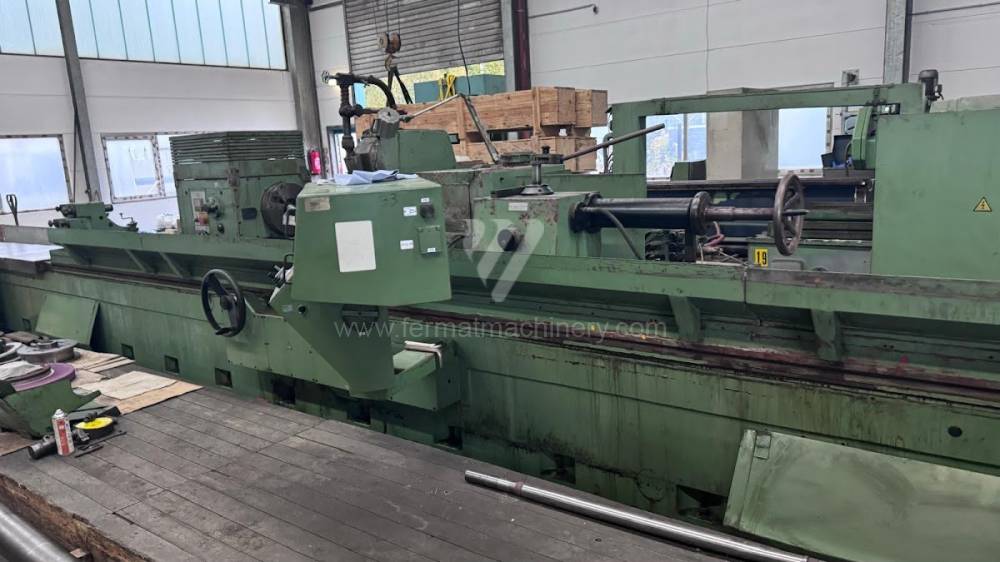
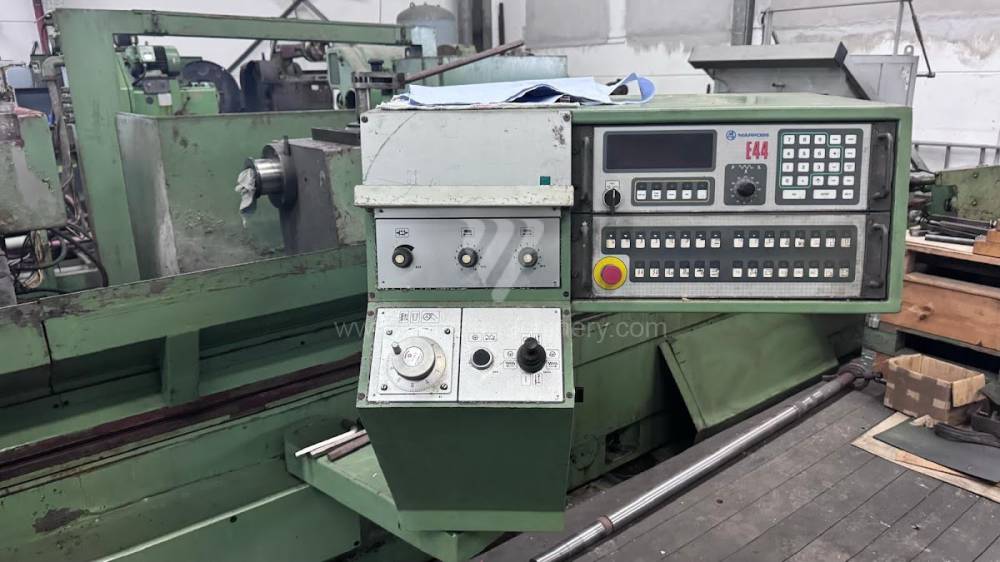
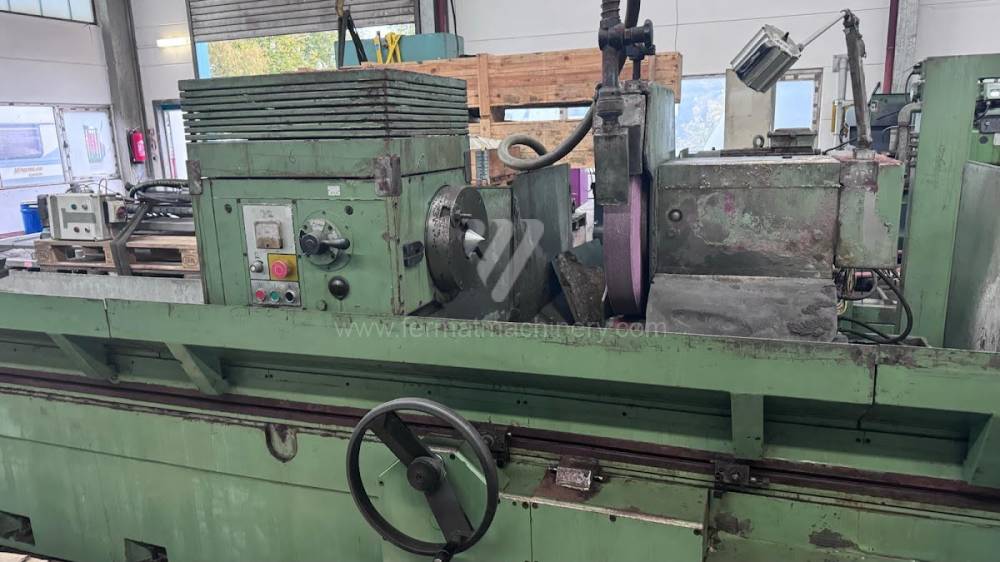
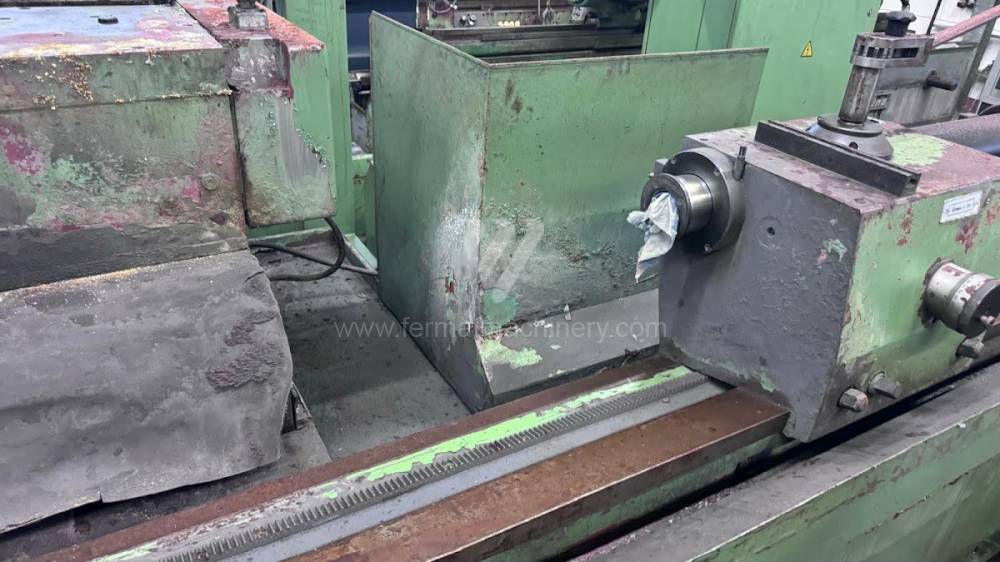
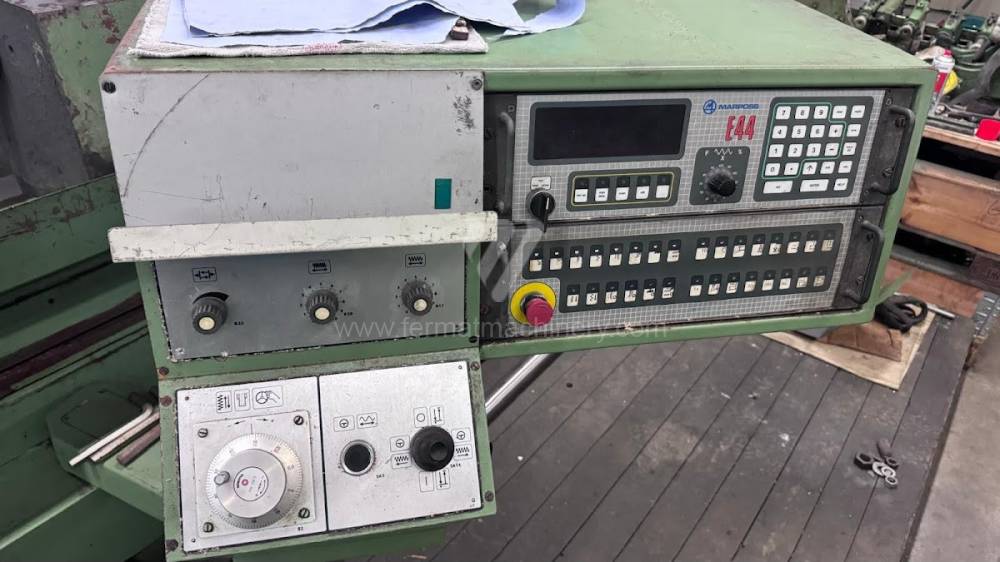
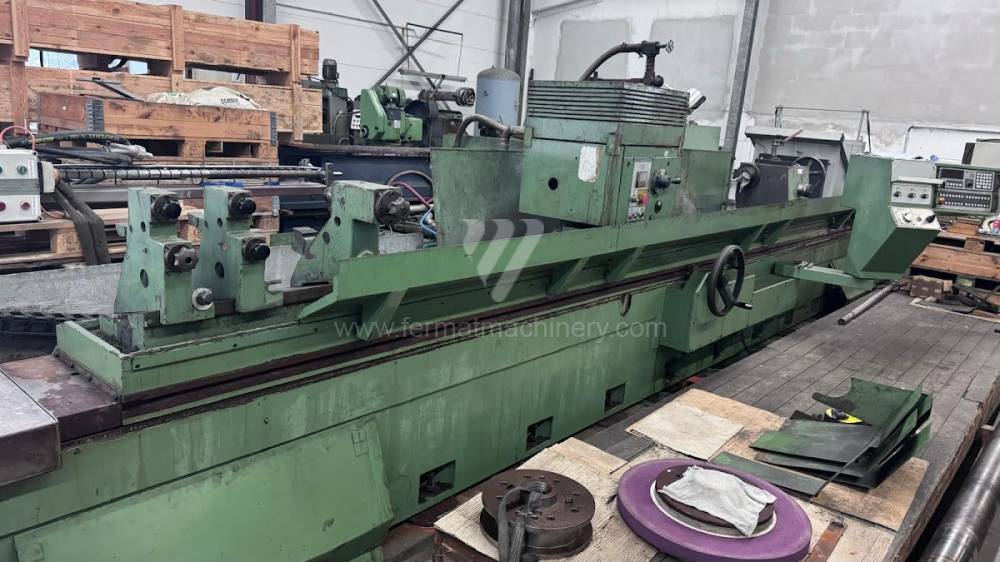
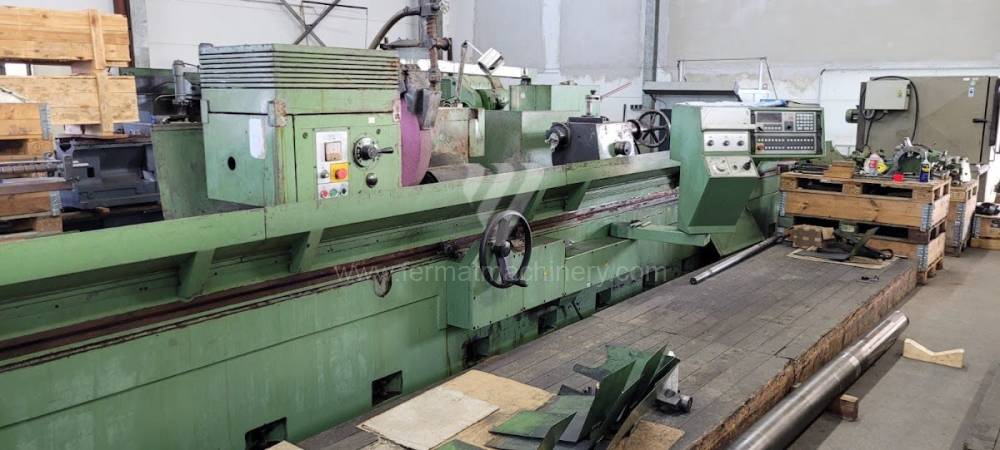
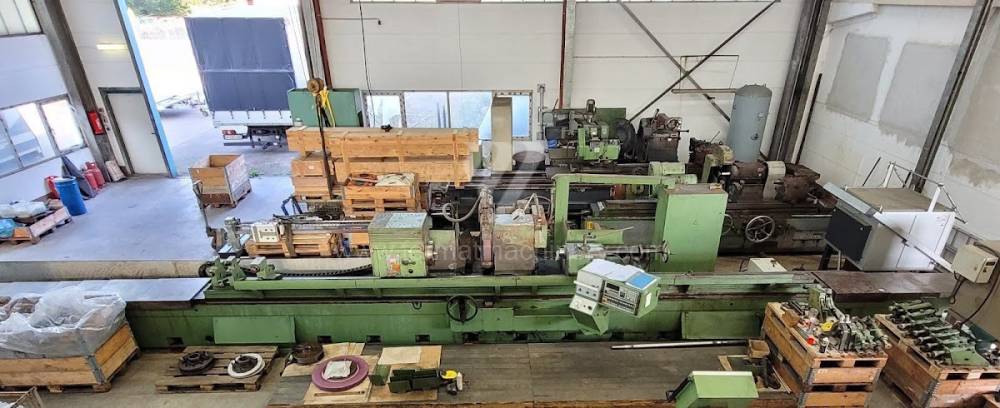
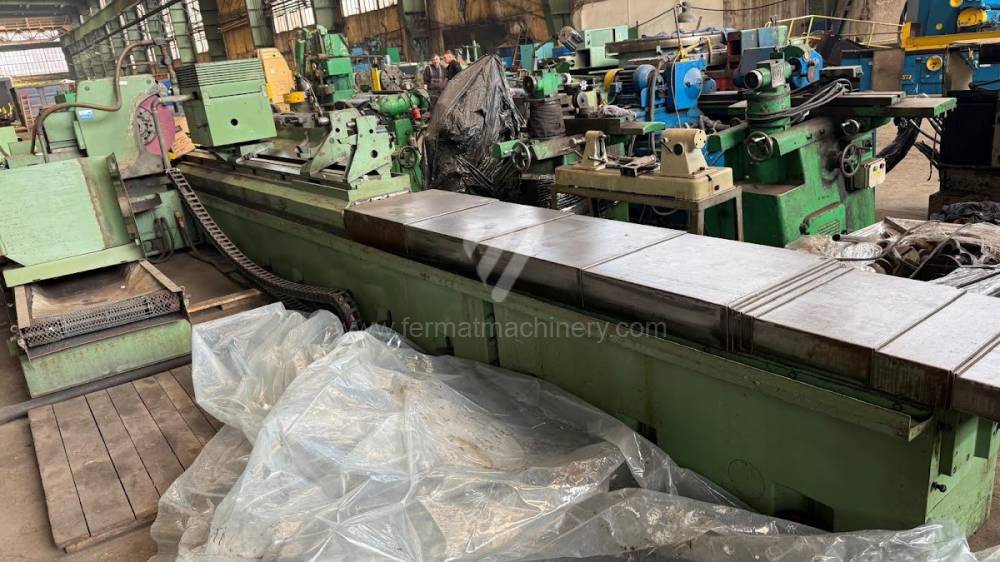
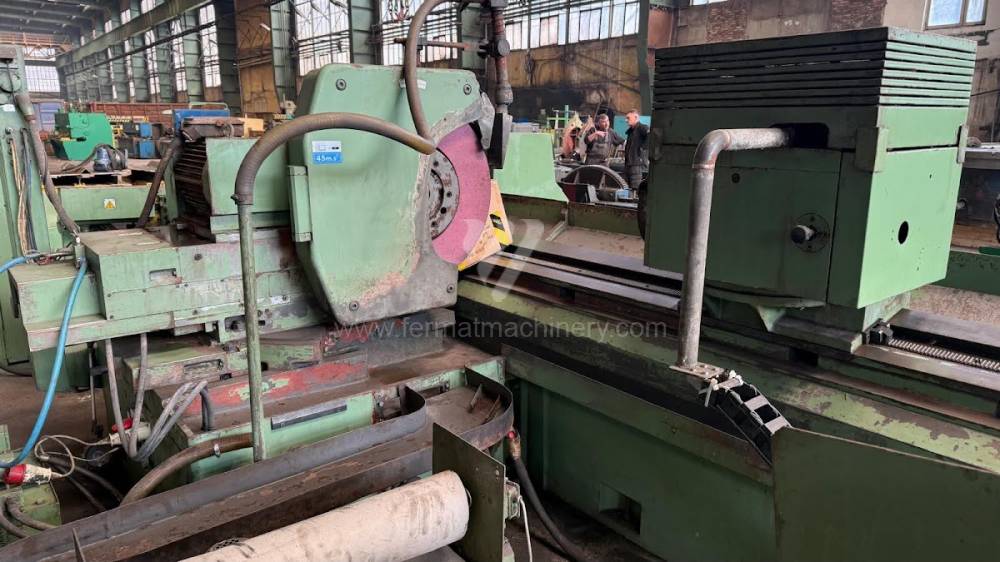
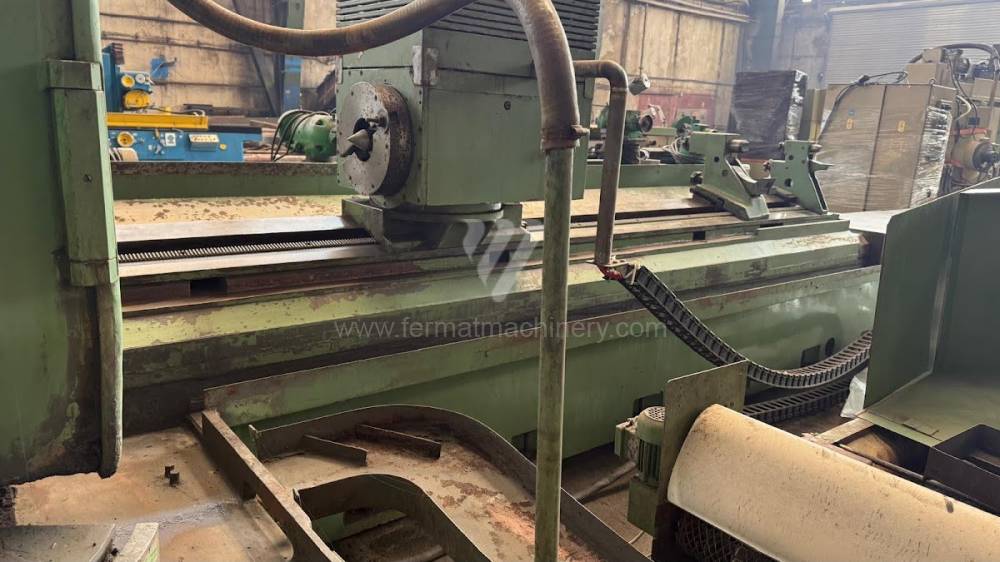
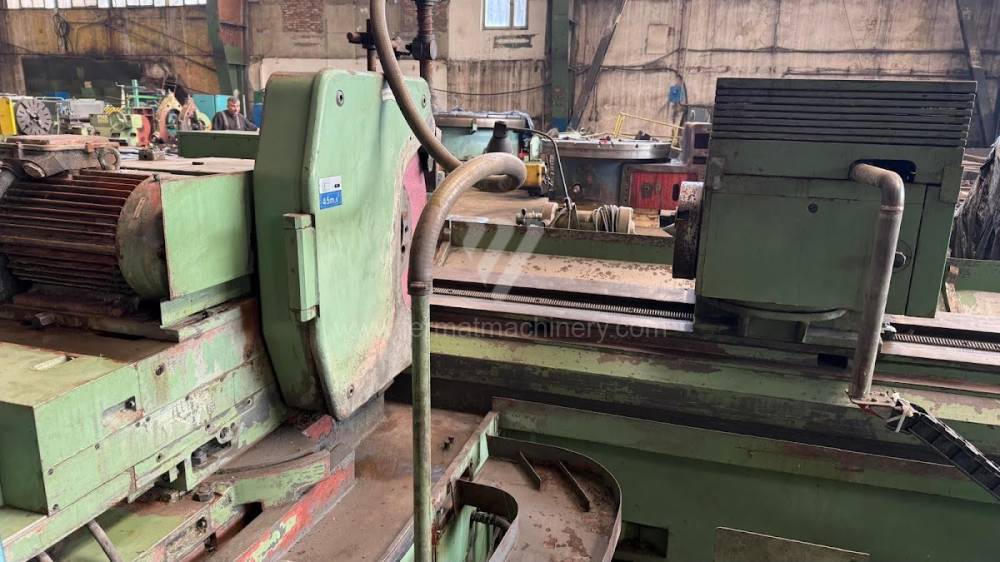
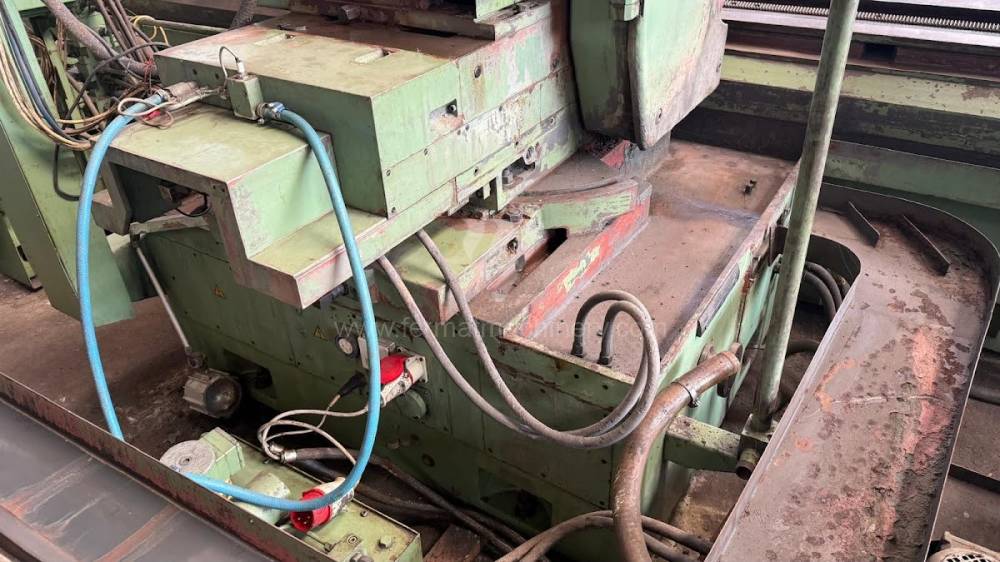
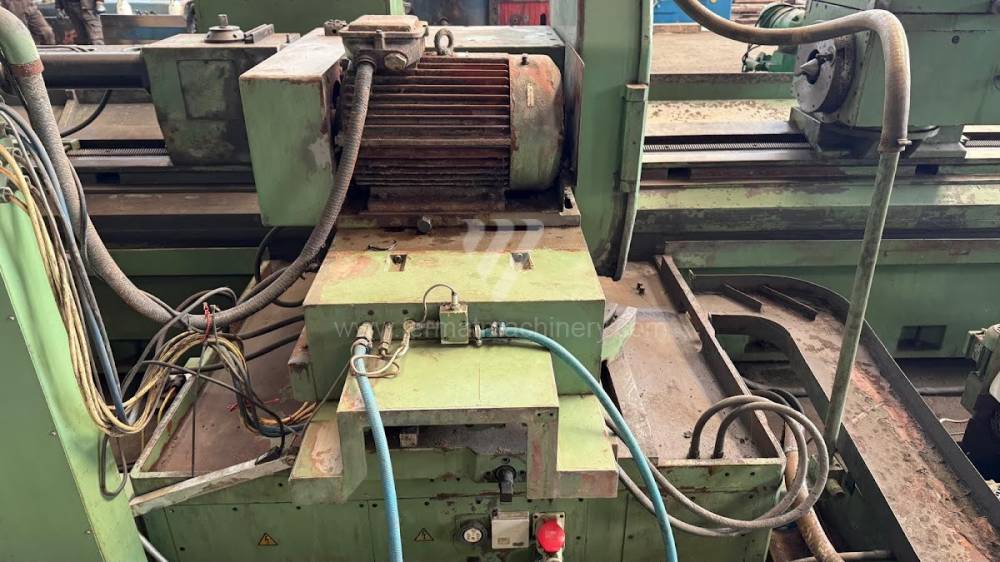
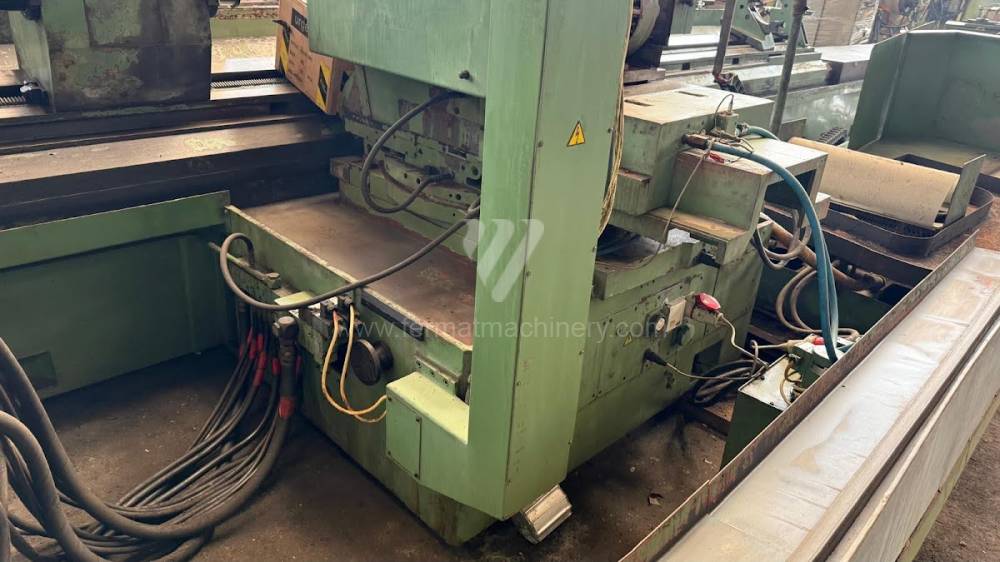





















Anno di fabbricazione:1991
Sistema di controllo Marposs:
Diametro massimo di rettifica: 630 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 6000 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 3000 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: No
Cono per fissare mandrino: MORSE 6 .
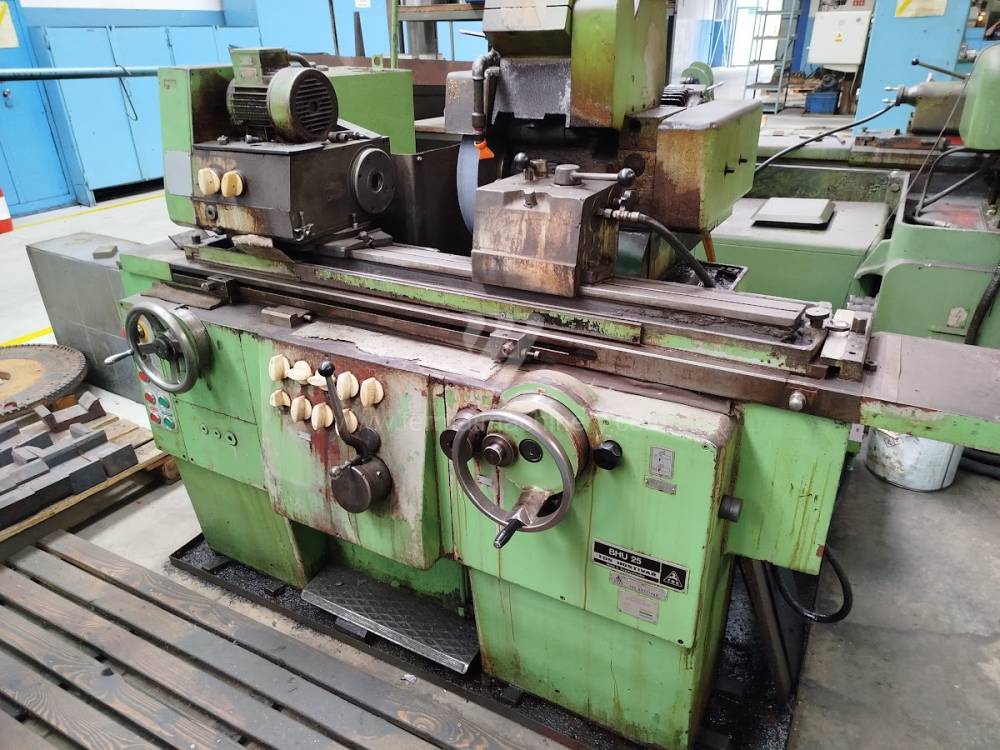


Diametro massimo di rettifica: 350 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 600 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 60 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: No
Dimensioni lungh. x largh. x alt.: 2000x1700x1300 mm
Peso della macchina: 2300 kg
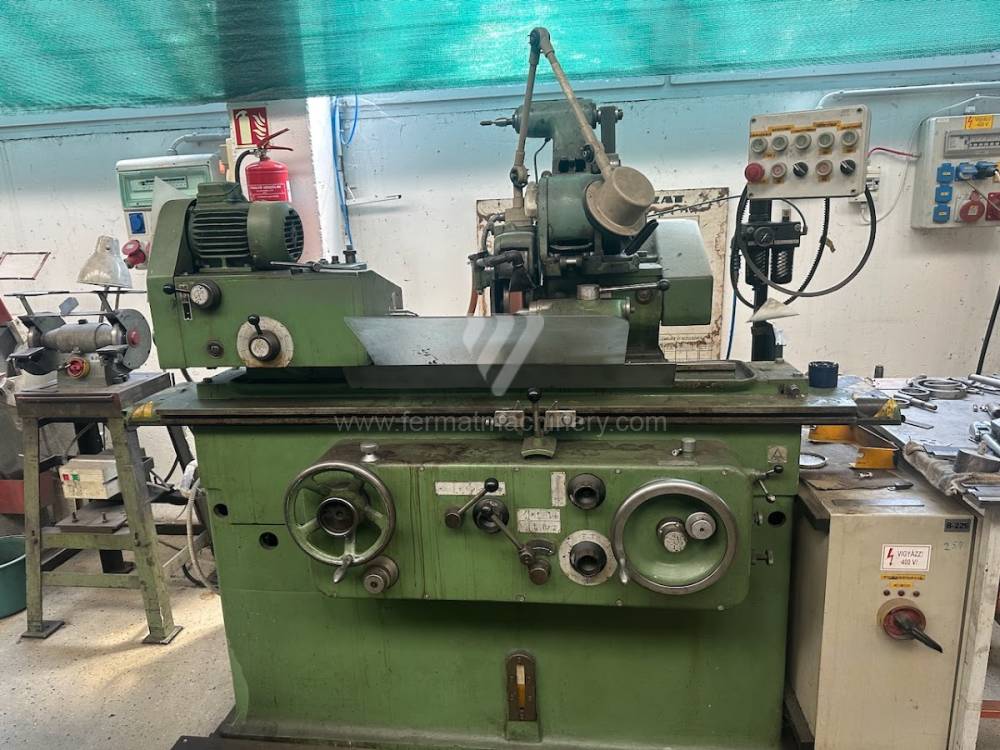
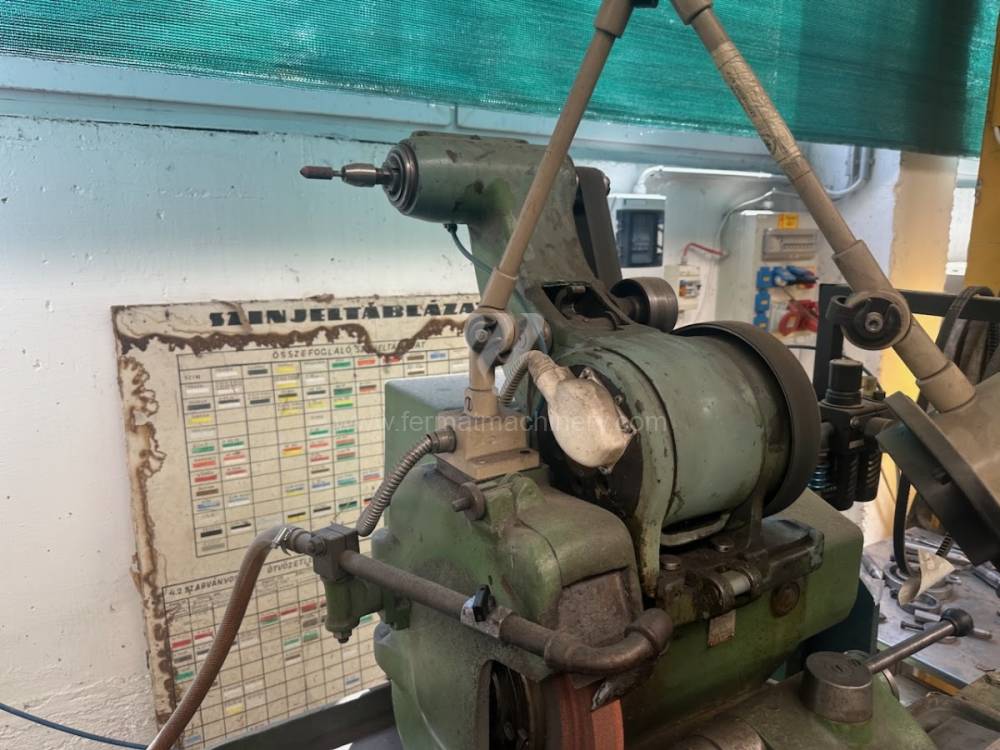






Diametro massimo di rettifica: 250 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 750 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 120 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: Sì
Potenza del motore elettrico principale: 4 kW
Dimensioni lungh. x largh. x alt.: 1400x1420x1500 mm
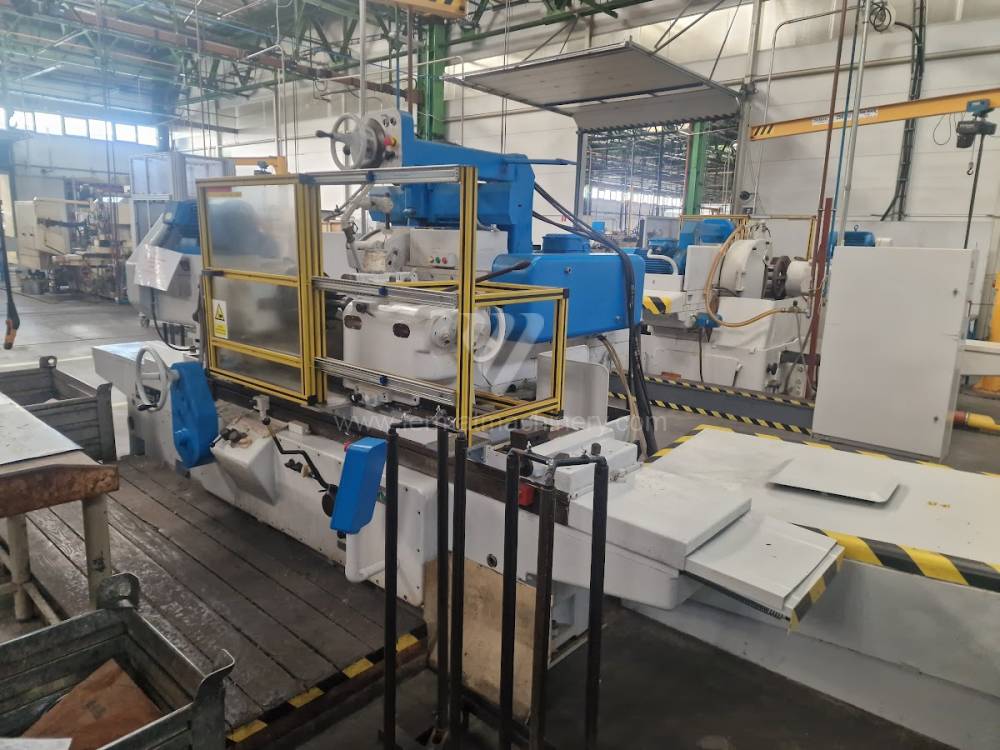
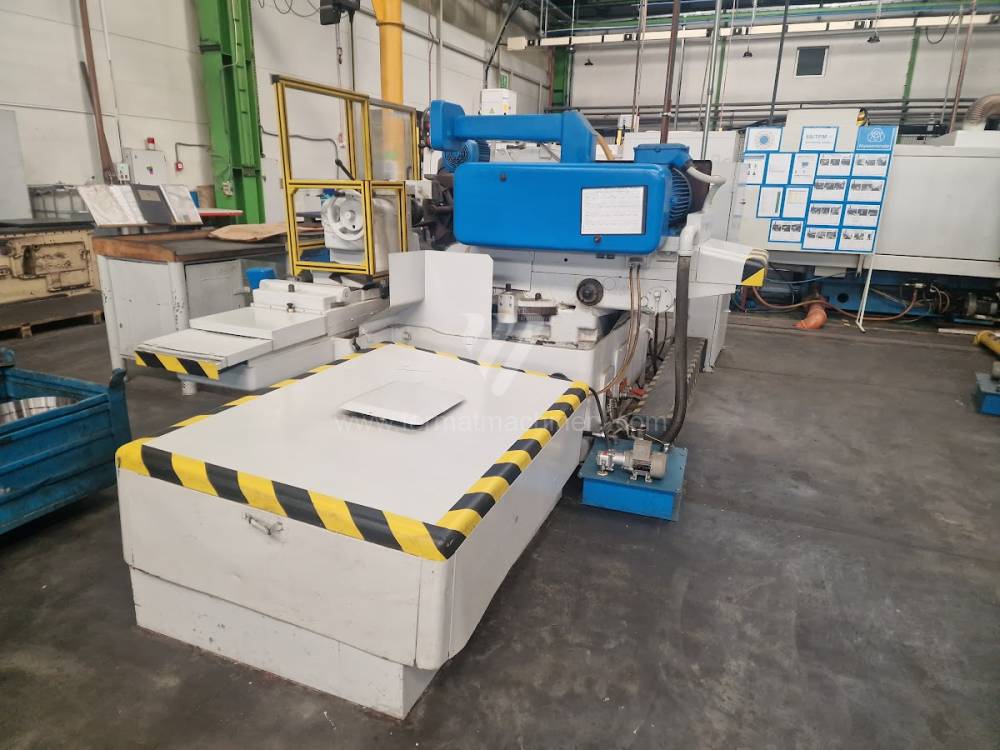
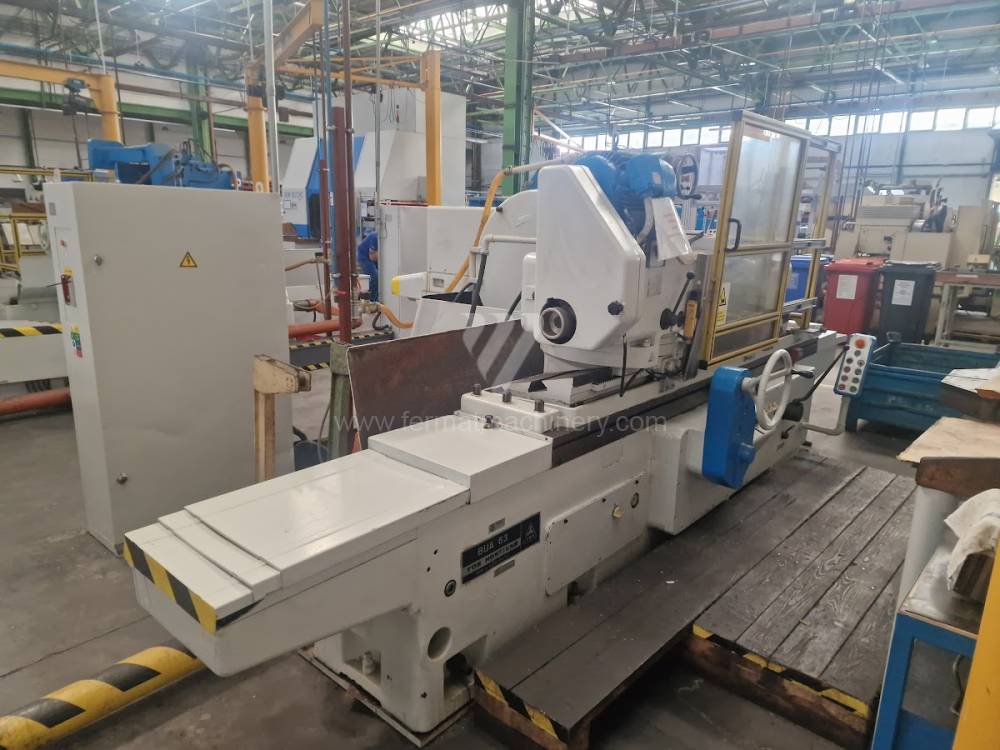
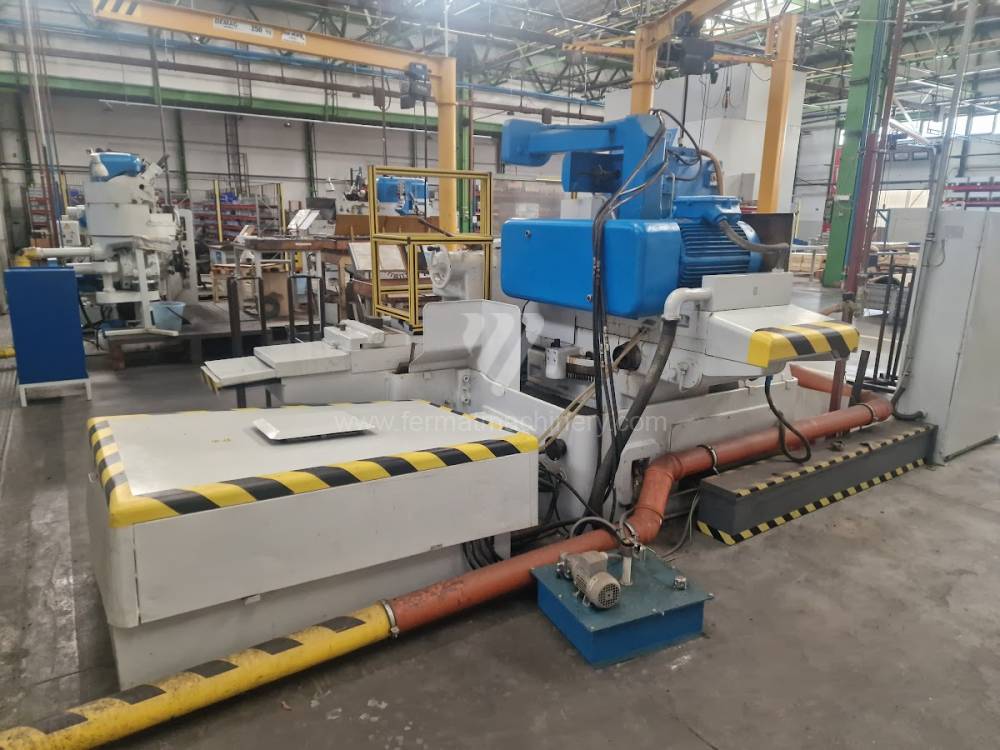




Anno di fabbricazione:1976
Diametro massimo di rettifica: 630 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 1000 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 900 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna:
Cono per fissare mandrino: MORSE 6 .
Diametro del mandrino: 315 mm
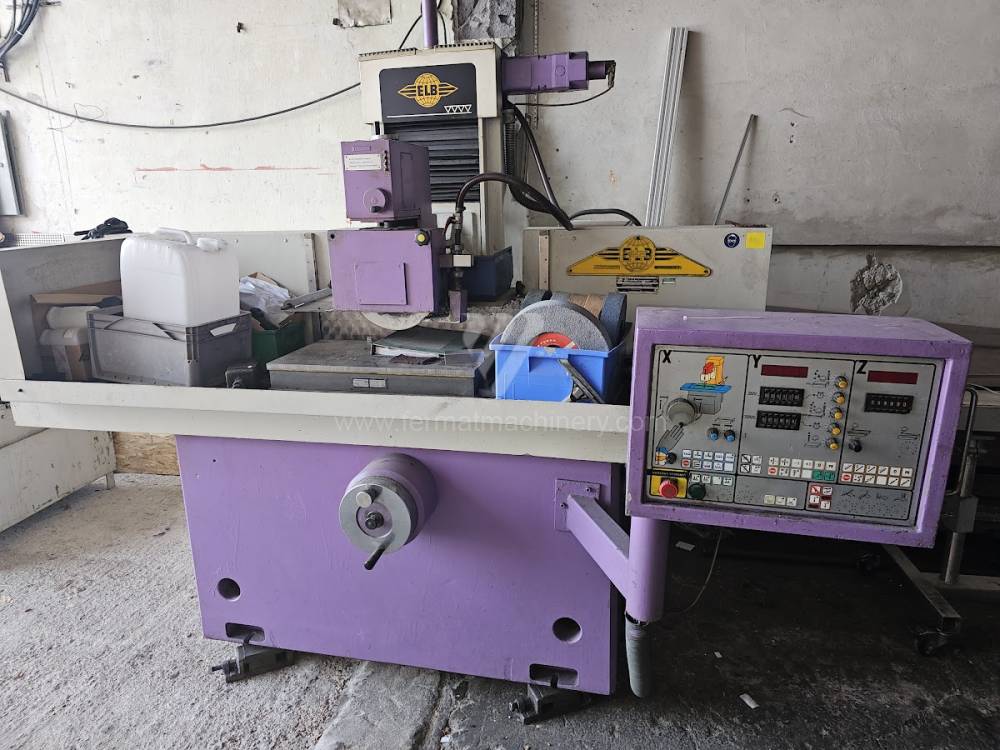
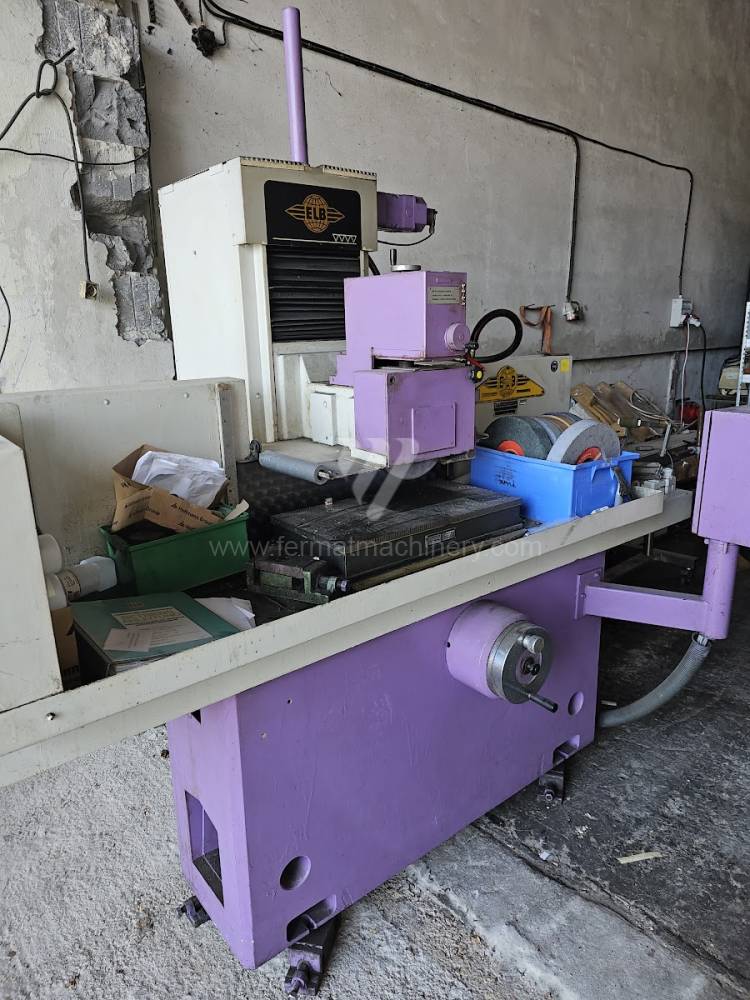




Lungh. max. della rettifica: 600 mm
Largh. max. della rettifica: 300 mm
Altezza max. del pezzo lavorato: mm
Alloggiamento mandrino mola: Horizontální
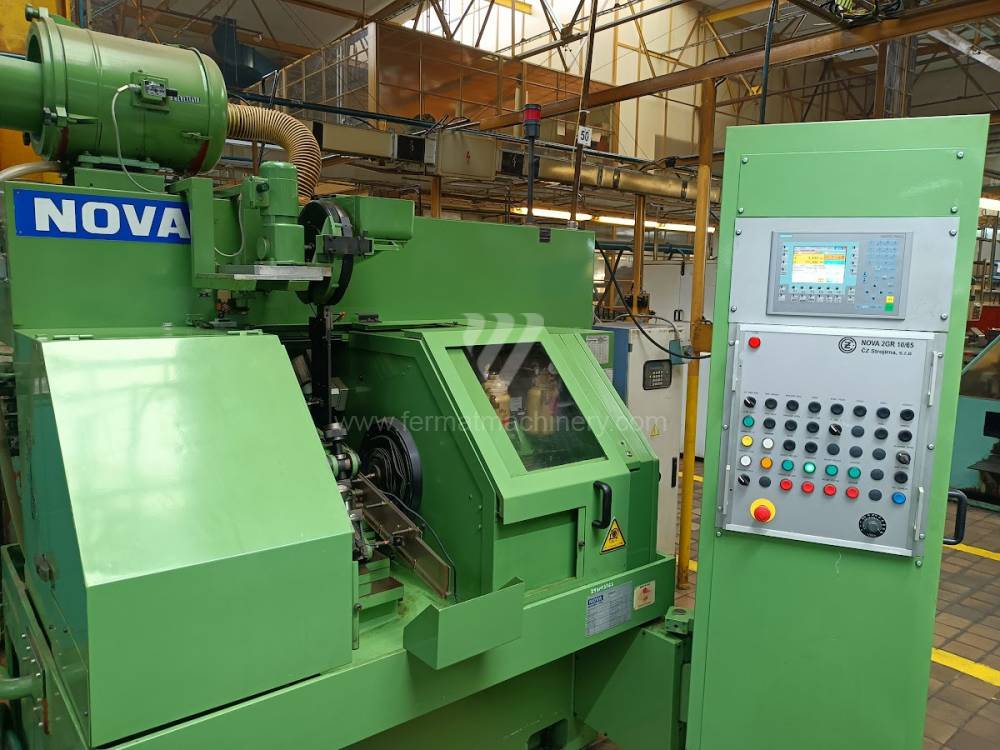
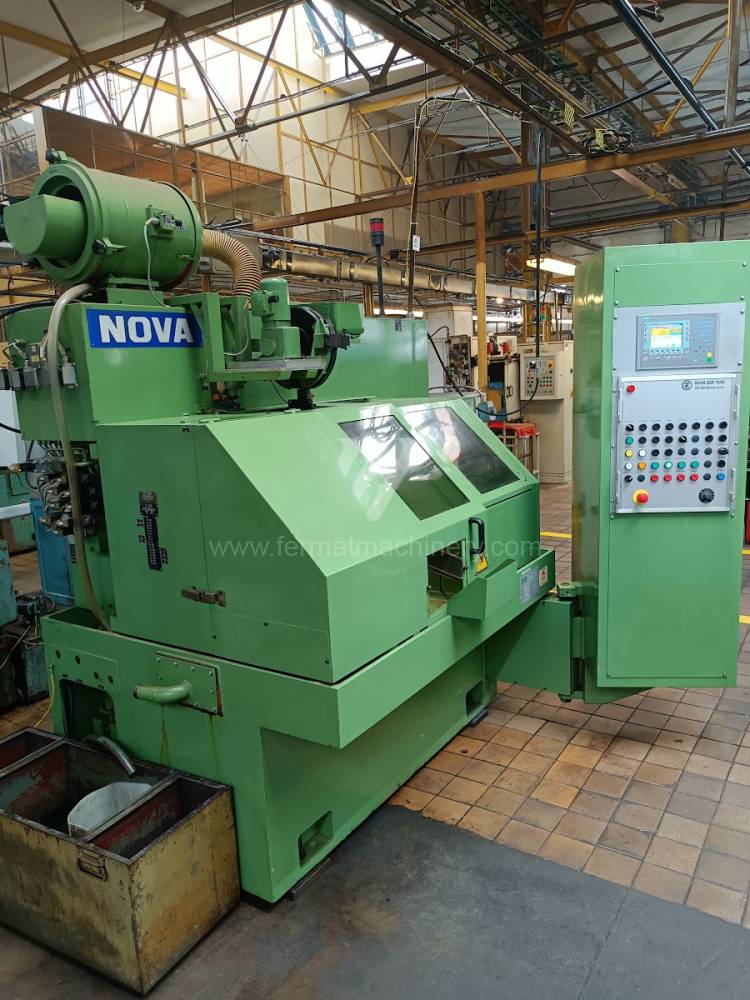

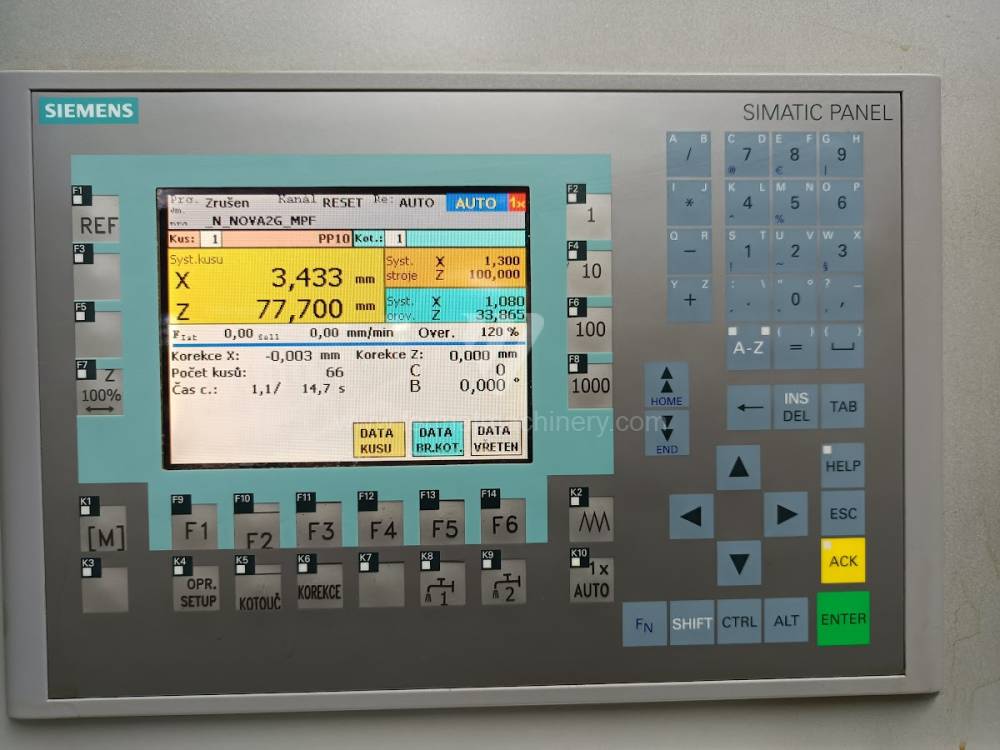




Anno di fabbricazione:1989
Sistema di controllo Siemens: Simatic S7-300
Diametro max. del pezzo lavorato: 65 mm
Diametro max. del foro a rettificare: 65 mm
Max. profondità di rettifica: 40 mm
Il diametro minimo di molatura: 10 mm
Spostamento asse X: 40 mm
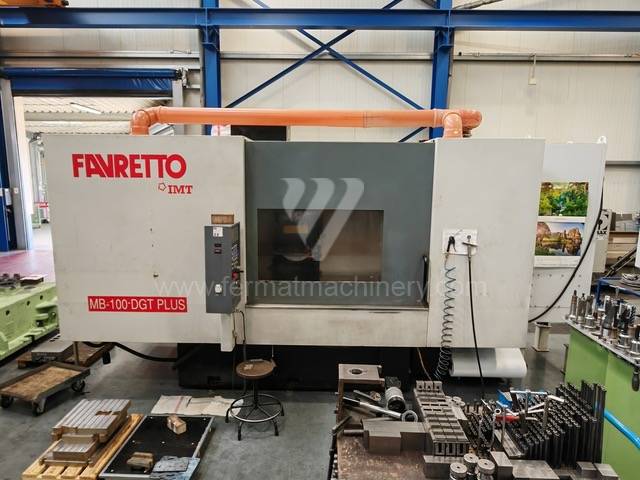
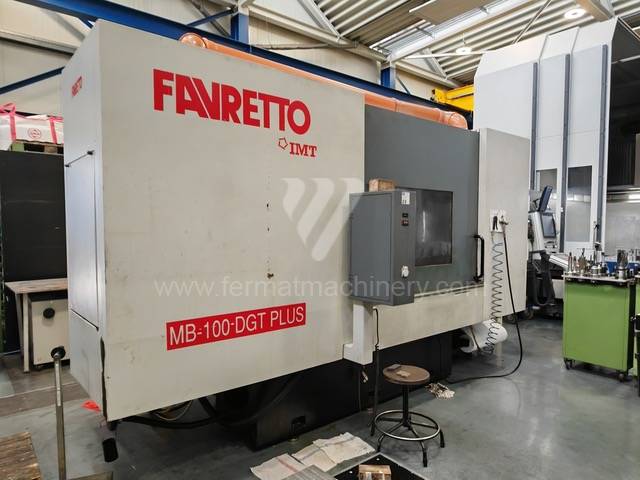
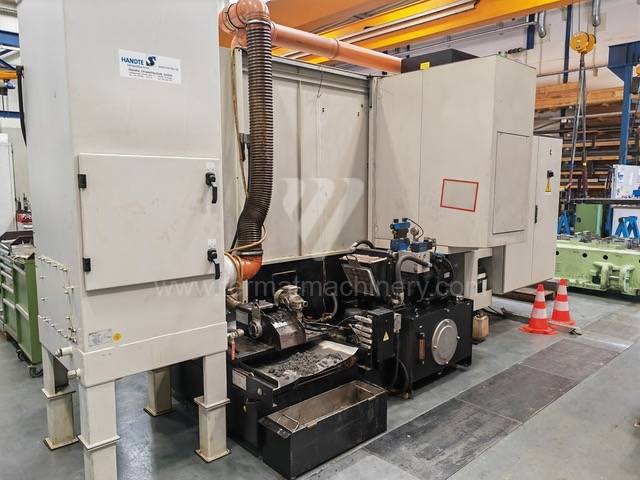
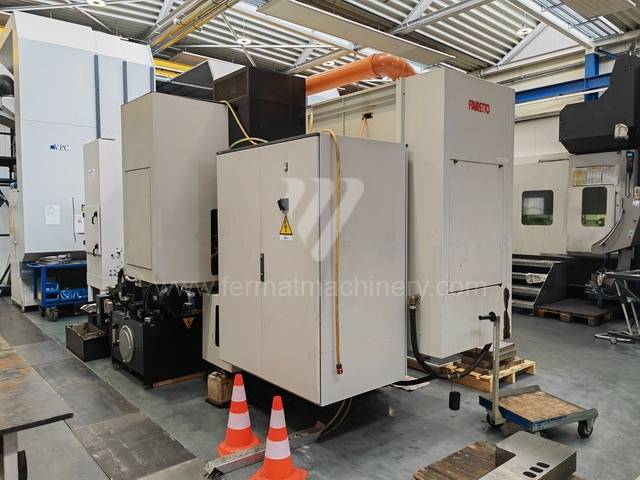












Anno di fabbricazione:2011
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 1200 mm
Largh. max. della rettifica: 600 mm
Altezza max. del pezzo lavorato: 550 mm
Alloggiamento mandrino mola:
Dimensioni del piano di lavoro del banco: 1200x400 mm
Massimo carico banco: 975/1200 kg
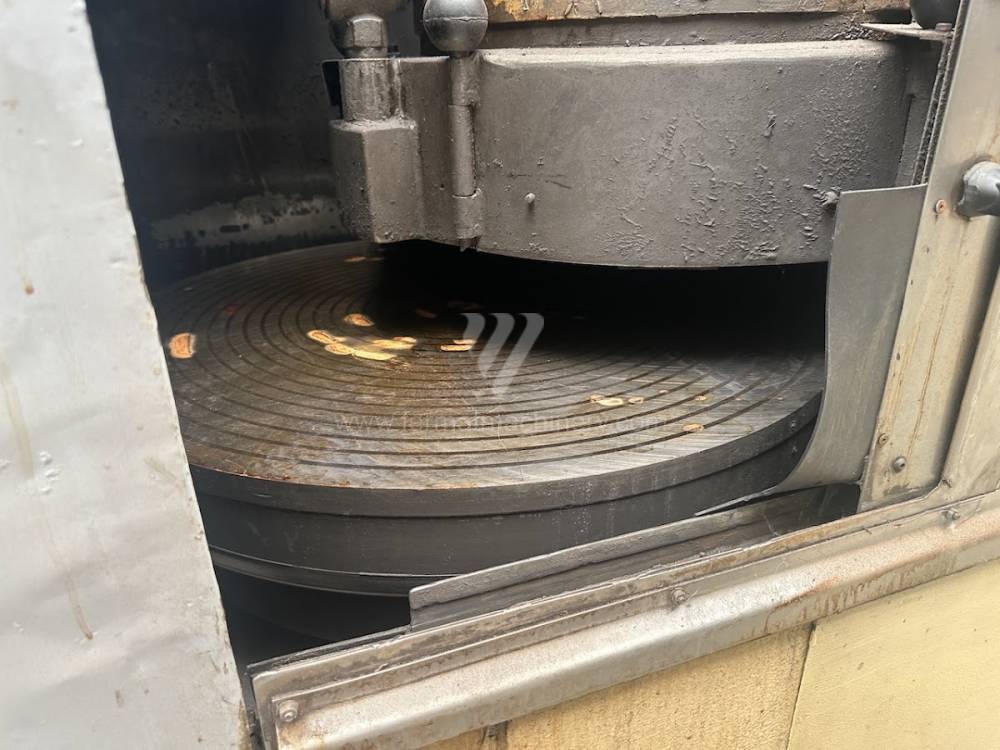
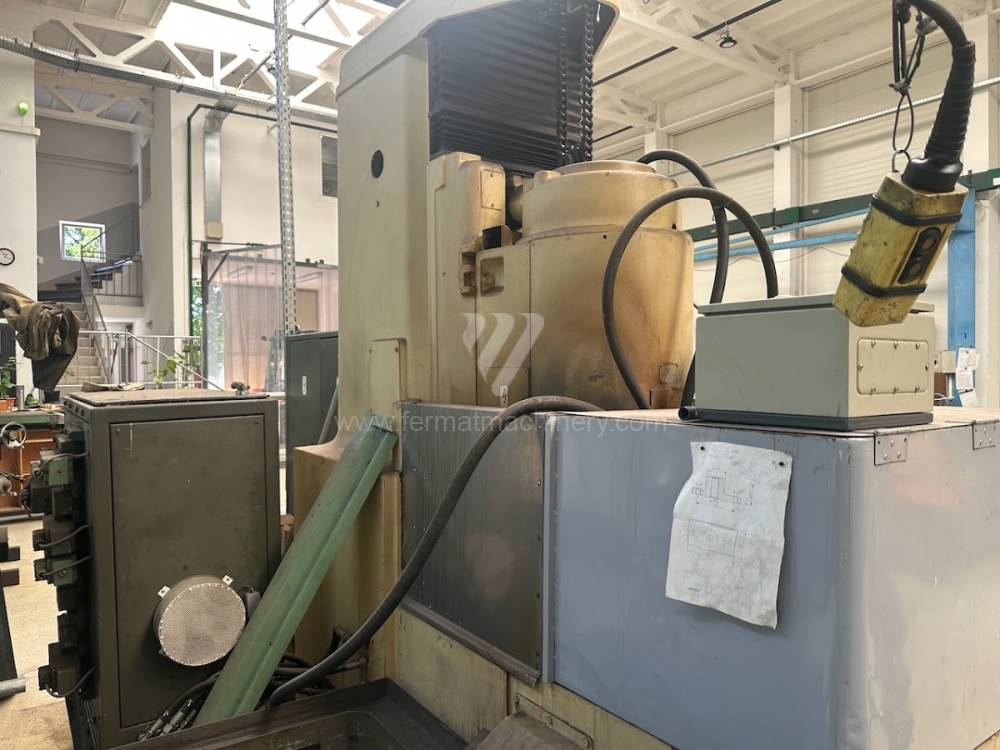



Lungh. max. della rettifica: d=800 mm
Largh. max. della rettifica: mm
Altezza max. del pezzo lavorato: mm
Alloggiamento mandrino mola: Vertikální
Peso della macchina: 9500 kg
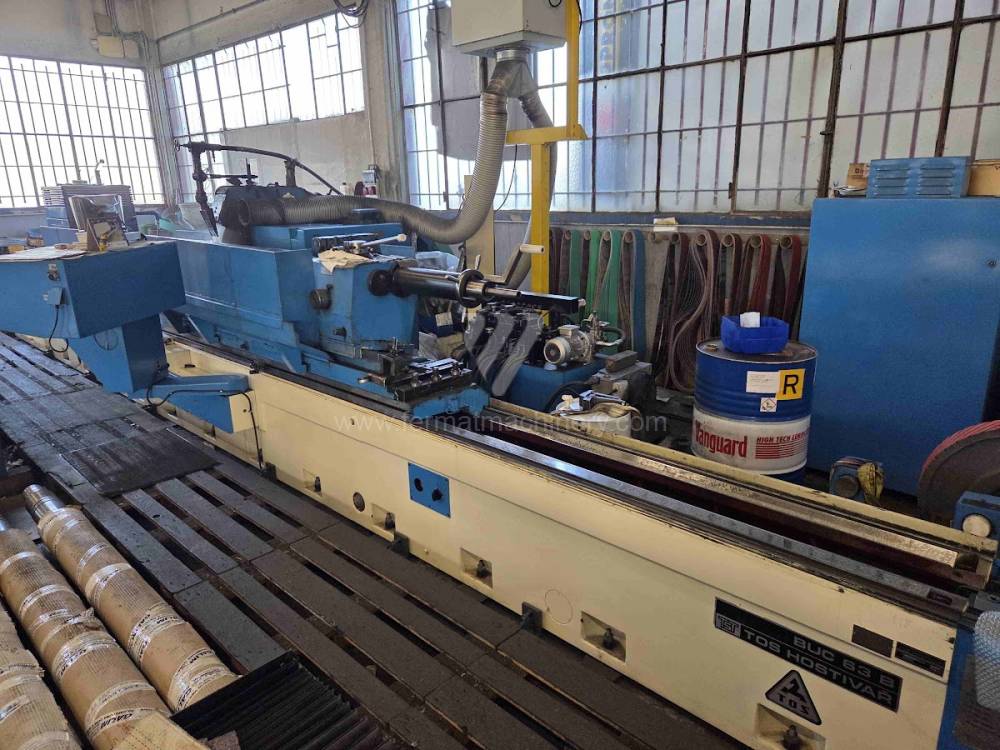
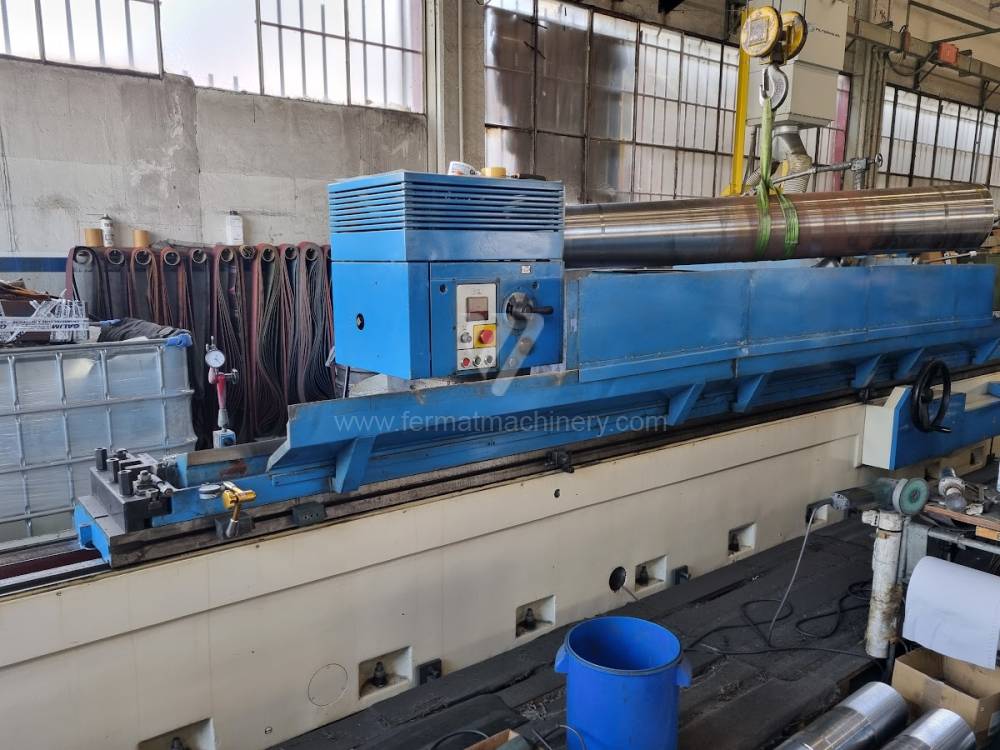
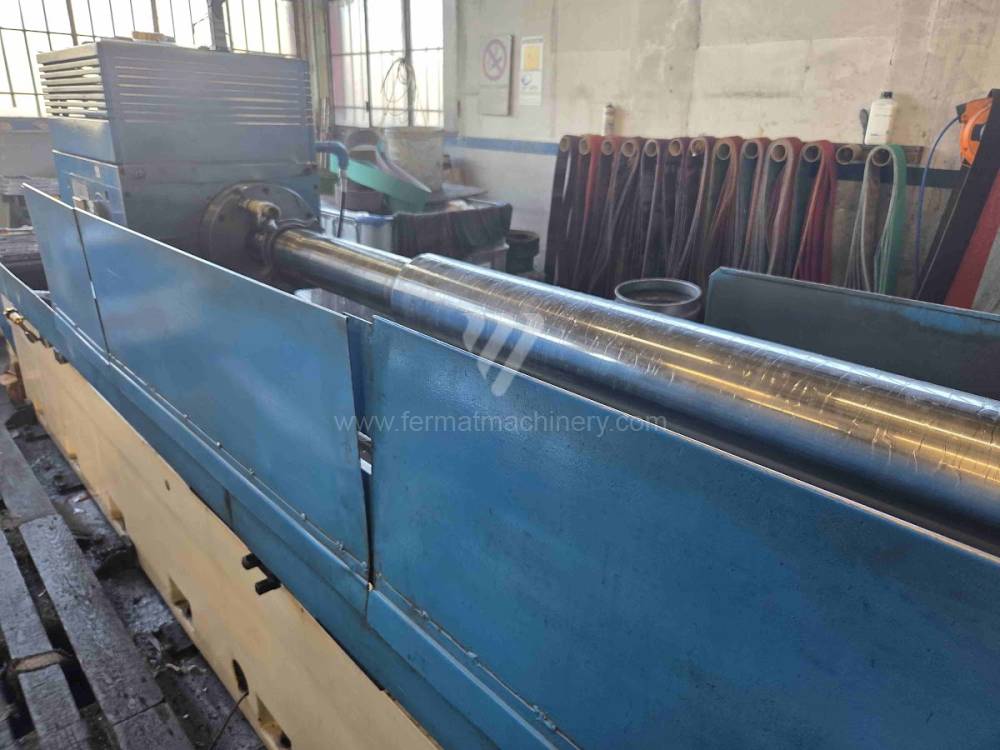
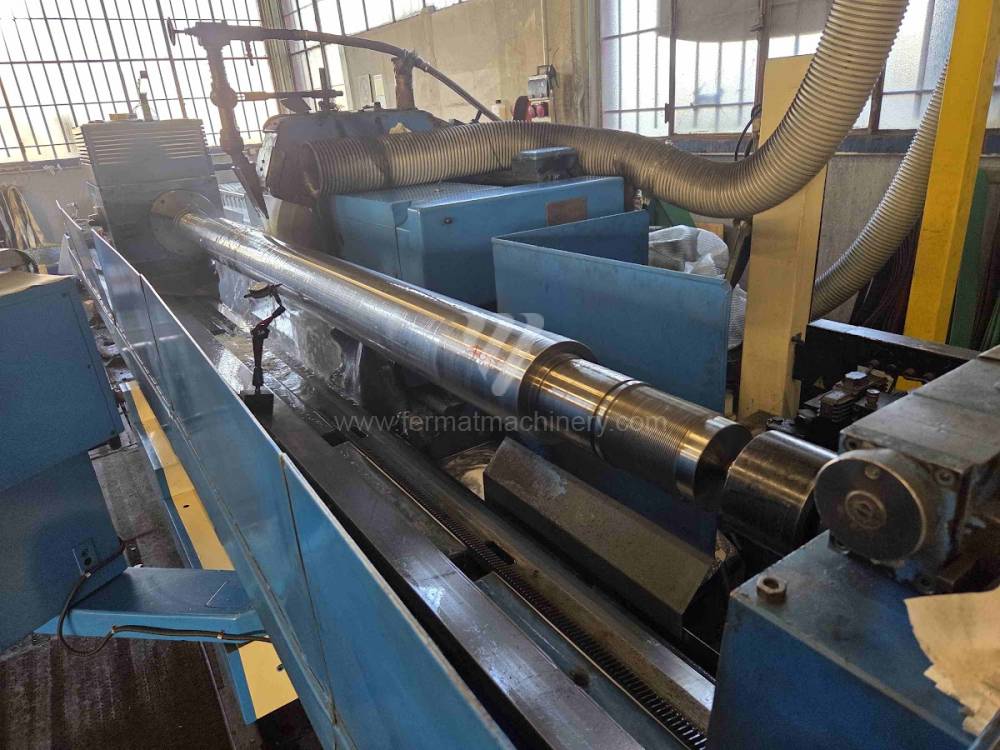








Anno di fabbricazione:1988
Sistema di controllo Kavalír: K51-1
Diametro massimo di rettifica: 630 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 4000 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 2500 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: Sì
Potenza del motore elettrico principale: 15 kW
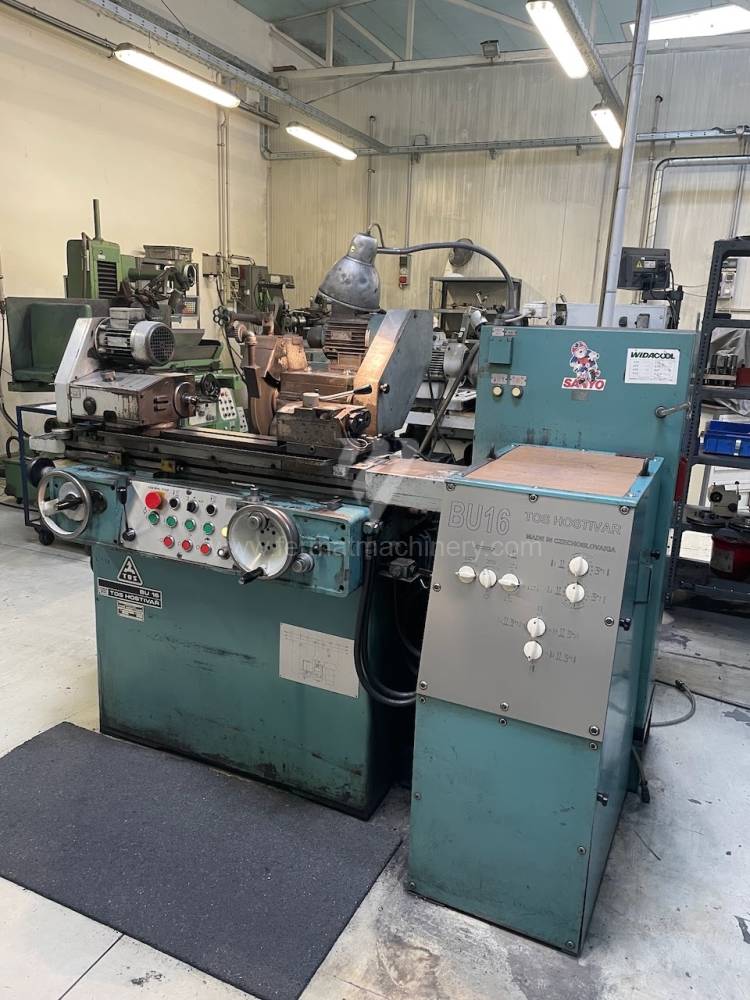
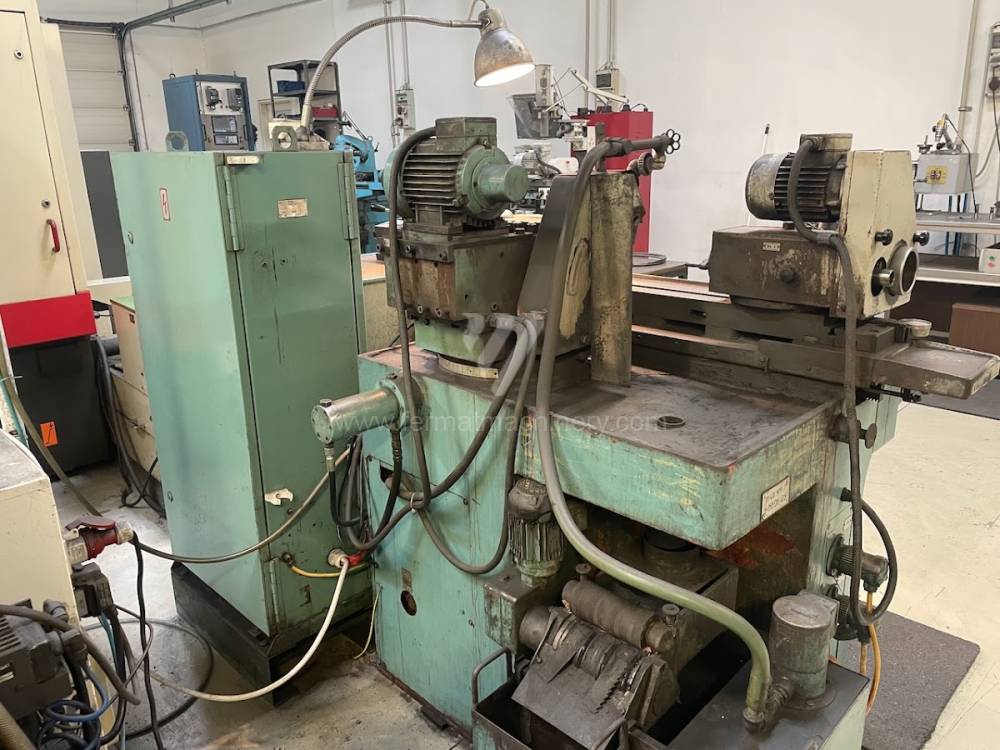
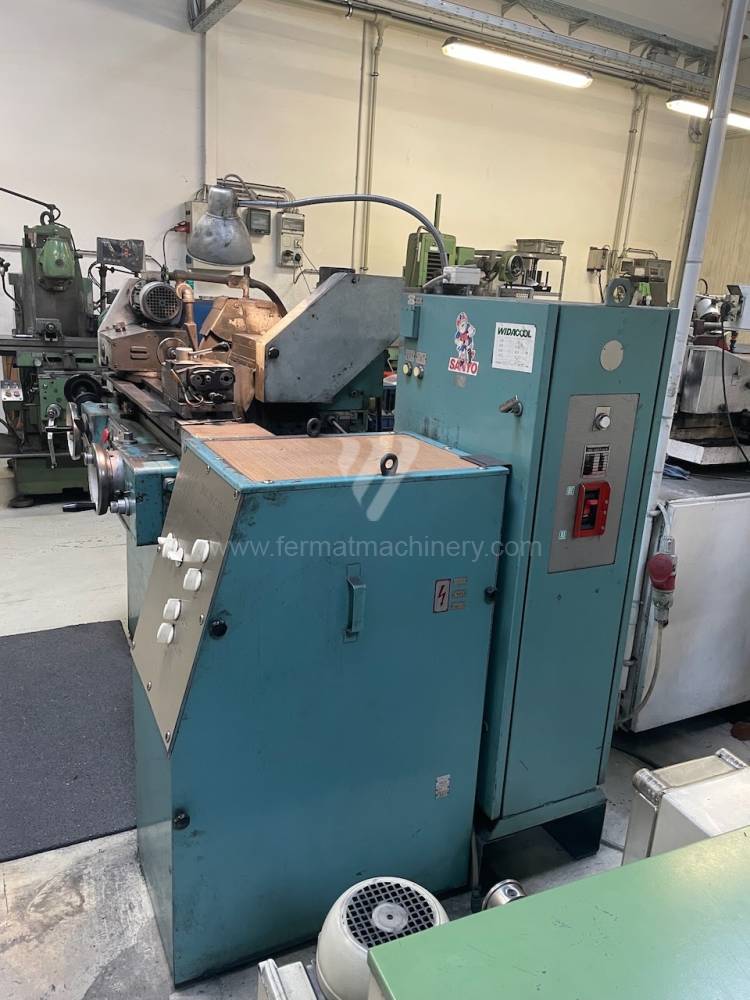



Anno di fabbricazione:1988
Diametro massimo di rettifica: 160 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 320 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 25 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: No
Cono per fissare mandrino: Morse 3 .
Giri del mandrino: 0 - 2812 /min.
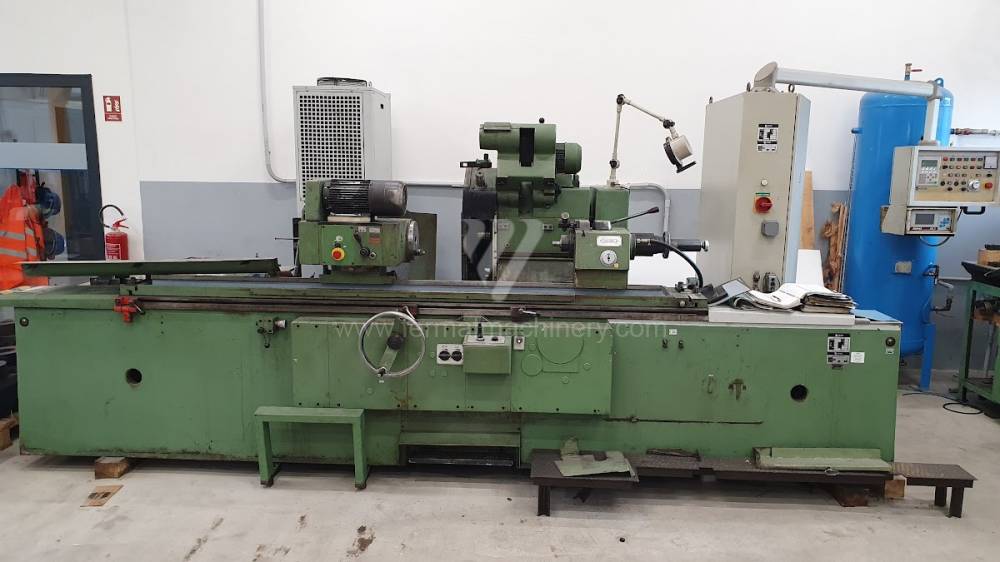
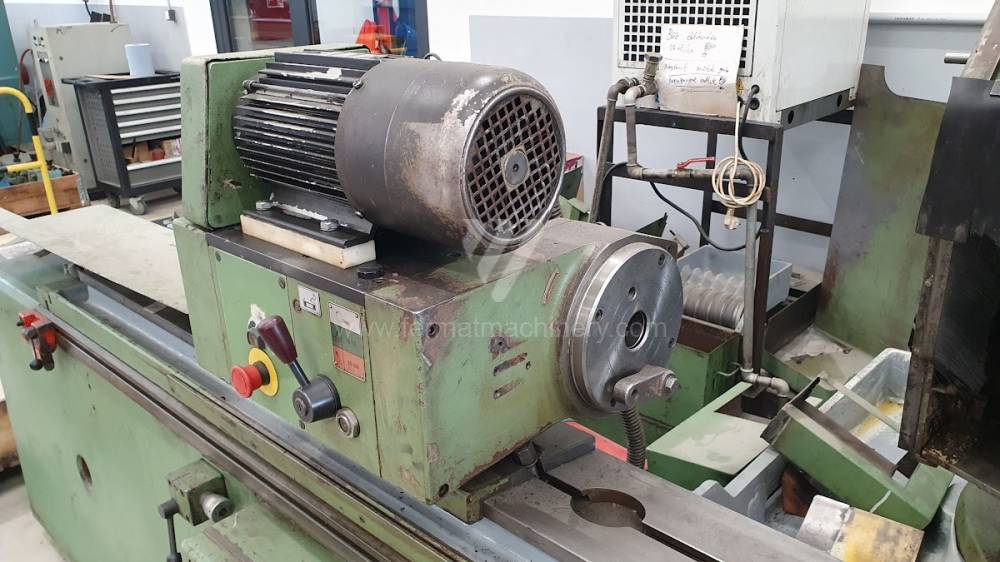
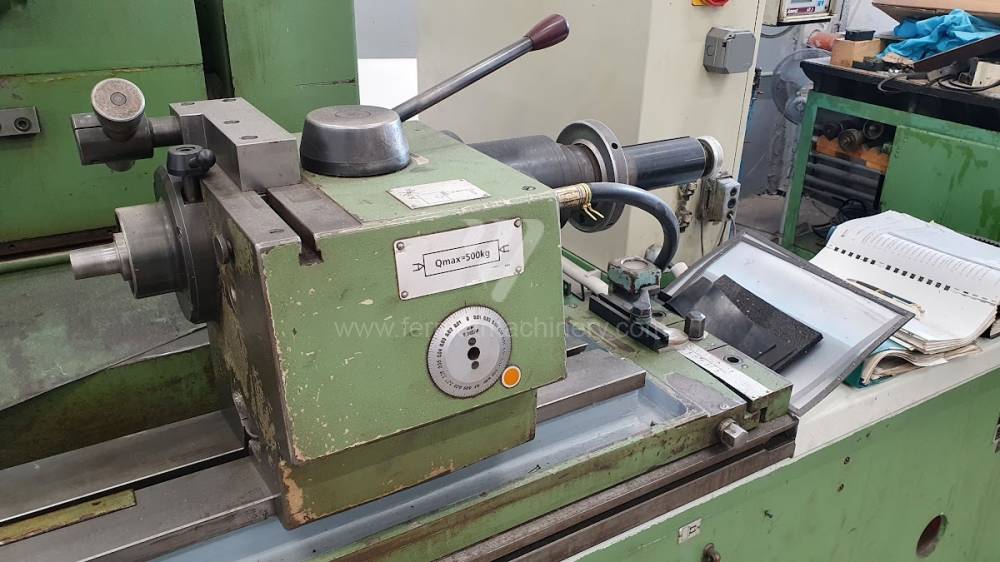
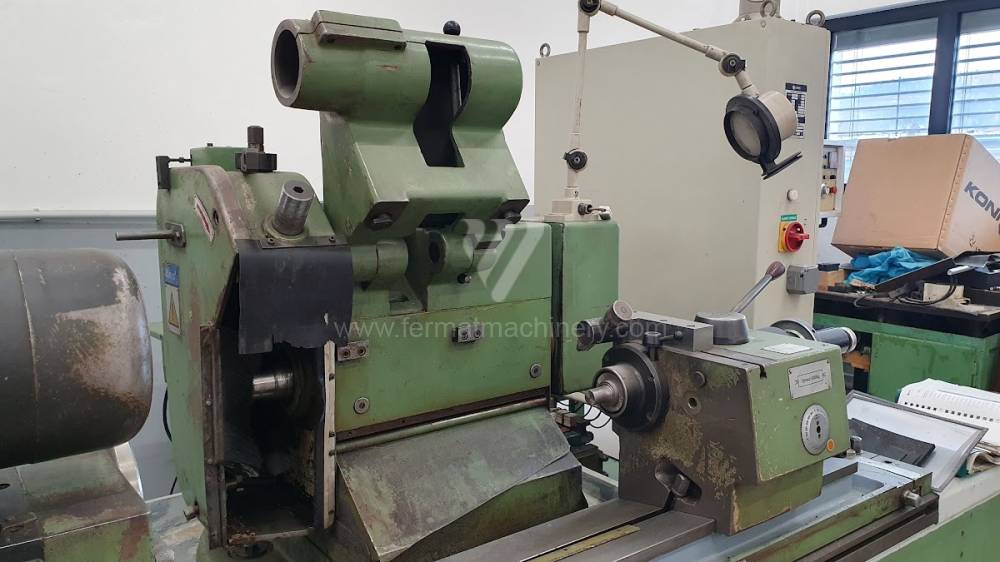









Anno di fabbricazione:1993
Sistema di controllo Siemens: Simatic S7
Diametro massimo di rettifica: 400 mm
Lungh. max. della rettifica: 1500 mm
Peso max. del pezzo lavorato: 250 kg
Attrezzature per la rettifica interna: Sì
Potenza del motore elettrico principale: 7,5 kW
Grinding is a technology of precision chip machining. Nowadays, it is possible to reach precision in order of tenths of micrometers and surface roughness of up to 0,2 micrometer. Grinders are thus indispensable in the machinery industry and form an important part of the production process. In general, grinding is a technology that works on the principle of the material removal from the surface layer of the workpiece with fine grains of abrasive material, which are most often bonded to the grinding wheel.
Among the cylindrical grinders we differentiate grinders with centers and without centers. These machines are used for grinding internal and external rotating surfaces.
In case of center grinders the workpiece is usually clamped between centers and rotation is realized using a driver, which is fixed to the surface of the workpiece and tied to headstock. In most cases the workpiece rotates against the direction of rotation of the grinding wheel. Most common models from producer TOS we can mention:
Grinding is realized using the rotation of the grinding wheel, which grinds the surface of the workpiece as it rotates. Most popular producers of such grinders are: FERMAT, TOS, STUDER, DANOBAT, KELLENBERGER, ERWIN JUNKER, SCHAUDT.
Centerless grinders are also intended for grinding rotary surfaces. The clamping of the workpiece on the machine is different. It is supported with support ruler and the workpiece is placed between two discs – abrasive and drifting. The grinding wheel usually spins faster and does the grinding itself. The drive disc is most often made of flexible material (for example rubber) and ensures sufficient pressure.
A special category of grinders are grinders used for grinding of internal rotating surfaces. They works similarly to center grinders. However, the workpiece is just clamped on one side in the chuck or collet so that the hole can be ground from the other side.